Orbital resonance facts for kids
Orbital resonance happens when two objects orbiting each other have a regular, repeating pull of gravity. Imagine two planets or a planet and its moon. Their orbital periods (the time it takes them to go around once) are often related by a simple ratio of small whole numbers, like 1:2 or 2:3.
This effect is caused by the way gravitational forces change as these bodies move around each other. The stability of our Solar System has been studied for a long time, starting with scientists like Laplace. There's still a lot to learn about how these gravitational dances work!
How Orbits Affect Gravity
When a moon goes around a planet, or two stars orbit each other, the gravitational forces between them can change a lot. This is partly because orbits are usually ellipses (oval shapes), not perfect circles. So, the distance between the objects changes, and with it, the strength of gravity.
Also, planets and stars are usually not perfect spheres. They spin, and some are a bit flattened at their poles. This shape difference also affects the gravitational forces on an orbiting body.
Stable and Unstable Orbits
Sometimes, these gravitational forces can be unstable. This means the smaller object in orbit might change its path until the forces become stable. A common example is when a moon ends up always showing the same face to its planet. This is called tidal locking, and it's the most stable position for the moon. Our Moon is tidally locked with Earth!
There are other cool stability effects too:
- Gaps in Rings: The gaps we see in Saturn's rings are caused by orbital resonance. Tiny particles in the rings shift into more stable positions, creating clear lanes.
- Cassini Division: A famous gap in Saturn's rings is the Cassini Division. It was cleared by a 2:1 resonance with Saturn's moon Mimas. This means Mimas orbits Saturn once for every two times the particles in the Cassini Division would have orbited.
- Pluto and Neptune: Neptune and Pluto have a stable 2:3 resonance. For every two times Pluto orbits the Sun, Neptune orbits three times. This special relationship keeps them from colliding, even though their orbits cross.
The study of how these objects move and interact in space is called celestial mechanics. It helps us understand the amazing dance of planets, moons, and stars.
Images for kids
-
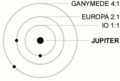
The three-body Laplace resonance exhibited by three of Jupiter's Galilean moons. Conjunctions are highlighted by brief color changes. There are two Io-Europa conjunctions (green) and three Io-Ganymede conjunctions (grey) for each Europa-Ganymede conjunction (magenta). This diagram is not to scale.
-
Spiral density waves in Saturn's A Ring excited by resonances with inner moons. Such waves propagate away from the planet (towards upper left). The large set of waves just below center is due to the 6:5 resonance with Janus.
-
The eccentric Titan Ringlet in the Columbo Gap of Saturn's C Ring (center) and the inclined orbits of resonant particles in the bending wave just inside it have apsidal and nodal precessions, respectively, commensurate with Titan's mean motion.
-
Depiction of asteroid Pallas' 18:7 near resonance with Jupiter in a rotating frame (click for animation). Jupiter (pink loop at upper left) is held nearly stationary. The shift in Pallas' orbital alignment relative to Jupiter increases steadily over time; it never reverses course (i.e., there is no libration).
-
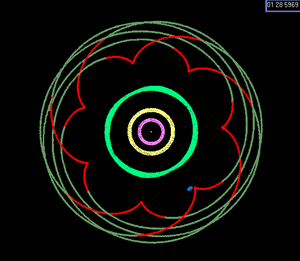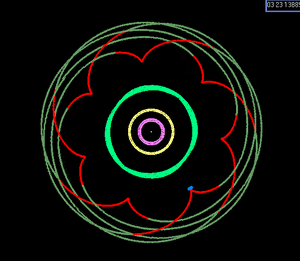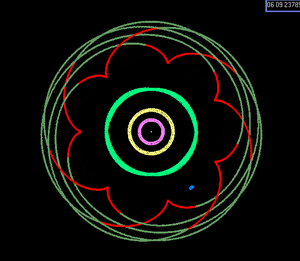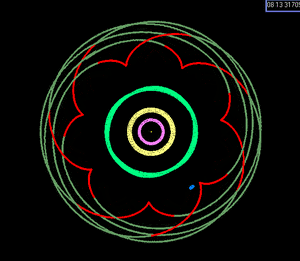
Depiction of the Earth:Venus 8:13 near resonance. With Earth held stationary at the center of a nonrotating frame, the successive inferior conjunctions of Venus over eight Earth years trace a pentagrammic pattern (reflecting the difference between the numbers in the ratio).
-
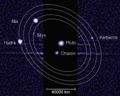
Diagram of the orbits of Pluto's small outer four moons, which follow a 3:4:5:6 sequence of near resonances relative to the period of its large inner satellite Charon. The moons Styx, Nix and Hydra are also involved in a true 3-body resonance.
See also
 In Spanish: Resonancia orbital para niños
In Spanish: Resonancia orbital para niños