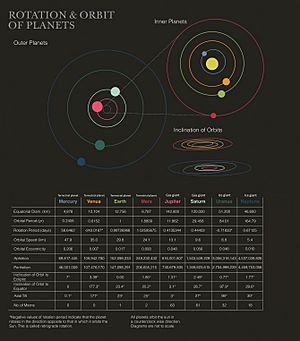
Orbit facts for kids
An orbit is the curved path that an object in space takes as it moves around another, much larger object. Think of it like a giant invisible track! For example, the Earth orbits around the Sun, and the Moon orbits around the Earth.
The words "orbit" and "revolve" mean almost the same thing when talking about space objects moving around each other. However, "rotate" means something different. When an object rotates, it spins around its own center, like a top spinning. The Earth rotates once every 24 hours, which gives us day and night.
Many years ago, people believed that the Sun orbited around the Earth. This seemed to make sense because the Sun appears to rise in the east and set in the west every day. But thanks to smart thinkers like Nicolaus Copernicus and Galileo Galilei, we now know that the Sun is actually the center of our Solar System. The Earth and all the other planets orbit around the Sun!
Isaac Newton later discovered that a force called gravity is what controls these orbits. Gravity is like an invisible pull that keeps planets orbiting stars and moons orbiting planets. Any object in space that orbits another object is called a satellite. So, the Earth is a satellite of the Sun, and the Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth. Our Sun has many satellites, including all the planets, thousands of asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. The Earth has one natural satellite (the Moon) and many artificial satellites built by humans.
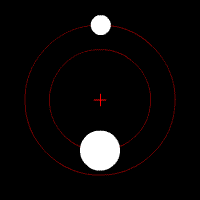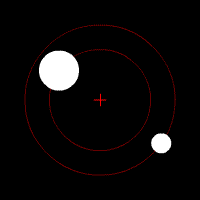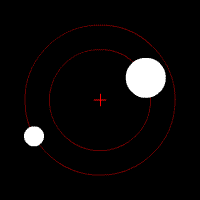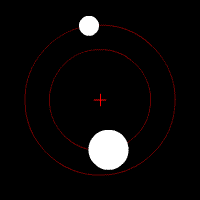
When scientists first thought about orbits, they imagined them as perfect circles. They believed the circle was the "perfect" shape. But as they studied the planets more closely, they realized that planets don't move in perfect circles. Some orbits are very close to a circle, while others are more stretched out, like an egg shape.
How Long Does an Orbit Take?
An orbital period is the amount of time it takes for one object to complete one full orbit around another. For example, the Earth's orbital period around the Sun is one year, which is about 365.25 days. That extra ".25" is why we have a leap day every four years!
The Moon takes about 27 days to orbit the Earth. Interestingly, it also takes the Moon about 27 days to spin once on its own axis. Because these two times are almost the same, we always see the same side of the Moon from Earth. The side we don't see is sometimes called the "dark side of the Moon" because it's hidden from us, not because it's always dark. All sides of the Moon get sunlight!
Elliptical Orbits and Eccentricity
Johannes Kepler (who lived from 1571 to 1630) was a brilliant scientist who figured out important mathematical "laws of planetary motion." He discovered that the orbits of planets in our Solar System are not perfect circles. Instead, they are ellipses, which are shapes like flattened circles. This is why orbits are often described as elliptical.
The more "flattened" or stretched out an orbit is, the more eccentric it is. This is known as orbital eccentricity. An orbit that is almost a perfect circle has very low eccentricity, while a very stretched-out orbit has high eccentricity.
Later, Isaac Newton (who lived from 1642 to 1727) used his ideas about gravity to explain why Kepler's laws worked. Newton's laws showed how gravity causes objects to follow these elliptical paths.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Órbita para niños
In Spanish: Órbita para niños