Microsoft SQL Server facts for kids
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | April 24, 1989, as SQL Server 1.0 |
| Stable release |
SQL Server Lua error in Module:Wd at line 1575: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). (CU18 16.0.4185.3) / Lua error in Module:Wd at line 1571: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).
|
| Written in | C, C++ |
| Operating system | Linux, Microsoft Windows Server, Microsoft Windows |
| Available in | English, Chinese, French, German, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese (Brazil), Russian, Spanish and Indonesian |
| Type | Relational database management system |
| License | Proprietary software |
Microsoft SQL Server is a special computer program made by Microsoft. It helps store and manage lots of information, like a giant digital filing cabinet. This program uses a language called Structured Query Language (SQL) to organize and find data.
Think of it as a "database server." Its main job is to keep data safe and give it back when other computer programs ask for it. These other programs can be on the same computer or on different computers connected through a network, like the internet. Microsoft offers many different versions of SQL Server. Each version is designed for different needs, from small apps on one computer to huge websites used by many people at once.
Contents
History of SQL Server
The story of Microsoft SQL Server began in 1989. The very first version, SQL Server 1.0, was made for an operating system called OS/2. Its name tells you what it does: it's a server program that answers questions (or "queries") using the SQL language.
Key Moments in SQL Server
- In 1989, Microsoft worked with Sybase and Ashton-Tate to bring SQL Server to OS/2.
- SQL Server 4.2 came out in 1993. This was the first version to work with Windows NT.
- In 1995, SQL Server 6.0 was released. This marked the end of Microsoft's partnership with Sybase.
- SQL Server 7.0, released in 1998, was a big change. Its main code was rewritten from C to C++.
- SQL Server 2000 was released in the year 2000.
- SQL Server 2005, released in 2005, finished rewriting all the old Sybase code into Microsoft's own code.
- SQL Server 2008, released in 2008, added new ways to store data, like for locations (SPATIAL data).
- SQL Server 2012, released in 2012, added a feature called xVelocity for faster data storage.
- SQL Server 2017, released in 2017, became available for Linux operating systems like Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Ubuntu.
- SQL Server 2019, released in 2019, added features for handling very large amounts of data.
- The latest version, SQL Server 2022, was released on November 16, 2022.
Current Supported Versions
As of August 2025, Microsoft supports these versions of SQL Server:
- SQL Server 2016
- SQL Server 2017
- SQL Server 2019
- SQL Server 2022
From SQL Server 2016 onwards, the program only works on x64 processors. It needs a processor speed of at least 1.4 GHz, but 2.0 GHz or faster is recommended for best performance.
Different Versions of SQL Server
Microsoft offers SQL Server in many different versions, called "editions." Each edition has different features and is made for different kinds of users or businesses.
Main Editions
- Enterprise
- This is the most powerful version. It includes the main database engine and many extra tools. It can manage huge databases, up to 524 petabytes of data, and use a lot of computer memory.
- Standard
- This edition also has the main database engine and some extra tools. It's similar to Enterprise but for slightly smaller needs. It doesn't have some of the super-advanced features for keeping things running all the time.
- Web
- This version is designed to be affordable for websites.
- Business Intelligence
- Introduced in SQL Server 2012, this version focuses on tools that help businesses make smart decisions by analyzing their data. It includes features like Power Pivot and Power View.
- Express
- SQL Server Express is a smaller, free version of SQL Server. It's great for learning or for small projects. It has some limits, like using only one processor and a maximum database file size of 10 GB. It comes in different versions, some with extra tools like SQL Server Management Studio Basic.
Special Editions
- Azure
- Microsoft Azure SQL Database is a version of SQL Server that runs in the cloud. This means you can use it over the internet without needing to set up your own server.
- Compact (SQL CE)
- This is a tiny version of the database engine. It's designed to be used inside other applications, especially for mobile devices. It's very small but has fewer features than the main SQL Server.
- Developer
- This edition has all the same features as the Enterprise Edition. However, it's only for testing and developing new programs, not for running a live business system. Microsoft made this edition free in early 2016.
- Evaluation
- This is a trial version. It has all the features of the Enterprise Edition but only works for 180 days. After that, the server services stop, but the tools still work.
- LocalDB
- Introduced in SQL Server Express 2012, LocalDB is a simple version of SQL Server for app developers. It can also be used as a database built right into an application.
- Analytics Platform System (APS)
- This is a special SQL Server system designed for very large data warehouses, which are huge collections of data used for analysis.
Older Versions (No Longer Used)
Some versions of SQL Server are no longer supported by Microsoft:
- Microsoft Data Engine (MSDE): This was an older, smaller version often included with other Microsoft tools. It was replaced by SQL Server Express.
- Datacenter: This was a powerful edition for very large data centers. Its features are now part of the SQL Server 2012 Enterprise Edition.
- Windows CE Edition and Mobile Edition: These were versions for mobile devices, later replaced by SQL Server Compact.
How SQL Server Works
SQL Server has different parts that work together. The "protocol layer" is like the front door. All commands sent to SQL Server go through this layer using a special language called Tabular Data Stream (TDS). TDS helps send data between the database server and the client program. This means you can access SQL Server over networks, like the internet.
Storing Data
Data in SQL Server is kept in a database, which is like a collection of tables. Each table has columns that hold specific types of information, like numbers, text, or dates. SQL Server supports many data types, such as Integer (whole numbers), Float (numbers with decimals), Char (text), and Binary (for things like images).
A database can hold many different items, like views (which are like saved searches), stored procedures (saved sets of commands), and indexes (which help find data faster). A SQL Server database can be very large and spread across several files on your computer. The main data files usually end with `.mdf`, and extra data files use `.ndf`. Log files, which record changes, end with `.ldf`.
The storage space is divided into small pieces called pages, each 8 KB in size. A page is the smallest amount of data SQL Server reads or writes at one time. These pages are grouped into extents, which are 8 pages together.
Managing Memory (Buffer)
SQL Server uses your computer's RAM (memory) to store copies of data pages. This is called the "buffer cache." When you ask for data, SQL Server first checks if it's already in the buffer cache. If it is, it's much faster to get it from memory than from the hard drive. The "Buffer Manager" handles this. It also makes sure that changes made in memory are eventually saved to the hard drive.
Handling Many Users (Concurrency)
Many people can use the same SQL Server database at the same time. SQL Server needs to make sure that when multiple users try to change the same data, everything stays organized and correct. It does this in two main ways:
- Pessimistic Concurrency (Locks): When someone is changing data, SQL Server can "lock" that data. This means no one else can change it until the first person is done. Locks can be on a whole table, a page, or even just one row of data.
- Optimistic Concurrency (Versions): Instead of locking, SQL Server can create a new version of a row every time it's updated. If someone else tries to read that data while it's being updated, they just see the older version. This allows more people to work at the same time without waiting.
SQL Server also watches out for "deadlocks," which happen when two users are waiting for each other to release a lock. If this happens, SQL Server will stop one of the users to keep things moving.
Getting Data and Programming
The main way to get data from SQL Server is by asking it questions, called "queries." These queries are written using a special version of SQL called T-SQL. T-SQL is a language that Microsoft SQL Server shares with other database systems because of its history.
When you send a query, SQL Server's "query processor" figures out the best way to get the data you asked for. This plan is called a "query plan." SQL Server tries to find the fastest way to get the results, considering how the data is organized and how busy the system is. Once a plan is made, SQL Server saves it for a while. If you ask the same question again, it can use the saved plan, which makes things faster.
SQL Server also lets you create "stored procedures." These are like saved sets of T-SQL commands that live on the server. You can run them by just saying their name, which saves time and network traffic.
T-SQL Language
T-SQL (Transact-SQL) is Microsoft's special version of the SQL language. It adds extra commands to standard SQL for managing the database, changing data, and controlling security. Client programs use T-SQL to talk to SQL Server, sending commands and getting results back.
SQL CLR (.NET Integration)
Since SQL Server 2005, there's a feature called SQL CLR (Common Language Runtime). This allows you to write special database programs, like stored procedures, using popular programming languages like C# and VB.NET. This means developers can use familiar tools to build powerful features right inside the database.
Extra Services
SQL Server also comes with many extra services that add more features beyond just storing data. These services run alongside the main database system.
Machine Learning Services
These services let you do machine learning and data analysis directly inside SQL Server. This means you don't have to move large amounts of data to another computer. It includes tools for R and Python to build smart models that can learn from your data.
Service Broker
Service Broker helps different parts of SQL Server applications talk to each other by sending messages. It's like a reliable mail system for your database programs, making sure messages get delivered and processed.
Replication Services
SQL Server Replication Services help you make copies of your database and keep them in sync across different servers or even on client computers. There are three main types:
- Transaction replication
- Copies every change from one database to others almost instantly.
- Merge replication
- Tracks changes on all copies and syncs them up, even if changes were made in different places. It can also help fix conflicts if the same data was changed differently.
- Snapshot replication
- Makes a copy of the entire database at one moment in time and sends it out. Future changes are not tracked.
Analysis Services
SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) adds powerful tools for analyzing data. It helps you create "cubes" of data, which are like multi-dimensional spreadsheets, to quickly answer complex business questions. It also includes tools for data mining, which helps find hidden patterns in your data.
Reporting Services
SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) is a tool for creating reports from your SQL Server data. You can design reports using tools like Microsoft Visual Studio and then view them in many different formats, like PDF or Excel.
Integration Services
SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) helps you move and transform data. It's used for tasks like taking data from different sources, cleaning it up, changing its format, and then putting it into a new database or file.
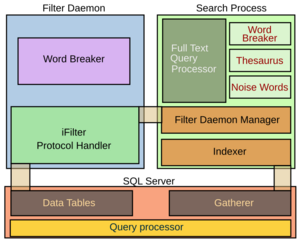
Full Text Search Service
This service helps you search through large amounts of text stored in your database, like searching for words in documents. It's much more powerful than a simple search. It can find words even if they are spelled slightly differently (like "run," "running," "ran") and can rank how well a search matches. It also filters out common words like "a" or "and" to give you better results.
Tools for SQL Server
Microsoft provides several tools to help you work with SQL Server.
SQLCMD
SQLCMD is a command-line tool that lets you type SQL commands directly into a text window and run them. It's useful for managing databases and running scripts (saved sets of commands).
Visual Studio
Microsoft Visual Studio is a popular programming environment. It has built-in support for working with SQL Server. You can use it to design your database, write code for SQL CLR, and create queries.
SQL Server Management Studio
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is a graphical tool that helps you set up, manage, and control all parts of SQL Server. It's like a control panel for your database. You can use it to see how your database is organized, create new databases, change tables, and check how well your queries are performing.
Azure Data Studio
Azure Data Studio is a newer tool for writing queries and managing SQL Server. It works on Windows, Mac, and Linux computers. It's good for writing SQL code, looking at results, and connecting to online code repositories like Git.
Business Intelligence Development Studio
Business Intelligence Development Studio (BIDS) was an older tool for creating data analysis and business intelligence solutions. For newer versions of SQL Server (2012 and later), this tool is now called SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT).
See also
 In Spanish: Microsoft SQL Server para niños
In Spanish: Microsoft SQL Server para niños
- Comparison of relational database management systems
- List of relational database management systems
 | Charles R. Drew |
 | Benjamin Banneker |
 | Jane C. Wright |
 | Roger Arliner Young |