Jojoba facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Jojoba |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) shrub | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Simmondsiaceae |
| Genus: | Simmondsia Nutt. |
| Species: |
S. chinensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Simmondsia chinensis (Link) C. K. .
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
List
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Jojoba (say "ho-HO-ba") is a special plant known by its scientific name Simmondsia chinensis. People also call it by fun names like goat nut, deer nut, or wild hazel. This plant naturally grows in the southwestern parts of the United States. It is the only type of plant in its family, called Simmondsiaceae.
Jojoba is grown on farms to make jojoba oil. This oil is a liquid wax that comes from the plant's seeds. It's used in many products we use every day.
Contents
Where Jojoba Grows
Jojoba is a shrub that grows in the Sonoran Desert and other dry areas. You can find it in places like southern California, Arizona, and Utah in the U.S. It also grows in Baja California in Mexico.
This plant is special because it only grows naturally in North America. It covers a large area, about 260,000 square kilometers (100,000 square miles).
What Jojoba Looks Like
Jojoba plants usually grow to be about 1 to 2 meters (3 to 6.5 feet) tall. They have a wide, bushy top. Some plants have even been seen growing as tall as 3 meters (10 feet)!
The leaves grow in pairs and are shaped like ovals. They are about 2 to 4 centimeters (0.8 to 1.6 inches) long and 1.5 to 3 centimeters (0.6 to 1.2 inches) wide. Jojoba leaves are thick and waxy. They have a pretty gray-green color.
The flowers are small and greenish-yellow. They have 5 or 6 outer leaf-like parts called sepals, but no petals. Jojoba plants usually bloom, or flower, from March to May.
How Jojoba Reproduces
Each jojoba plant is either male or female. This means a single plant cannot make seeds by itself. The male plants produce pollen, and the female plants produce seeds. It is very rare to find a plant that has both male and female parts.
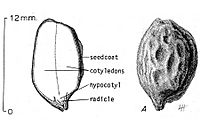
The fruit of the jojoba plant looks like a small acorn. It is about 1 to 2 centimeters (0.4 to 0.8 inches) long. Inside the fruit is a hard, dark brown oval seed. This seed is very important because it holds a lot of oil, about 54% of its weight!
Male jojoba bushes can produce about 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds) of pollen. This pollen is carried by the wind to the female flowers. The leaves of the jojoba plant are shaped in a way that helps the wind carry the pollen. In the northern part of the world, this happens in February and March. In the southern part, it happens in August and September.
The Name of Jojoba
Even though its scientific name is Simmondsia chinensis, jojoba does not come from China. A scientist named Johann Link made a mistake when he first named it. He read "Calif" (for California) as "China" on a plant label.
Later, another scientist named Thomas Nuttall gave it a new name, Simmondsia californica. But because of naming rules, the first specific name, chinensis, had to be kept.
The common name "jojoba" comes from the O'odham people. They are a Native American group who called the plant Hohowi. It's important not to confuse jojoba with jujube, which is a different plant that grows in China.
How People Use Jojoba

Jojoba leaves provide food all year for many animals. These include deer, javelina (a type of wild pig), bighorn sheep, and farm animals. Squirrels, rabbits, and other small animals also eat the jojoba nuts. Even large birds enjoy them.
Only a small animal called Bailey's pocket mouse can properly digest the wax inside the jojoba nut. Eating too many jojoba seeds can be harmful to many mammals. This is because the seeds contain a substance called simmondsin, which makes animals feel full and stops them from wanting to eat. In humans, the wax in the seeds can act as a laxative.
Native American Uses
Native Americans were the first people to use jojoba. About 300 years ago, missionaries saw native people in Baja California heating jojoba seeds. This made the seeds soft. Then, they would grind the seeds to make a salve or a buttery cream.
This cream was put on skin and hair to help heal and make them soft. The O'odham people, who lived in the Sonoran Desert, used a paste made from jojoba nuts to treat burns.
Native Americans also used the salve to soften and protect animal hides. Pregnant women sometimes ate jojoba seeds. They believed it would help them during childbirth. Hunters would eat jojoba seeds to help them feel less hungry when they were on long trips.
The Seri people, another Native American group, usually eat almost every plant in their area. However, they did not see jojoba beans as real food. They only ate them in emergencies.
Modern Uses of Jojoba
Jojoba is grown for the liquid wax, or jojoba oil, found in its seeds. This oil is special because it is a very long chain of wax, not like regular vegetable oils. This makes jojoba oil similar to whale oil.
Jojoba oil is mostly used in personal care products. You can find it in shampoos, conditioners, lotions, and makeup. It is not grown enough to be used as a fuel like gasoline.
Growing Jojoba Plants
Jojoba farms have been started in many dry and semi-dry places around the world. These include Argentina, Australia, Israel, Mexico, Peru, and the United States. In the Sonoran Desert, jojoba is the second most valuable native plant.
Jojoba grows best in light, sandy soils. The soil needs to drain water well. Jojoba can handle salty soil and soil that doesn't have many nutrients. The soil's pH level should be between 5 and 8. Jojoba plants can handle hot temperatures, but frost can harm them.
Jojoba plants do not need a lot of special care. Weeds are only a problem for the first two years after planting. Insects usually don't cause much damage either. If there isn't much rain, extra watering can help the plants produce more. Jojoba plants don't need a lot of fertilizer, but adding nitrogen in the first year can help them grow.
Jojoba seeds are usually picked by hand because they don't all ripen at the same time. A farm can produce about 3.5 tons of seeds per hectare (about 1.4 tons per acre). This amount can change depending on how old the farm is.
Scientists are working to grow new types of jojoba plants. These new plants will produce more beans with more wax. They are also trying to make plants that are easier to harvest.
Jojoba can grow well in salty conditions. This, along with the high value of its products, makes jojoba a good plant to help fight desertification. Desertification is when land turns into desert. Jojoba has been used to help stop this in the Thar Desert in India.
Images for kids
-
Plaque describing jojoba in the Lost Dutchman State Park (Arizona)
See also
 In Spanish: Jojoba para niños
In Spanish: Jojoba para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |