Nicolaus Copernicus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Nicolaus Copernicus
|
|
|---|---|

The "Toruń portrait" (anonymous, c. 1580)
|
|
| Born | 19 February 1473 |
| Died | 24 May 1543 (aged 70) Frauenburg, Royal Prussia, Poland
|
| Education |
|
| Known for |
|
| Scientific career | |
| Fields |
|
| Academic advisors | Domenico Maria Novara da Ferrara |
| Influences |
|
| Influenced | Johannes Kepler |
| Signature | |
Nicolaus Copernicus (born February 19, 1473 – died May 24, 1543) was a famous Polish astronomer. An astronomer is someone who studies stars, planets, and space. Copernicus came up with a revolutionary idea. He said that the Sun, not the Earth, was the center of our Solar System. This idea is called heliocentrism.
His theory was one of the most important scientific ideas ever. It completely changed how people understood the universe. It also marked the beginning of modern astronomy.
Copernicus was a true polymath. This means he was skilled in many different areas. He worked as a priest, mathematician, physician, and economist. Even with all these jobs, he loved studying the stars as a hobby.
Nicolaus Copernicus was a brave thinker. He dared to question old beliefs. His work helped to start the Scientific Revolution. This was a time when people began to use science and reason to understand the world.
Contents
- Who was Nicolaus Copernicus?
- Where did Copernicus study?
- What was Copernicus's big idea?
- His famous book: "De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium"
- What was the Copernican System?
- Why was his book so important?
- What tools did Copernicus use?
- How did people react to his ideas?
- Copernicus and money
- When did Copernicus die?
- What is Copernicus's legacy?
- Fun facts about Copernicus
- Images for kids
- See also
Who was Nicolaus Copernicus?

Nicolaus Copernicus was born on February 19, 1473. He was born in a town called Toruń. This town was in a special region of Poland called Royal Prussia. He lived during the Renaissance. This was a time of great learning and new ideas.
Nicolaus came from a large family. His parents spoke German. He had three siblings. His brother was named Andreas. His two sisters were Barbara and Katharina.
- His brother, Andreas, became a church leader.
- His sister, Barbara, became a nun.
- His sister, Katharina, got married and had five children. Nicolaus helped to care for them.
Nicolaus Copernicus never married or had children of his own.
His father was a merchant who sold copper. His mother came from a wealthy family. Sadly, his father died when Nicolaus was only 10 years old. His uncle, Lucas Watzenrode the Younger, helped raise him. He also made sure Nicolaus received a good education.
Where did Copernicus study?

Copernicus went to many schools to learn different subjects.
- First, he attended St. John's School in Toruń.
- Then, he went to Cathedral School at Włocławek.
- After that, he studied at the University of Kraków in Poland. There, he learned about math, astronomy, and philosophy.
- Later, he traveled to Italy for more studies. He went to the University of Bologna to learn about law and astronomy. He also studied medicine at the University of Padua.
After finishing his studies in Italy, Copernicus returned to Warmia. He was 30 years old. He spent the next 40 years of his life there. He worked as a church canon. This meant he helped manage the church's affairs. He lived in Frombork. He had a house and a tower there. From his tower, he could observe the stars.
What was Copernicus's big idea?
In Copernicus's time, most people believed a different idea. They thought the Earth was the center of the universe. They believed the Sun, Moon, and stars all moved around the Earth. This old idea was called the geocentric model.
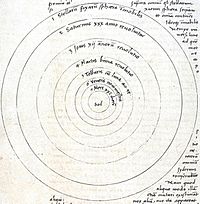
But Copernicus had a very different idea. He thought the Sun was actually at the center. He believed the Earth and all other planets revolved around the Sun. This new idea is called the heliocentric model.
This was a huge and important idea. It completely changed how people understood the universe. It took a lot of courage for Copernicus to share this idea. It was very different from what everyone else believed.
His famous book: "De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium"
Copernicus wrote a book about his heliocentric theory. The book's full title was "De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium." This means "On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres." It was published in 1543. This was just before he passed away.
In this book, he explained his idea clearly. He said the Sun is the center of our solar system. He showed that the Earth and other planets orbit around it. He used math and his own observations to prove his theory.
What was the Copernican System?
Copernicus's heliocentric model had several key ideas:
- The Sun is located at the very center of the solar system.
- The Earth and other planets move around the Sun. They follow nearly circular paths called orbits.
- The Earth spins on its own axis. This spinning causes us to have day and night.
- The stars are incredibly far away. They are much further than the Sun and planets.
Ideas before Copernicus
Even before Copernicus, some people had similar ideas. They also thought about a Sun-centered universe.
- Philolaus: He believed there was a "Central Fire." Everything revolved around this fire.
- Heraclides Ponticus: He suggested that the Earth spins on its axis.
- Aristarchus of Samos: He was the first to propose that the Earth orbits the Sun!
Copernicus knew about these earlier ideas. They might have helped him develop his own theory.
Why was his book so important?
Copernicus's book was a major turning point in science. It started something called the Copernican Revolution. This was a huge shift in how people thought about the universe. It also helped to kick off the wider Scientific Revolution. This was a time when people began to use science and reason to understand the world.
What tools did Copernicus use?
Copernicus used simple tools for his observations. He did not have telescopes like we do today.
- Quadrant: This tool helped him measure angles in the sky.
- Triquetrum: He used this tool to measure the positions of stars and planets.
- Armillary Sphere: This was a model of the celestial sphere. It showed the positions of stars and planets.
How did people react to his ideas?
At first, many people did not believe Copernicus's theory. It was very different from what they had always been taught. Some people even made fun of him. But over time, more and more scientists studied his ideas. They began to realize that he was right.
Copernicus and money
Copernicus also studied money and economics. He came up with an idea known as Gresham's Law. This law says that "bad" money drives "good" money out of circulation. This means if there are two types of money, and one is worth less, people will spend the less valuable money. They will save the more valuable money.
When did Copernicus die?

In late 1542, Copernicus became very ill. He suffered from apoplexy and paralysis. He died at age 70 on May 24, 1543. A story says that he saw the final printed pages of his book, De revolutionibus orbium coelestium, on the very day he died. This allowed him to see his life's work completed.

Copernicus was buried in Frombork Cathedral. For over 200 years, people searched for his remains without success. In 2004, a team of archaeologists began a new search. In August 2005, they found what they believed were his remains. They found them under the cathedral floor.
The discovery was announced on November 3, 2008. Experts used the skull to reconstruct his face. The reconstructed face looked very much like Copernicus's self-portrait. It even showed a broken nose and a scar above his left eye. The experts also confirmed the skull belonged to a man who died around age 70. This was Copernicus's age when he passed away.
The grave was not in perfect condition. Not all parts of the skeleton were found. For example, his lower jaw was missing. DNA from the bones matched hair samples. These samples came from a book owned by Copernicus. The book was kept at the University of Uppsala in Sweden.
On May 22, 2010, Copernicus had a second funeral. His remains were reburied in the same spot in Frombork Cathedral. A black granite tombstone now marks his grave. It identifies him as the founder of the heliocentric theory. It also shows him as a church canon. The tombstone has a picture of Copernicus's model of the Solar System. It shows a golden Sun with six planets orbiting it.
What is Copernicus's legacy?
Nicolaus Copernicus is remembered as one of the most important scientists in history. His heliocentric theory changed how we understand the universe. It helped create modern astronomy. He taught us that it's important to question old ideas. We should use science and reason to find the truth.
After Copernicus died, other scientists continued his work. They made even more discoveries.
- Tycho Brahe: He made very careful observations of the stars and planets.
- Johannes Kepler: He used Brahe's data. He showed that planets orbit the Sun in ellipses (oval shapes), not perfect circles.
- Galileo Galilei: He used a telescope to make new discoveries. These discoveries supported Copernicus's theory.
- Isaac Newton: He developed the laws of motion and gravity. These laws explained why the planets orbit the Sun.
These scientists helped to prove that Copernicus was right. They changed how we understand the universe forever.
Fun facts about Copernicus
- Copernicus could speak many languages. These included Latin, German, Polish, Greek, and Italian.
- He built his own tools to observe the stars and planets.
- A type of palm tree is named after him: Copernicia.
- A chemical element, copernicium, is also named in his honor.
- NASA named one of its space missions "Copernicus."
- An asteroid is named 1572 Koppernicus.
- The Copernicus crater on the Moon is named after him.
- There is a Copernicus Award. It helps promote scientific cooperation between Poland and Germany.
Images for kids
-
Collegium Maius at Kraków University, Copernicus's Polish alma mater
-
Collegiate Church of the Holy Cross and St. Bartholomew in Wrocław
-
Copernicus's translation of Theophylact Simocatta's Epistles. Cover shows coat of arms of (clockwise from top) Poland, Lithuania, and Kraków
-
1735 epitaph, Frombork Cathedral
-
1541 German-language letter from Copernicus to Duke Albert of Prussia, giving medical advice for George von Kunheim
See also
 In Spanish: Nicolás Copérnico para niños
In Spanish: Nicolás Copérnico para niños
- Copernican principle
- Copernicus Science Centre
- History of philosophy in Poland
- List of multiple discoveries
- List of Roman Catholic scientist-clerics