Pañcāla facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kingdom of Panchala
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 1100 BCE (in Late Vedic period)–c. 400 CE (in Gupta Empire) | |||||||||||||
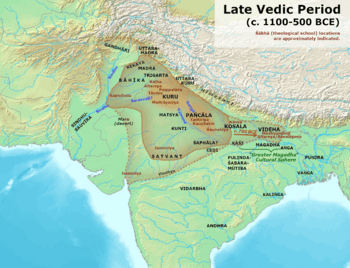
Panchala and other kingdoms in the Late Vedic period.
|
|||||||||||||
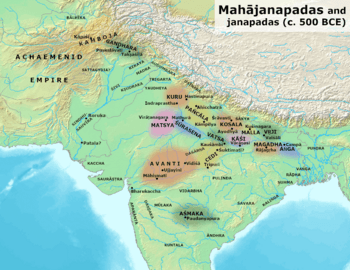
Panchala and other Mahajanapadas in the Post Vedic period.
|
|||||||||||||
| Capital | Ahichatra (northern), Kampila | ||||||||||||
| Common languages | Vedic Sanskrit | ||||||||||||
| Religion | Historical Vedic religion | ||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||||
| Raja | |||||||||||||
|
• c. 850 BCE
|
Keśin Dālbhya | ||||||||||||
|
• c. 750 BCE
|
Pravahana Jaivali | ||||||||||||
|
• c. 400 CE
|
Achyuta | ||||||||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||||||||
|
• Established
|
c. 1100 BCE (in Late Vedic period) | ||||||||||||
|
• Disestablished
|
c. 400 CE (in Gupta Empire) | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Today part of | India | ||||||||||||
Panchala (IAST: Pañcāla) was an ancient kingdom in northern India. It was located in a fertile area between the Ganges and Yamuna rivers. This region is near where the city of Kannauj is today.
During the Vedic period (around 1100–500 BCE), Panchala was one of the strongest states in ancient India. It was a close friend of the Kuru Kingdom. By about 500 BCE, it became a group of states working together. It was known as one of the sixteen mahajanapadas (major states) of the Indian subcontinent.
Panchala later became part of the Mauryan Empire (322–185 BCE). But it gained its freedom again. Finally, the Gupta Empire took over Panchala in the 4th century CE.
Contents
Where Was Panchala Located?
The Panchala kingdom was west of the Gomti River and north of the Chambal River. To its west were the Surasena people. To the northwest, thick forests separated it from the Ganges River and the Kuru Kingdom.
The northern border of Panchala was near the forests where the Ganges River starts. Today, the land of Panchala covers parts of Uttar Pradesh. This includes areas like Bareilly, Budaun, Farrukhabad, and Kannauj. It also included northern Awadh districts like Kanpur and Unnao.
Panchala in the Mahabharata
The famous Hindu epic, the Mahabharata, tells us about King Drupada of Panchala. His daughter, Draupadi, is a main character in the story. She married the five Pandava brothers.
King Drupada fought alongside the Pandavas in the Kurukshetra War. He wanted to get revenge for Draupadi's humiliation during a dice game. Important warriors like Bhishma called him a Maharathi (a very powerful warrior). His son, Dhrishtadyumna, was an Atirathi (even stronger). Another son, Shikhandi, was a Rathi (a strong chariot warrior). King Drupada gave three large armies to the Pandavas for the war.
Panchala in Ancient Times
Historians believe the Panchala kingdom was formed by several different tribes. One ancient text, the Shatapatha Brahmana, suggests that Panchala was the later name for the Krivi tribe. These Krivi people used to live near the Indus River. Later Vedic writings often mention Panchala as close allies of the Kuru Kingdom.
The capital city of Panchala was Kanyakubja, which is modern-day Kannauj. Later, the Panchala country was divided into two parts:
- Northern Panchala: Its capital was Ahichchhatra.
- Southern Panchala: Its capital was Kampilya.
Some experts think the name Panchala means "fusion of five tribes." These five tribes might have been the Krivis, Turvashas, Keshins, Srinjayas, and Somakas. Each of these tribes had important leaders mentioned in ancient texts. The Somakas and Srinjayas are also mentioned in the Mahabharata.
King Drupada, from the Mahabharata, belonged to the Somaka tribe. The Mahabharata also says that the ruling family of Northern Panchala came from the Bharata clan. Famous rulers from this line included Divodasa, Sudas, Srinjaya, Somaka, and Drupada.
Panchala became very powerful after the Kuru Kingdom started to decline. King Keśin Dālbhya (around 900 to 750 BCE) was a nephew of the Kuru king. When the Kuru king died without an heir, Keśin took over. He made Panchala a new center for politics and culture. His family ruled for many years. A later ruler was the wise king Pravahana Jaivali (8th–7th centuries BCE). He was a contemporary of King Janaka of Videha.
Panchala Under Magadhan Rule
Panchala started as a kingdom ruled by a single king. But around 500 BCE, it changed to a republic. This means it was ruled by a group of elected leaders. The Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya lists Panchala as one of the sixteen mahajanapadas (major states) of that time.
Later, in the mid-4th century BCE, the powerful Magadha empire took over Panchala. This happened during the rule of Mahapadma Nanda.
Panchala After the Mauryan Empire
After the Mauryan Empire fell, Panchala became independent again. We know this from old coins found in the area, mostly around Ahichchhatra. These coins are round and made of copper. They have a special design: a square punch with three symbols and the ruler's name. On the other side, they show pictures of gods or symbols related to them. The names of the gods often match part of the ruler's name. For example, coins of Agnimitra show the god Agni.
The last independent ruler of Ahichchhatra was Achyuta. He was defeated by Samudragupta, a powerful ruler of the Gupta Empire. After this defeat, Panchala became part of the Gupta Empire. Achyuta's coins have a wheel with eight spokes on one side and his name, Achyu, on the other.
Images for kids
-
Coin of Agnimitra, showing the depiction of Agni with flaming hair on the obverse, and a reverse showing the three dynastic symbols of the Panchala rulers and a legend naming the king: Agimitasa.
-
A bronze currency of 1⁄2 karshapana of King Indramitra (ca 75-50 BC?) Of Ahichatra of Panchala. Obv: A inside a rectangle, a line of 3 symbols, under the name of the king. Rev: Indra standing on a pedestal without pillars. Dimensions: 15 mm. Weight: 4.18 g.
Important Rulers of Panchala
Here are some of the notable rulers and figures connected to the Panchala Kingdom:
- Mudgala: One of the founders of the Panchala Kingdom.
- Kampilya: He founded the city of Kampilya, which became the capital of Southern Panchala.
- Divodasa: A significant ruler from the Bharata clan.
- Sudas: Another important ruler from the Bharata clan.
- Somaka: His son, Prishata, became king.
- Prishati: The father of the famous King Drupada.
- Drupada: A key figure in the Mahabharata, father of Draupadi, Dhrishtadyumna, and Shikhandi.
- Dhrishtadyumna: Son of Drupada, a powerful warrior.
- Keśin Dālbhya: A king who made Panchala a major political and cultural center after the Kuru Kingdom declined.
- Pravahana Jaivali: A philosopher-king known for his wisdom.
- Achyuta: The last known independent ruler of Panchala. He was defeated by Samudragupta of the Gupta Empire around 350 CE.
See also
- Vedic period
- Mahabharata
- History of India
- History of Hinduism
- Indus Valley civilization
- Painted Grey Ware culture
- Janapadas & Mahajanapadas
- Historicity of the Mahabharata
- Kuru Kingdom & Gandhara Kingdom





