Sotho language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sotho |
|
|---|---|
| Sesotho | |
| Pronunciation | IPA: [sɪ̀sʊ́tʰʊ̀] |
| Native to | |
| Ethnicity | Basotho |
| Native speakers | 7.8 million (2001–2023)e18 7.9 million L2 speakers in South Africa (2002) |
| Language family |
Niger–Congo
|
| Writing system | Latin (Sesotho alphabet) Sotho Braille Ditema tsa Dinoko |
| Official status | |
| Official language in | |
| Regulated by | Pan South African Language Board |
| Guthrie code | S.33 |
| Linguasphere | 99-AUT-ee incl. varieties 99-AUT-eea to 99-AUT-eee |
| Sotho | |
|---|---|
| Person | Mosotho |
| People | Basotho |
| Language | Sesotho |
| Country | Lesotho |
Sesotho (say "seh-SOO-too"), also known as Southern Sotho, is a language spoken in Southern Africa. It belongs to the Bantu language family.
Sesotho is the national and official language of Lesotho. It is also one of the 12 official languages in South Africa. In Zimbabwe, it is one of the 16 official languages.
Like many Bantu languages, Sesotho is an agglutinative language. This means it builds long words by adding many small parts (like prefixes and suffixes) to a main word. These parts change the word's meaning or how it works in a sentence.
Contents
What Kind of Language is Sesotho?
Sesotho is part of the Niger-Congo language family. It belongs to the Southern Bantu group. Within this group, it's part of the Sotho-Tswana branch.
Even though it shares the name "Sotho" with Northern Sotho, they are not as similar to each other as they are to Setswana. The name "Sotho" can sometimes refer to the whole Sotho-Tswana group. When this happens, Sesotho is called "Southern Sotho."
Sesotho is most closely related to the Lozi language. Lozi is spoken mainly in Zambia. The Sotho-Tswana group is also related to other Southern Bantu languages. These include Venda, Tsonga, and Nguni languages.
The word Sotho is the base word. You can add different beginnings to it. For example, Sesotho means the Sotho language. Basotho refers to the Sotho people. Using Sesotho for the language has become more common since the 1980s.
Different Ways of Speaking Sesotho
Sesotho does not have many different dialects. There are only small differences in words within Lesotho. There are also some differences between the language spoken in Lesotho and the Free State and in big cities like Soweto. These differences are often because of words borrowed from other nearby languages.
Sometimes, people get confused by the word Basotho. This word can mean different things. It can mean "people who speak Sotho-Tswana languages." It can also mean "people who speak Southern Sotho and Northern Sotho." Or it can simply mean "people from Lesotho."
The Phuthi language is spoken in Lesotho. It has been greatly influenced by Sesotho. However, Phuthi is not a dialect of Sesotho. Speakers of Sesotho cannot understand Phuthi easily. It is a separate language.
The Lozi language, spoken in Zambia, is also sometimes called a dialect of Sesotho. However, it is also a separate language.
Where Sesotho is Spoken
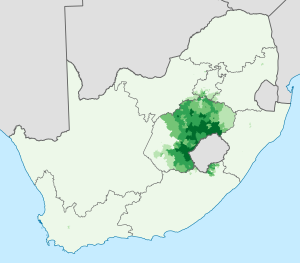
In 2011, almost four million people in South Africa spoke Sesotho as their first language. This was about eight percent of the country's population. Most Sesotho speakers in South Africa live in the Free State and Gauteng provinces.
Sesotho is also the main language in Lesotho. In 1993, about 1.5 million people there spoke it. This was 85% of Lesotho's population. Many other people in South Africa speak Sesotho as a second or third language. You can find these speakers in big cities like Johannesburg.
Official Status of Sesotho
Sesotho is one of the eleven official languages of South Africa. It is also one of the two official languages of Lesotho. And it is one of the sixteen official languages of Zimbabwe.
Languages That Come From Sesotho
Sesotho is one of the languages that helped create tsotsitaals. Tsotsitaal is not a full language on its own. It is a special way of speaking that uses unique words and phrases. But it uses the grammar rules of another language, usually Sesotho or Zulu.
Tsotsitaal is popular with young people in many townships in Southern Gauteng. It is also the main language used in Kwaito music.
How Sesotho Sounds
The sounds in Sesotho are quite special. It has sounds called ejective consonants. These are made by pushing air out quickly from the throat. It also has click sounds, which are made by clicking the tongue.
Sesotho has a sound called a uvular trill. This is like a rolling "r" sound made at the back of the throat. The language also has many affricate sounds. These are sounds that start like a stop and end like a hiss.
The language has about 39 consonant sounds and 9 vowel sounds. Sesotho also has many sound changes. These changes happen when sounds in words affect each other.
Sesotho Grammar Basics
The grammar of Sesotho shows it is a Bantu language. One important feature is its noun class system. This system groups nouns into different categories. These categories do not relate to male or female gender.
Another key feature of Bantu languages like Sesotho is their agglutinative nature. This means words are built by adding many small parts. Sesotho also tends to use word order to show how nouns relate in a sentence. It does not use grammatical case systems like some other languages.
See also
 In Spanish: Sesoto para niños
In Spanish: Sesoto para niños
- Sotho calendar
- Sotho people
- South African Translators' Institute