Pembina River (Manitoba – North Dakota) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Pembina River |
|
|---|---|

The Pembina River at Pembina, North Dakota, as viewed upstream from its mouth
|
|
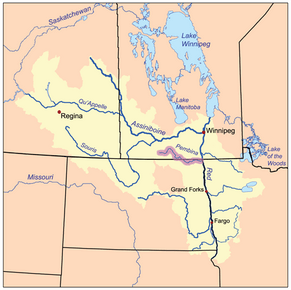
The Red River drainage basin, with the Pembina River highlighted
|
|
| Other name(s) | Rivière Pembina |
| Countries | Canada, United States |
| States/Provinces | Manitoba, North Dakota |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Turtle Mountain (plateau) Manitoba, Canada 49°05′06″N 100°03′05″W / 49.08500°N 100.05139°W (near Turtle Mountain) |
| River mouth | Red River of the North Pembina, North Dakota, United States 48°57′59″N 97°14′21″W / 48.96639°N 97.23917°W |
| Length | 319 mi (513 km) |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Red River drainage basin |
| Basin size | 3,282 sq mi (8,500 km2) |
The Pembina River is a long river, about 319 mi (513 km) (513 km) in length. It flows through southern Manitoba in Canada and northeastern North Dakota in the United States. This river is a branch, or tributary, of the Red River of the North.
The Pembina River flows through a large area of flat, grassy land called the prairie. This area is close to the border between Canada and the United States. The river eventually joins the Red River, which then flows into Lake Winnipeg. From there, the water travels through the Nelson River all the way to Hudson Bay. This entire journey is part of the Pembina River's watershed, which is the area of land where all the water drains into one main river.
Contents
Where the Pembina River Begins and Ends
The Pembina River starts from several small streams. These streams are found on the eastern side of the Turtle Mountains. The Turtle Mountains are located on both sides of the Canada-US border.
River's Journey
The small streams come together near a place called Neelin, Manitoba. From there, the river first flows northeast. Then, it turns southeast, following the western edge of the Pembina Hills. It enters Cavalier County in northeastern North Dakota.
The river continues to flow east, staying just south of the international border. It passes by towns like Walhalla and Neche. Finally, the Pembina River joins the Red River from the west. This meeting point is just south of Pembina, about 2 miles (3 km) (3 km) from the international border.
Other Rivers Joining In
Another river, the Tongue River, also joins the Pembina River. The Tongue River flows in from the south. It meets the Pembina River about 2 miles (3 km) (3 km) before the Pembina joins the Red River.
What the Pembina River Looks Like
The Pembina River has several smaller streams that flow into it. The two main ones are Badger Creek and Long River. Many other smaller streams also join, such as Mary Jane, Pilot, Crystal, and Snowflake Creeks.
River Size and Surroundings
The depth of the Pembina River can change. In the middle, it can be from 1.5 to 4 metres (4.9 to 13.1 ft) (5 to 13 feet) deep. The width of the river also varies a lot. It can be as narrow as 6 metres (20 ft) (20 feet) in some spots. In other areas, it can be as wide as 40 metres (130 ft) (130 feet).
Around the river, there are many wet areas. These include wetlands and small ponds called prairie potholes. These areas are important for many plants and animals.
Land Elevation
The land around the Pembina River changes in height. In the southwest part of the area, it is about 721 metres (2,365 ft) (2,365 feet) above sea level. As you move towards the southeast, near the river, the land drops to about 330 metres (1,080 ft) (1,083 feet) above sea level. The central and eastern parts of the area are mostly flat. However, the land rises by about 200 metres (660 ft) (656 feet) in the 25-kilometre (16 mi) (15.5 mile) area around the Turtle Mountain Provincial Park.
How the River's Water Changes
The amount of water flowing in the Pembina River can change a lot throughout the year. Special stations called hydrometric stations measure how fast the river flows and how high the water levels are. This information helps predict floods and manage water resources.
Water Flow and Run-off
Water levels in the river usually get highest during the spring. This is when snow melts and creates a lot of "run-off" water. The water levels then drop quickly, often in just a few days. Even so, water from underground sources usually keeps the river flowing all year long.
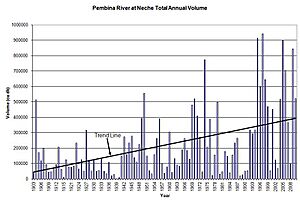
Most of the run-off happens in March, April, and May. These three months account for 68% of the water that flows into the river each year. The amount of spring run-off can be very different from one year to the next. For example, in Neche, North Dakota, the lowest amount of water recorded in a year was in 1939. The highest amount was in 1997, which was much, much more.
Keeping the River Healthy
There is a station that checks the water quality of the Pembina River. It is located near the international border in the southeast part of the watershed. This station regularly collects information about the water. They check for many things, including pesticides, metals, nutrients, and bacteria.
Phosphorus Levels
A study done in 2001 looked at the river's water over 25 years (from 1974 to 1999). It found that the amount of phosphorus in the Pembina River had gone up by 52%. Phosphorus is a type of nutrient. This increase likely happened because of more nutrients entering the river. These nutrients can come from wastewater treatment, farms, and even from the air.
Too much phosphorus can cause too many algae to grow. These large growths of algae are called "algal blooms." They can cause problems for the river and for Lake Winnipeg, where the Pembina River's water eventually goes. Scientists and environmental groups work to understand and reduce these impacts.