Plant cell facts for kids
Like all living things, plants are made of tiny building blocks called cells. Plant cells have a special control center called a nucleus, which holds all their instructions (their DNA and chromosomes). They also have tiny powerhouses called mitochondria. These parts are common in many types of cells, including animal cells. But plant cells have some unique features that make them different from animal cells and the cells of other eukaryotes.
Contents
What Makes Plant Cells Special?
Plant cells have several unique parts that help them survive and grow. These special features allow plants to make their own food and stand tall.
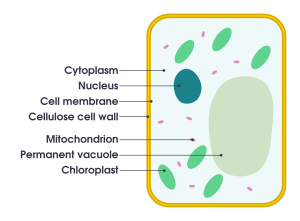
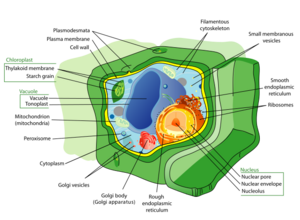
Strong Outer Walls
Plant cells have a strong outer layer called a cell wall. This wall is mostly made of a tough material called cellulose. Other materials like pectin and sometimes lignin are added to the outside of the cell membrane. This is different from the cell walls of fungi, which are made of chitin, or bacteria, which use peptidoglycan. The cell wall gives the plant cell a fixed shape and helps it stay strong.
Tiny Tunnels for Talking
Plant cells can talk to each other through special tiny tunnels called plasmodesmata. These are small holes in the cell wall. They allow the inside parts of one cell to connect directly with the inside parts of its neighbors. This helps cells share materials and signals easily.
Food Factories and Storage Units
Plant cells have special parts called plastids. The most famous plastids are chloroplasts. These contain a green color called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is amazing because it can capture sunlight. This sunlight energy is then used by the plant to make its own food through a process called photosynthesis.
Other types of plastids store different things. For example, amyloplasts store starch, which is like a plant's energy savings. Elaioplasts store fat, and chromoplasts make and store other colors or pigments. Just like mitochondria, plastids have their own set of instructions (genomes). Scientists think plastids started out as tiny living things (prokaryotic endosymbionts) that moved into early plant cells a long, long time ago.
The Big Water Balloon
Plant cells usually have one very large central vacuole. Imagine it like a big water balloon inside the cell. This vacuole is filled with water and surrounded by a membrane. It helps the cell stay firm and stiff, which is called turgor. The vacuole also controls what moves between the cell's main fluid (cytosol) and the sap. It can store useful materials and even help clean up by digesting waste proteins and old organelles.
How Plant Cells Divide
When plant cells divide to make new cells, they build a special "cell plate." This plate forms in the middle of the cell late in the division process (cytokinesis). This way of dividing is unique to land plants and some types of algae.
Plant Cell Movement Parts
The tiny swimming parts (flagella) of sperm cells in some simpler plants, like bryophytes, pteridophytes, cycads, and Ginkgo, are similar to those found in animal cells. However, more advanced plants, such as gymnosperms and flowering plants, do not have these flagella or the centrioles that are found in animal cells.
Images for kids
-
cells of Arabidopsis thaliana epidermis
See also
 In Spanish: Célula vegetal para niños
In Spanish: Célula vegetal para niños