Plant anatomy facts for kids
Plant anatomy is the study of the inside parts of plants. Think of it like learning about the bones, muscles, and organs inside your own body, but for plants! It's also called phytotomy.
Long ago, plant anatomy also included studying the outside shape of plants, like how their leaves or flowers look. But now, plant anatomy focuses only on what's inside. Scientists often use powerful microscopes to look closely at plant cells and tissues (groups of cells working together).
Contents
Discovering Plant Parts
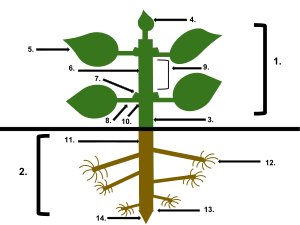
When scientists study plant anatomy, they often look at different parts of the plant. Each part has a special job. Here are some of the main areas they explore:
Inside Flowers
Flowers are amazing! Scientists study their parts like the sepals (which protect the bud), petals (often colorful to attract pollinators), and the parts that help with reproduction, like the androecium (male parts) and gynoecium (female parts).
Inside Leaves
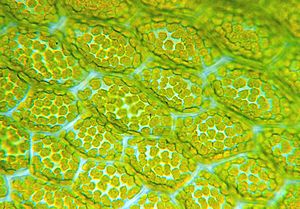
Leaves are like tiny food factories for plants. Their anatomy includes the epidermis (the outer skin of the leaf), stomata (tiny pores that let the plant breathe), and palisade cells (packed with chloroplasts to make food).
Inside Stems
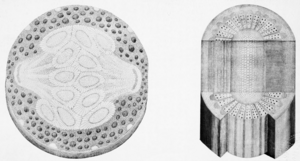
The stem is like the plant's backbone. Scientists look at its structure, including the vascular tissues (special tubes that carry water and nutrients up and down the plant), buds (where new leaves or flowers grow), and the shoot apex (the very tip of the stem where it grows taller).
Inside Fruits and Seeds
Fruits protect the seeds, and seeds grow into new plants. Studying their anatomy involves looking at the ovule (which becomes the seed), the seed itself, and the pericarp (the part of the fruit that surrounds the seed).
Inside Wood
Wood is what makes trees strong. Wood anatomy includes the bark (the outer protective layer), cork (a tough, waterproof tissue), Xylem (tubes that carry water), Phloem (tubes that carry food), and the Vascular cambium (a layer that helps the tree grow wider). Scientists also study the difference between heartwood (the older, darker wood in the center) and sapwood (the newer, lighter wood closer to the bark).
Inside Roots
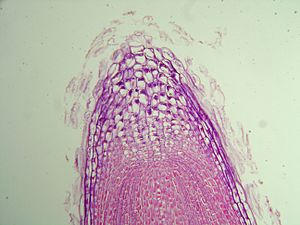
Roots anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Root anatomy includes the overall structure of the root, the root tip (where the root grows), and the endodermis (a layer that controls what enters the root's center).
Images for kids
-
Nehemiah Grew is often called the "Father of Plant Anatomy" because of his important studies.
See also
 In Spanish: Anatomía vegetal para niños
In Spanish: Anatomía vegetal para niños
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |