Region of Murcia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Region of Murcia
Región de Murcia
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Región de Murcia (Spanish) |
|||
|
|||
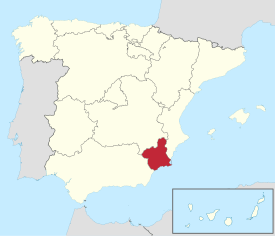
Location of the Region of Murcia within Spain
|
|||
| Country | Spain | ||
| Capital | Murcia | ||
| Area
(2.2% of Spain; Ranked 9th)
|
|||
| • Total | 11,313 km2 (4,368 sq mi) | ||
| Population
(2018)
|
|||
| • Total | Lua error in Module:Wd at line 1,575: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). | ||
| • Pop. rank | 10th | ||
| • Percent | 3.0% of Spain | ||
| Demonym(s) | English: Murcian Spanish: murciano (m), murciana (f) |
||
| Ethnic groups | |||
| ISO 3166 code |
ES-MC (region) ES-MU (province)
|
||
| Official languages | Spanish | ||
| Parliament | Regional Assembly of Murcia | ||
| Congress seats | 10 (of 350) | ||
| Senate seats | 6 (of 265) | ||
| HDI (2017) | 0.869 very high · 12th |
||
| Website | Comunidad Autónoma de la Región de Murcia | ||
The Region of Murcia is a special part of Spain, located in the southeast. It's found between Andalusia and the Valencian Community, right on the Mediterranean Sea coast.
Unlike most other Spanish regions, Murcia is made up of just one province. This means the region and the province work together as one government unit. The city of Murcia is the capital of the region. Most government offices are there. However, the region's parliament, called the Regional Assembly of Murcia, is in Cartagena. The whole region is divided into smaller areas called municipalities.
The Region of Murcia shares borders with Andalusia (specifically the provinces of Almería and Granada), Castile–La Mancha (the province of Albacete), and the Valencian Community (province of Alicante). It also borders the Mediterranean Sea. The region covers about 11,313 square kilometers and has around 1.4 million people. About one-third of these people live in the capital city of Murcia. The highest point in the region is Los Obispos mountain, which is 2,015 meters tall.
Murcia is a big producer of fruits, vegetables, and flowers for Spain and Europe. You can find wineries near Bullas, Yecla, and Jumilla. Olive oil is also made near Moratalla. The region's warm climate is great for farming. However, it doesn't rain much, so water supply is a big topic. Water comes from the Segura River and, since the 1970s, from the Tajo transvasement. This is a huge project that brings water from the Tajo river to the Segura.
Contents
Exploring Murcia's Geography
Understanding the Landscape
The Region of Murcia is in the eastern part of the Cordilleras Béticas mountains. These mountains shape the land. They are divided into three main ranges: Prebética, Subbética, and Penibética.
For a long time, people thought Revolcadores was the highest point in Murcia, at 2,027 meters. But newer maps show Revolcadores is 1,999 meters high. The mountain called Los Obispos ("The Bishops"), which is a bit further north, is actually taller at 2,015 meters.
About 27% of Murcia is mountainous. Another 38% has valleys and dips between mountains. The remaining 35% is made up of flat lands and plateaus.
What's the Climate Like?
The Region of Murcia has a Mediterranean climate that is quite dry. Winters are mild, with an average of 11°C in December and January. Summers are warm, often reaching over 40°C. The average temperature for the whole year is 18°C.
There isn't much rain, only about 300 to 350 mm per year. The sky is clear for 120 to 150 days each year. April and October usually get the most rain, often with heavy downpours in just one day.
Temperatures can be different between the coast and inland areas. This is because of the distance from the sea and the mountains. In winter, the coast rarely drops below 10°C. However, inland areas often have minimum temperatures below 6°C. Inland areas also get more rain, up to 600 mm.
The city of Murcia holds a record for the highest temperature in Spain during the 20th century. It reached 46.1°C on July 4, 1994. The winter of 2005 was very cold, with snow even falling on the Murcian coast.

Waterways of Murcia
Rivers that Flow Through Murcia
The main river system in the region is the Segura river and its smaller rivers, called affluents:
- The Mundo river starts in Albacete and brings the most water to the Segura.
- The Alhárabe river and its affluent, the Benamor.
- The Mula river.
- The Guadalentín, also known as Sangonera or Reguerón, starts before Lorca.
Because the Segura river basin doesn't have enough water on its own, water is also brought from the Tajo river basin. This is done through a project called the Tajo-Segura transvasement.
The Mar Menor: Spain's Largest Lagoon
The biggest natural lake in Spain is found in this region. It's called the Mar Menor (Small Sea). This is a salt water lagoon right next to the Mediterranean Sea. The Mar Menor is a very special natural place and is the largest saltwater lake in Europe. It's shaped like a half-circle and is separated from the Mediterranean Sea by a sand strip. This strip is 22 km long and between 100 and 1200 meters wide, and it's known as La Manga del Mar Menor (the Minor Sea's Sandbar).
The United Nations has named the Mar Menor a "Specially Protected Zone of Importance for the Mediterranean." Its coastline is 73 km long, with many beaches that have clear, shallow water (the deepest part is only 7 meters). The lake covers an area of 170 square kilometers.
Images for kids
-
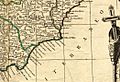
Map of the Kingdom of Murcia in 1795
-
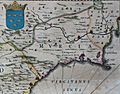
Map of the Kingdom of Murcia in La Geographia Blaviana by Joan Blaeu (1659). In the upper left quadrant appears the coat of arms of the kingdom, which was included in the flag and coat of arms of the Region of Murcia.
-
Ibn Hud as depicted in the Cantigas de Santa Maria
See also
 In Spanish: Región de Murcia para niños
In Spanish: Región de Murcia para niños
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |