Ray-finned fish facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Ray-finned fish |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Superclass: | Osteichthyes |
| Class: | Actinopterygii Klein, 1885 |
| Subclasses | |
|
|
Actinopterygii are also known as ray-finned fishes. They are a huge group of bony fishes. In fact, more than half of all living vertebrate species are ray-finned fish!
These fish get their name because their fins are like webs of skin. These webs are held up by bony or tough spines, which are called rays. This is different from "lobe-finned fish," which have fleshy, muscular fins. The fin rays of ray-finned fish connect directly to their inner skeleton.
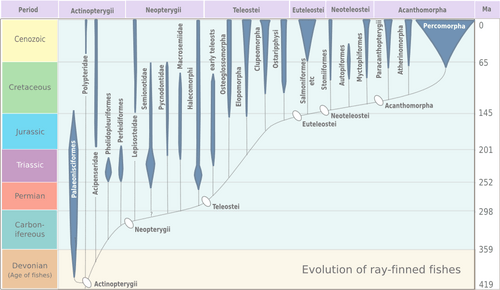
Ray-finned fish are the most common type of vertebrate. They make up almost 99% of the over 30,000 known fish species. You can find them almost everywhere, from freshwater rivers and lakes to the deepest parts of the ocean. They come in all sizes, from tiny Paedocypris, which is only 8 mm (0.3 in) long, to the huge ocean sunfish, which can weigh 2,300 kg (5,070 lb). The long-bodied oarfish can even grow up to 11 m (36 ft) long! Most ray-finned fish (about 95%) are a type called teleosts.
Contents
What Makes Ray-Finned Fish Special?
.
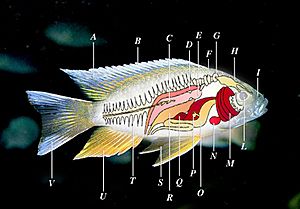
Ray-finned fish come in many different shapes and sizes. The picture next to this text shows the main parts of a typical ray-finned fish. One important part is the swim bladder, which helps the fish control its buoyancy (how it floats or sinks).
These fish have many kinds of scales. However, most advanced ray-finned fish, called teleosts, have special scales called leptoid scales. The outer part of these scales has bony ridges, and the inner part is made of thin, flexible tissue. Leptoid scales are thinner and more see-through than other scales. They don't have the hard, enamel-like layers found on other fish scales. As a teleost fish grows, new layers are added to its scales, like the rings on a tree.
Long ago, both ray-finned and lobe-finned fish (which include animals like us!) had lungs to breathe air. Today, only bichirs, a type of ray-finned fish, still have these lungs.
Amazing Body Shapes and Fins
Ray-finned fish show incredible variety in their size, shape, and how they eat. Their ray-fins also come in many different numbers and arrangements.
-
Tuna are shaped like torpedoes for super fast swimming
-
The swordfish is even faster and more streamlined than the tuna
-
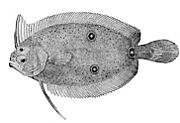
Flatfish have special dorsal and pelvic fins that are partly symmetrical
-
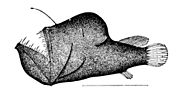
The first spine of the dorsal fin of anglerfish acts like a fishing rod with a light-up lure
-
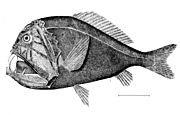
European conger are ray-finned fish
-
The bottom-dwelling batfish Ogcocephalus notatus
-
The sturgeon Acipenser oxyrhynchus has a skeleton mostly made of cartilage
-
Seahorses are part of the extended pipefish family
-
The "flying fish" Exocoetus obtusirostris has special pectoral fins for gliding
-
The hoodwinker sunfish Mola tecta has no tail fin
-
The Jurassic †Leedsichthys was a giant filter-feeder
Reproduction and Life Cycle

For almost all ray-finned fish, there are separate male and female fish. In most species, the females lay eggs, and the males fertilize them outside the body. Then, the eggs hatch into free-swimming larvae.
However, some fish have different ways of reproducing. One common way is called sequential hermaphroditism. This means a fish can change its sex during its life. Most often, fish start as females and later turn into males. This is called protogyny. It's much less common for a fish to start as a male and then become a female.
Most ray-finned fish lay eggs and do not take care of their young. But about 21% of teleost fish families do show some form of parental care. This care can be given by the male, the female, or both parents. The oldest known example of live birth in ray-finned fish is from a Middle Triassic species called †Saurichthys. Live birth is quite rare, happening in about 6% of living teleost species. When there is parental care, it's more often the male fish that takes care of the eggs or young.
There are even a few fish that can fertilize their own eggs! For example, the mangrove rivulus is a fish that can live both in water and out of it. It is a hermaphrodite, meaning it produces both eggs and sperm. It fertilizes its eggs internally. This special way of reproducing might help it survive when it spends a lot of time out of water in mangrove forests.
History and Classification
Ray-finned fish are divided into two main groups: Cladistia and Actinopteri. The Actinopteri group includes Chondrostei and Neopterygii. Most living fish, about 96% of all fish species, belong to the Neopterygii group, especially the Teleostei (teleosts). Other groups of ray-finned fish have fewer species today.
Here's a simpler way to see how ray-finned fish are grouped:
- Cladistia: This group includes bichirs and reedfish.
- Actinopteri: This group includes:
- Chondrostei: This includes sturgeons and paddlefishes.
- Neopterygii: This is the largest group and includes:
- Teleostei: Most of the fish you know today belong here.
- Holostei: This includes gars and bowfin.
The oldest known fossil of a ray-finned fish is Andreolepis hedei. It lived about 420 million years ago, during the Late Silurian period. Fossils of this ancient fish have been found in Russia, Sweden, and Estonia. The first fossil relatives of modern teleosts appeared during the Triassic period.
| Chondrostei | The Chondrostei are a group of fish that mostly have skeletons made of cartilage, not hard bone. There are 52 species in this group, including sturgeons and paddlefishes. Long ago, scientists thought these fish were related to sharks because they both have cartilage skeletons and similar jaw structures. However, fossils show that chondrosteans are more closely related to teleosts. | |
|---|---|---|
| Neopterygii | The Neopterygii group of ray-finned fish first appeared in the Late Permian period. These fish are very successful because they can move much faster than their ancestors. Over time, their scales and skeletons became lighter. Their jaws also became stronger and more effective for catching food. |
Images for kids
-
Fossil of the Devonian †Cheirolepis canadensis
-
Fossil of the Carboniferous †Elonichthys peltigerus
-
Fossil of the Permian †Aeduella blainvillei
-
Fossil of the Permian †Palaeoniscum freieslebeni
-
Fossil of the Triassic †Bobasatrania canadensis
-
Fossil of the Triassic †Thoracopterus magnificus
-
Fossils of the Triassic †Prohalecites sp., an early teleosteomorph
-
Fossil of the Jurassic †Aspidorhynchus sp.
-
Fossil of the Jurassic †Pachycormus curtus
-
Fossil of the Cretaceous †Yanosteus longidorsalis
-
Fossil of the Cretaceous †Nematonotus longispinus
-
Fossil of the Cretaceous †Thrissops formosus
-
Fossil of the Cretaceous †Mene oblonga
-
Fossil of the Cretaceous †Amphistium paradoxum
-
Fossil of the Miocene †Nerophis zapfei
-
Skeleton of the angler fish, Lophius piscatorius. The first spine of the dorsal fin of the anglerfish is modified so it functions like a fishing rod with a lure
-
Skeleton of another ray-finned fish, the lingcod
-
Blue catfish skeleton
See also
 In Spanish: Peces con aletas radiadas para niños
In Spanish: Peces con aletas radiadas para niños
 | Sharif Bey |
 | Hale Woodruff |
 | Richmond Barthé |
 | Purvis Young |