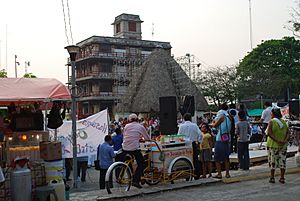Palenque, Chiapas facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Palenque
|
|
|---|---|
|
Municipality and city
|
|

Main plaza in the city
|
|
| Country | |
| State | Chiapas |
| Founded | 1567 |
| Municipal Status | 1915 |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 2,888 km2 (1,115 sq mi) |
| • Seat | 18.62 km2 (7.19 sq mi) |
| Elevation
(of seat)
|
60 m (200 ft) |
| Population
(2020 census)
|
|
| • Municipality | 132,265 |
| • Density | 45.798/km2 (118.617/sq mi) |
| • Seat | 51,797 |
| • Seat density | 2,781.8/km2 (7,204.8/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central (US Central)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (Central) |
| Postal code (of seat) |
29960
|
| Area code(s) | 916 |
Palenque is a city and municipality in the Mexican state of Chiapas. It is located in southern Mexico. The city was named long before the famous Mayan ruins were found in the 1700s. Many Ch'ol people live here. They are an indigenous group descended from the ancient Mayans.
Palenque city is the only large urban area in its municipality. The municipality has over 600 smaller communities. The city is surrounded by thick rainforest. Sadly, deforestation has changed the local environment a lot. Sometimes, howler monkeys come into the city looking for food. Most people in the municipality work in farming. The ancient Palenque archeological site is a very important place for tourists. It helps the local economy and is a major attraction for Chiapas.
Contents
Palenque City and Municipality
The name Palenque refers to both the modern city and the larger area it governs. This larger area is called a municipality. In 2010, the Palenque municipality had a population of 110,918 people.
The city of Palenque itself had 42,947 people in 2010. This was an increase from 37,301 people in 2005. Besides the main city, the municipality has 950 smaller towns and villages. Some of the larger rural communities include Río Chancalá, Doctor Samuel León Brindis, and Agua Blanca Serranía.
The city of Palenque is the only urban area in the municipality. The municipality covers a large area of 2,888 square kilometers (about 1,115 square miles). The city was started in 1567 by a person named Pedro Lorenzo. In 1573, the community received three bells as a symbol of its founding. One of these old bells is still in the city's main church today.
Even though it's a city, Palenque is surrounded by jungle. It sits only 60 meters (about 197 feet) above sea level. This jungle is home to many famous Chiapas animals, like the howler monkey. These monkeys sometimes come into the city because they lose their natural homes. They might get confused and hit by cars. Injured monkeys are sometimes taken to a special park called Eco Parque Aluxes for care.
The Palenque municipality shares borders with other municipalities in Chiapas. It also borders the state of Tabasco and the country of Guatemala to the east. The city itself is about 60 meters (197 feet) above sea level.
Most homes in the municipality are owned by the people who live in them. About 80% of homes are owned by residents. The average home has about 4.84 people living in it. Many homes have dirt floors, but more than half have cement floors. Most walls are made of wood, but some are made of concrete blocks. About 86% of homes have electricity. About 75% have running water, and over half have sewer systems.
The municipality has many post offices and a telegraph office. There are also public telephone centers for people without home phones. The area has 569.99 kilometers (about 354 miles) of roads. Most of these are rural roads and state highways. You can reach Palenque by Highway 199 from San Cristóbal or Highway 186 from Escárcega.
The population of Palenque has grown a lot over the years. From 1990 to 2000, it grew from 63,209 to 85,464 people. About 35% of the people live in the city. The rest live in 679 smaller communities. The population density is 76 people per square kilometer.
Education has improved in Palenque. In 2000, the number of people who could not read or write was 23.77%. This was lower than in 1990. Many people over 15 have finished primary school or studied even further.
Indigenous Culture and Language
The city and municipality of Palenque have a large Ch'ol indigenous population. In 2005, about 37,032 people spoke an indigenous language. This means about 40% of the population is indigenous. The main indigenous group is the Ch'ol. About 20% of indigenous residents do not speak Spanish.
The municipality holds an annual Festival Mundo Maya (Mayan World Festival) in April. This festival celebrates the culture, traditions, crafts, food, and clothing of the Mayan people. People from other states like Tabasco and Yucatán also join in the event.
Religion and Celebrations
About 53% of the people in Palenque are Catholic. About 25% are Protestant, and some are Evangelical. About 14% say they have no religion. The most important religious celebrations are the feasts of Saint Dominic and Francis of Assisi.
Every year, the city of Palenque puts on a passion play. This play tells the story of Jesus's last days. A young man from the area is chosen to play Jesus. The play follows the 14 Stations of the Cross and ends with the crucifixion. It starts at the Santo Domingo de Guzmán church.
History of Palenque
The name Palenque comes from Spanish. It means "wood stake fence." This is a direct translation of the Ch’ol word "otulún," which means a fenced or strong place. The modern town was started by Friar Pedro Lorenzo in 1567. He founded it near the famous ruins to bring together the Ch’ol families living in the Lacandon rainforest.
In 1768, the state of Chiapas was divided into larger areas. Palenque became part of the area governed by Ciudad Real (now San Cristóbal de las Casas). In 1813, Palenque was officially called a town. A road was built connecting Bachajon and Palenque in 1821. The town's first school opened in 1828.
In 1883, the state was reorganized. Palenque became the head of one of the new departments. A railroad was built to connect the town with the Gulf of Mexico. The Pakalna station, which is still there, was part of this railroad. In 1915, Palenque became the head of its own municipality.
The first airfield was built in 1931. Mail and telegraph services arrived in 1941. In 1972, the governor of Chiapas declared Palenque a city. The Casa de Cultura (House of Culture) was founded in 1980. The main road was paved in 1990. The modern airport, Palenque International Airport, was built in 1997. There are also plans to build a train station here for the Tren Maya project.
Discovery of the Ancient Mayan City
The ancient Mayan city of Palenque was unknown to the Spanish when they founded the modern town. It was discovered in 1740 by Father Antonio Solís. Since then, it has been very important to the city and municipality. The ruins were visited by explorers and officials over the years.
In 1951, the tomb of Pakal was discovered by Alberto Ruz Lhuillier. This was a huge discovery! The Palenque site museum was opened in 1958. Today, the ancient site is one of the most important tourist attractions in Chiapas.
Geography and Nature
Most of the Palenque municipality is flat land that stretches north to the Gulf of Mexico. Some parts are in the mountains, like the Montañas del Oriente and the Montañas del Norte. It is part of the Selva region of the state and borders the Lacandon Jungle.
The climate here is hot and humid. It rains all year round. The area has mostly tropical rainforest plants. Sadly, much of this forest has been cut down, causing damage to the environment. Important rivers include the Usumacinta and its smaller rivers like Chamacax and Chancalá. There is also one lake called Lago Metzaboc.
Palenque National Park
The municipality is home to the Palenque National Park. This park was created in 1981. It covers an area of 1,771.95 hectares (about 4,378 acres). The park was made to protect the rainforest and many endangered animals. The park surrounds the ancient Palenque archeological site. Both the site and the park are together listed as a World Heritage Site.
The national park is home to many important Chiapas animals. This includes the howler monkey, which is endangered because of deforestation. The park has hiking trails where you can see different plants, streams, and small waterfalls.
Economy and Tourism
Many people in the Palenque municipality work in farming and raising animals. About 51% of working people are in this field. A smaller number, about 10%, work in construction and industry. About 35% work in shops and services, including tourism.
In 2015, the city of Palenque was named a "Pueblo Mágico" (Magical Town). This is a special title given to towns in Mexico that have unique cultural or historical importance.
Main Tourist Attractions
The main reason tourists visit Palenque is the ancient archeological site. It is located about 7 kilometers (4.3 miles) from the city. This site is famous around the world and is one of the most important in Chiapas. It is part of the Maya Route, which includes other Mayan sites like Yaxchilan and Bonampak in the Lacandon Jungle.
Palenque has many hotels, mostly in the city itself. It is one of the places in Mexico that gets many visitors during the spring equinox. This is when the sun crosses the equator, and many people visit ancient sites. During Holy Week, a major vacation time in Mexico, many tourists come to the area. Extra safety measures are put in place to protect the ancient ruins.
The ancient city of Palenque was a major center of the Mayan civilization. It grew during the Classic period. The most famous buildings at the site are the Temple of the Inscriptions and the Palace. The site is known for its large buildings and many carvings with Mayan writing. It is also where the tomb of King Pakal was found in the 1950s. This was one of the most important Mayan discoveries of the 20th century. The Palace is the largest and most complex building, with a four-story tower. Other important buildings include the Temple of the Cross and the Temple of the Sun. There is a museum at the site in the National Park area. It tells the story of the ancient city and its discoveries.
Ecotourism and Natural Wonders
Besides the ancient ruins, Palenque also has many ecotourism sites. One of the newest is the "Ecoparque los Aluxes" near the city. This park helps rescue and care for wildlife. It has natural areas for animals like jaguars, ocelots, macaws, spider monkeys, and turtles. The park works with other similar places like Xcaret Park. One of its goals is to release 50 macaws into the Palenque National Park each year.
The Palenque National Park surrounds the archeological site. It has dense tropical rainforest and streams with beautiful blue waters. The park and the ancient site are together a World Heritage Site. Near the park are two famous waterfalls: Agua Azul and Misol Há. The rainforest in the park is home to many birds and howler monkeys.
See also
 In Spanish: Palenque (Chiapas) para niños
In Spanish: Palenque (Chiapas) para niños
 | Frances Mary Albrier |
 | Whitney Young |
 | Muhammad Ali |