Lamoral, Count of Egmont facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Lamoral, Count of Egmont
|
|
|---|---|

Portrait of Lamoral, Count of Egmont by Frans Pourbus the Elder.
|
|
| Born | 18 November 1522 |
| Died | 5 June 1568 (aged 45) |
Lamoral, Count of Egmont, Prince of Gavere (born November 18, 1522 – died June 5, 1568) was an important general and leader in the Spanish Netherlands. This was a region that included parts of modern-day Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg. His execution helped start a big uprising that led to the independence of the Netherlands.
Contents
Who Was Lamoral, Count of Egmont?
Lamoral was born in a castle called Château de Lahamaide near Ellezelles. He came from the powerful and wealthy House of Egmond family in the Low Countries. His family had even ruled the duchy of Guelders for a time. Through his mother, he also inherited the title prince de Gavere. When he was young, he trained to be a soldier in Spain. In 1542, he inherited his older brother's lands in Holland.
His family became even more important in 1544. Lamoral married Countess Palatine Sabine of Simmern. Her brother later became a very important ruler, the Elector Palatine Frederick III.
Egmont's Military and Political Career
Lamoral was a skilled military leader. He was made Captain General of the Lowlands by Emperor Charles V. In 1546, he became a knight of the special Order of the Golden Fleece. He also served as an Imperial Chamberlain.
He led the Spanish army to victory against the French in two big battles:
- The Battle of Saint-Quentin in 1557.
- The Battle of Gravelines in 1558.
Because of his success, Lamoral was made stadtholder (a kind of governor) of Flanders and Artois in 1559. He was only 37 years old at the time.
Egmont's Role in the Dutch Revolt
As a leading nobleman, Egmont was part of King Philip II of Spain's official Council of State. He worked with William, Prince of Orange and the Count of Horn. They spoke out against the inquisition being brought into Flanders. The Inquisition was a powerful religious court that punished people who didn't follow Catholic rules. Egmont even threatened to quit his job.
In 1565, Egmont traveled to Madrid to ask King Philip II to change his harsh policies in the Netherlands. However, the king did not really listen to his concerns.
Soon after, a period called the 'Beeldenstorm' began. This was when people destroyed religious statues and art in Catholic churches across the Netherlands. Resistance against Spanish rule grew stronger. Lamoral was a very religious Catholic. He did not approve of the destruction of church art. He wanted to stay loyal to the Spanish king. However, he and Horn still opposed the Inquisition, which made King Philip angry.
Arrest and Execution
King Philip II sent the Duke of Alba to the Netherlands to stop the rebellion. William of Orange decided to leave Brussels for safety. But Egmont always refused to do anything that looked like he was betraying the king. So, he and Horn decided to stay in the city.
When the Duke of Alba arrived, he quickly arrested Egmont and Horn. They were accused of heresy (going against the church) and put in prison in Ghent. Egmont's wife and their eleven children had to find safety in a convent. Many powerful people across Europe, including other kings and the Emperor Maximilian II, asked King Philip to free them. Even the Order of the Golden Fleece argued that as knights, Egmont and Horn should only be judged by their fellow knights. But King Philip refused all pleas.
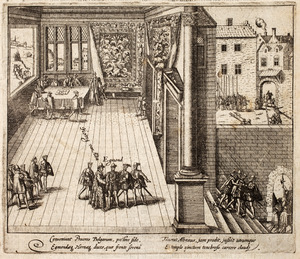
On June 4, Egmont and Horn were sentenced to death. The next day, June 5, 1568, they were executed in front of the Brussels Town Hall on the main square, the Grand-Place/Grote Markt. People noticed how calm and dignified Egmont was during his execution. Their deaths caused huge protests across the Netherlands. This event greatly helped to fuel the resistance against the Spanish rulers.
Legacy and Memorials
Count Lamoral of Egmont is buried in Egmont's crypt in Zottegem, a city in Belgium. Zottegem remembers him with two statues, a museum, and his castle.
Egmond Castle in Egmond aan den Hoef was destroyed in 1573. In 1997, a statue was put up there to remember him.
In Brussels, there is a statue on the Square du Petit Sablon/Kleine Zavelsquare. It honors both Egmont and Horn. They are often remembered together as the first leaders of the Dutch revolt. They came before William of Orange, who became the main leader after their deaths. William of Orange was later assassinated in 1584. He had managed to free parts of the Netherlands in the early years of the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648).
After his execution, Egmont's lands and titles were taken away. However, some of his lands were later given back to his family in 1600. Even with these difficulties, his niece, Louise of Lorraine-Mercœur, became the Queen consort of Henry III of France in 1575.
Egmont in Arts and Culture
Lamoral, Count of Egmont, is the main character in a play called Egmont by the famous writer Goethe. In 1810, the composer Ludwig van Beethoven wrote an overture and music for a new performance of this play.
Images for kids
-
Statue of Egmont and Hoorne, Square du Petit Sablon/Kleine Zavelsquare, Brussels.
-
Statue of Egmont on the market square in Zottegem.
-
The castle of La Hamaide, where Egmont was born.
See also
 In Spanish: Conde de Egmont para niños
In Spanish: Conde de Egmont para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |