Shephelah facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Shephela |
|
|---|---|
| Shfela, Judean Foothills, Judean Lowlands | |

The Shephela near Tarum
|
|
 |
|
| Coordinates | 30°41′N 34°52′E / 30.683°N 34.867°E |
| Part of | Israel |
| Length | 55 km |
| Width | 10-15 km |
| Geology | Rolling hills |
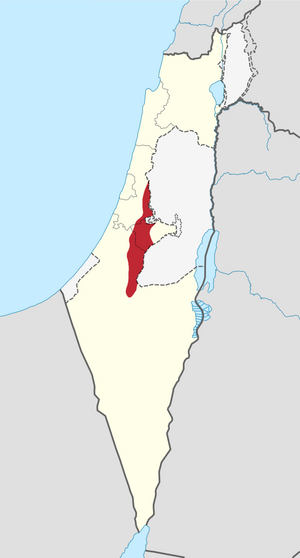
The Shephelah or Shfela means "lowlands" in Hebrew. It is a special area in south-central Israel. This region has gentle, rolling hills that stretch for about 10 to 15 kilometers. It sits between the taller Judaean Mountains and the flat Coastal Plain. Sometimes, people get confused about whether the "Judean Plain" means only the Coastal Plain or also includes the Shfela.
Today, the Shfela is mostly countryside with many farms. However, big cities like Ashdod, Ashkelon, Rehovot, Beit Shemesh, and Kiryat Gat are located around it.
In ancient times, the Bible says that the land in the Shfela was given to the tribes of Judah and Dan.
Contents
Understanding the Shephela's Geography
The Shfela is known for its rich, rolling hills. It acts like a bridge between the high, rough Judaean Mountains (which it borders) and the flat Coastal Plain. This area is about 60 kilometers (35 miles) long from north to south. It is only about 13 kilometers (8 miles) wide.
The Shfela is split into two main parts:
- The western "Low Shephelah" starts at about 150 meters (490 feet) above sea level. It rises to about 200 meters (650 feet) above the Coastal Plain.
- The eastern "High Shephelah" is higher, reaching between 250–450 meters (820–1,470 feet) above sea level.
In the higher parts, the valleys coming down from the Judean Mountains are deep. As they reach the lower Shfela, these valleys become wider. Rivers here can flow for long distances along the edge between the mountains and hills. This creates long valleys. Moving between these east-west and north-south valleys has always been important for travel and trade.
Geology of the Hills and Valleys
The Shfela was formed as a basin where rock layers folded downwards. This type of formation is called a syncline. The Shfela is known for its soft, chalky rock layers from the Senonian and Eocene periods.
The soft Eocene chalk is locally called kirton. This kirton often has a harder crust on top, called nari. In the past, people would dig out the soft kirton rock. They left the hard nari layer as a ceiling, creating underground spaces. These hollows were used for many things, like hiding places, burials, or storage.
The hills in the Shfela are mostly made of soft chalk covered in marl. This is different from the Judean Hills, which are made of hard chalk and dolomite. The valleys and lower areas of the Shfela have sandy soil and large areas of fertile land. Sometimes, temporary swamps can form during the rainy season. The southern part of the Shfela has a type of soil called loess, while the area north of Ashkelon has clay.
The Shfela has a climate that ranges from mild Mediterranean to semi-dry.
Important Valleys and Caves
Several east-west valleys cut through the Shfela, dividing it into different areas. From north to south, these valleys are:
- The Valley of Ayalon
- The Sorek Valley
- The Valley of Elah
- The Guvrin Valley
- The Valley of Lachish
- The Valley of Adorayim
Ancient towns were built in these valleys. They protected settlements further inland and benefited from trade routes that passed through. The Ayalon Valley was the main way to reach Jerusalem by climbing the ascent of Horon.
Caves are a very common feature in the southern part of the Shfela. Many of them are shaped like bells, such as those found in Beit Guvrin.
History and Archaeology of the Shephela
Archaeological studies in the Shephelah have found signs that people lived here during the Late Bronze Age. In the early Iron Age, the number of people living in this area, which was between the rising powers of Philistia (on the coast) and the Israelite/Judahite highlands, went down. However, some settlements on the eastern edge survived.
Later, in the Iron Age IIA–B, the population grew again. By the 8th century BCE, many people lived there. This growth was not just from natural births but also from new settlers. One of the first new settlements was at Khirbet Qeiyafa. It is thought that between 50,000 and 100,000 people lived in many sites. These sites included Tel Lachish, Azekah, Tel Burna, Tel Zayit, Khirbet el-Qom, Tel Erani, Tel Harasim, and Tel Nagila. This increase in population, along with the people already there, connected with the culture of the Israelite/Judahite highlands. This growth happened as Philistia became weaker.
When the kingdom of Judah was destroyed by the Neo-Assyrian Empire and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, the region was slowly taken over by the Edomites. It then became the main part of a region known as Idumea in Greek. The Shephela did very well during the Hellenistic period. However, it was greatly affected by the First Jewish-Roman War (66–70 CE). Many Jewish people left the area after the Bar Kokhba revolt (132–136 CE). The region became strong again during the Byzantine period. It was also the site of a major battle during the Muslim conquest of the Levant in the 7th century.
Important Archaeological Sites
- Azekah
- Tel Batash
- Beit Guvrin
- Beit Jimal
- Tell Beit Mirsim
- Beit Shemesh
- Tel Burna
- Tel Eton
- Gezer
- Imwas and Emmaus Nicopolis
- Tel Halif
- Hurvat Itri
- Jarmuth
- Tell ej-Judeideh
- Kharruba
- Keilah
- Tel Lachish
- Lavnin
- Khirbet Qeiyafa
- Khirbet a-Ra'i
- Sokho
- Tel Yona
- Tell Zayit
- Zorah
See also
 In Spanish: Sefelá para niños
In Spanish: Sefelá para niños
- Geography of Israel
- Kiryat Gat – a modern Israeli town
- Latrun – a historical site and monastery in the Ayalon Valley
- Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut – a modern Israeli town