Agnatha facts for kids
Quick facts for kids AgnathansTemporal range: Cambrian – Recent
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Lampetra fluviatilis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Superclass: |
Agnatha
Cope, 1889
|

Agnathans are a group of vertebrate animals. Their name comes from Greek words meaning 'no jaws'. This tells us their main feature: they are fish without jaws!
The Agnatha group includes both living and extinct animals. The living agnathans are lampreys and hagfish. Scientists call these two groups cyclostomes. There are about 100 known species of cyclostomes.
Hagfish are interesting because they are vertebrates but do not have a backbone made of vertebrae. Scientists think they lost their vertebrae over time as they adapted to their lifestyle.
Lampreys are often parasites that attach to other fish. Hagfish are scavengers, meaning they eat dead animals. These lifestyles are quite different from many of the ancient, fossil agnathans, which were free-swimming and often had tough armor.
Contents
What are Agnatha?
Agnathans are a very old group of fish. They first appeared during the Cambrian period and are still around today. They are known as "jawless fish" because they do not have jaws like most other fish.
Ancient Jawless Fish
Many ancient agnathans were covered in heavy, bony plates. The first armored agnathans were called Ostracoderms, which means "shell-skinned." These fish were very successful in the Silurian period. However, their numbers started to drop during the Devonian period, and they never fully recovered.
Body Features of Agnatha
Agnathans have some unique body features that set them apart from other fish.
Skeleton and Fins
Instead of bones, agnathans have a cartilaginous skeleton. This means their skeleton is made of cartilage, which is a flexible material, like the tip of your nose. Both young (larvae) and adult agnathans have a notochord, which is a rod that supports their body.
Unlike most fish, agnathans do not have paired fins. They also have several gill pouches, usually seven or more pairs, which they use for breathing underwater.
Digestion and Temperature
Agnathans do not have a clear stomach like many other animals. They are also cold-blooded, meaning their body temperature changes with the temperature of their surroundings. Their heart is quite simple, with only two chambers.
Senses and Reproduction
Agnathans have a special light-sensitive spot called a pineal eye. This helps them sense light.
When it comes to having babies, agnathans lay their eggs outside their body. The young develop outside the body, and the parents do not take care of them.
Classification of Agnatha
Scientists group agnathans into different categories:
- Agnatha: The main group of jawless fish. They have existed from the Cambrian period to today.
- †Pteraspids: These were ancient fish with large head-shields.
- Anaspids: These fish had gills that opened as small holes. They lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period.
- †Cephalaspids: These were early types of jawless fish.
- Cyclostomes: This group includes the living Lampreys and Hagfish.
- †Osteostraci: These were jawless fish covered in bony armor.
Images for kids
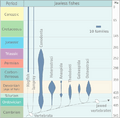
-
Evolution of jawless fishes. This diagram is based on Michael Benton, 2005.
See also
 In Spanish: Agnatha para niños
In Spanish: Agnatha para niños