Oarfish facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Oarfish |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Giant oarfish | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Lampriformes |
| Family: | Regalecidae |
| Genera | |
|
|

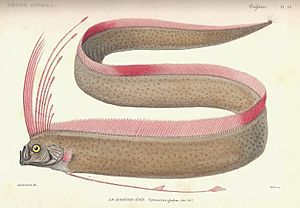
Oarfish are amazing, long, and rarely seen fish that live deep in the ocean. They belong to a small family called Regalecidae. You can find them in oceans all over the world, from cooler areas to warm tropical zones.
There are three types of oarfish. One of them, the giant oarfish, is the longest bony fish alive! It can grow up to 17 m (56 ft) long, which is like two school buses end-to-end!
People call them "oarfish" because of their long, flat bodies. Some people used to think they "rowed" through the water with their fins, but that's not true. The name "Regalecidae" comes from a Latin word meaning "royal."
Because oarfish are so rare and big, and sometimes wash up on beaches after storms, they might be the reason for many old sea serpent stories. Even though they are large, people don't usually eat them because their meat is soft and jelly-like.
Contents
What Do Oarfish Look Like?
Oarfish have a long fin on their back called a dorsal fin. It starts above their big eyes and goes all the way down their body. The first few rays of this fin are extra long and form a cool crest with reddish spots. Their pelvic fins are also long and decorated. Their side fins (pectoral fins) are very small. They don't have an anal fin, and their tail fin can be tiny or missing, making their body taper to a point. None of their fins have sharp spines.
Oarfish have small mouths that can stick out, but they don't have visible teeth. Their bodies don't have scales. Instead, their skin is covered with a silvery, easily scratched layer. Some oarfish have hard bumps on their skin. They also don't have a gas bladder, which most fish use to control their depth in the water.
Their colors can vary. They often have blue or black streaks, dots, and squiggles on their sides. These marks fade quickly after the fish dies. Scientists think these markings might glow in the deep, dark ocean.
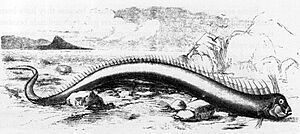
The giant oarfish is the biggest in its family. It's usually about 8 m (26 ft) long, but some unconfirmed reports say they can be 17 m (56 ft) and weigh up to 270 kg (600 lb)! Another type, the streamer fish, can reach 3 m (9.8 ft).
Sometimes, the end of an oarfish's tail looks like it's been cut off. This is probably because they can break off their own tails as a way to escape from predators.
Oarfish bones can grow extra thick, especially along their spine. This helps support their long bodies when they swim and prevents their spines from breaking. It might also help them float. Since they don't have a swim bladder, they have to move their tails a lot to stay at a certain depth.
Where Do Oarfish Live?
Oarfish usually live in the deep parts of the ocean, from about 250 m (820 ft) to 1,000 m (3,300 ft) below the surface. They are very rarely seen near the surface. If one does float up, it usually dies because of the change in pressure.
In these deep parts of the ocean, there are almost no currents. This means oarfish don't need strong muscles. Because of this, they can't survive in the shallower, rougher waters near the surface.
Oarfish are found all over the world in tropical, subtropical, and warm ocean areas. But since they live so deep, we mostly learn about where they live from fish that are caught by accident or wash up on shore.
Oarfish Behavior and Life Cycle
Scientists first described oarfish in 1772. We don't know much about their behavior because they are so hard to find. They are usually solitary, meaning they live alone.
In 2001, a 1.5-metre (4.9-foot) oarfish was filmed alive underwater by U.S. Navy personnel in the Bahamas. They saw it swimming by wiggling its dorsal fin while keeping its body straight. This is a special way of swimming called "amiiform" movement.
Sometimes, oarfish are seen swimming straight up and down, with their bodies pointing towards the surface. Scientists think they might do this to spot prey, as the light from above would make their food easier to see.
In 2008, scientists captured footage of an oarfish swimming in its natural home in the Gulf of Mexico. This was the first time a healthy oarfish was seen so deep. It was thought to be between five and ten metres (16 and 33 ft) long.
Between 2008 and 2011, several healthy oarfish were seen by underwater robots in the northern Gulf of Mexico, some as deep as 492 m (1,614 ft). One oarfish was even seen switching from swimming vertically to swimming sideways, wiggling its whole body. Oarfish don't seem to swim away quickly when robots approach, which suggests they don't have many natural predators.
From late 2009 to early 2010, many slender oarfish appeared in the waters and on the beaches of Japan. In Japanese stories, these fish are called the "Messenger from the Sea God's Palace" and are said to predict earthquakes. After the big 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, many people linked it to the oarfish sightings.
In 2016, a TV show called River Monsters filmed host Jeremy Wade interacting with live oarfish while diving. He even touched one! The oarfish were swimming using their special amiiform movement.
In January 2019, two oarfish were found alive in fishing nets off the Japanese island of Okinawa. In June 2023, divers filmed an oarfish off Taiwan that looked like it had been injured by a shark.
What Do Oarfish Eat?
Oarfish mostly eat tiny sea creatures called zooplankton. They filter small shrimp and other crustaceans from the water. They also eat small fish, jellyfish, and squid. Larger ocean predators like sharks and whales might eat oarfish. Oarfish are known to suck in their prey, like when there are lots of plankton in the water.
Oarfish Reproduction
Scientists don't know much about how oarfish breed. Female oarfish can produce hundreds of thousands, or even millions, of eggs! They release their brightly colored, floating eggs into the water, and they become part of the zooplankton. The eggs are about six millimetres (0.24 in) wide.
The eggs hatch after about three weeks. The baby oarfish, called larvae, are very active and eat other zooplankton. They look quite different from adult oarfish, with long dorsal and pelvic fins and mouths that can stretch out. Young oarfish have been seen floating just below the surface. But as they grow up, they probably go deeper into the ocean.
Recent studies of oarfish reproductive organs suggest that they release many eggs in batches during their breeding season. This means they might spawn multiple times over one or two months.
Who Eats Oarfish?
A recent study looked at parasites found in an oarfish. Based on these parasites, scientists think that shortfin mako sharks and sperm whales might be predators of the oarfish.
See also
 In Spanish: Pez remo para niños
In Spanish: Pez remo para niños
- List of fish families
- List of fish common names

