Sine and cosine facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sine and cosine |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| General information | |
| General definition | ![\begin{align}
&\sin(\alpha) = \frac {\textrm{opposite}} {\textrm{hypotenuse}} \\[8pt]
&\cos(\alpha) = \frac {\textrm{adjacent}} {\textrm{hypotenuse}} \\[8pt]
\end{align}](/images/math/2/d/c/2dc6c3512fe683647efa0bdd227de893.png) |
| Fields of application | Trigonometry, Fourier series, etc. |
In mathematics, sine and cosine are special trigonometric functions. They help us understand angles and shapes. You can think of them as tools to measure parts of a right triangle. For an angle, sine tells you the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse. Cosine tells you the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse.
These functions are super useful! They help us describe things that repeat, like sound waves, light waves, and even how long the day is. Scientists and engineers use them all the time. The ideas behind sine and cosine first appeared in Indian astronomy a long, long time ago.
Contents
Understanding Sine and Cosine
What Do Sine and Cosine Mean?
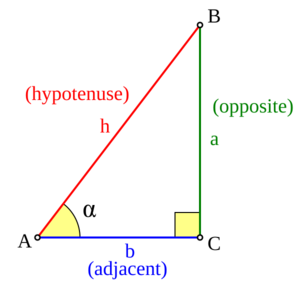
Let's look at a right triangle. This is a triangle with one angle that is exactly 90 degrees. Imagine an angle, let's call it α. We can name the sides of the triangle based on this angle:
- The opposite side is the side directly across from angle α.
- The hypotenuse is the longest side. It's always opposite the 90-degree angle.
- The adjacent side is the side next to angle α, but not the hypotenuse.
Now, here's how sine and cosine are defined for angle α:
- Sine of α (written as sin(α)) is the length of the opposite side divided by the length of the hypotenuse.
- Cosine of α (written as cos(α)) is the length of the adjacent side divided by the length of the hypotenuse.
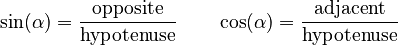 It doesn't matter how big or small the right triangle is. As long as the angle α is the same, the ratios for sine and cosine will always be the same! This is because all right triangles with the same angles are similar in shape.
It doesn't matter how big or small the right triangle is. As long as the angle α is the same, the ratios for sine and cosine will always be the same! This is because all right triangles with the same angles are similar in shape.
How We Write Sine and Cosine
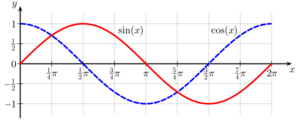
We usually write sine as sin and cosine as cos. So, for an angle θ, you'll see them written as sin θ and cos θ.
Angles can be measured in radians or degrees. In many math and science fields, especially higher up, angles are usually measured in radians. This article mostly talks about radians unless it says otherwise.
The Story of Sine and Cosine
Where Did They Come From?
The study of trigonometry (which is about triangles and angles) started a very long time ago. But the sine and cosine functions we use today really grew during the Middle Ages.
The idea of sine and cosine comes from ancient Indian astronomy. They used functions called jyā and koṭi-jyā. These ideas then traveled to the Arabic world and later to Europe.
By the 9th century, Islamic mathematics had all six main trigonometric functions. They also knew the law of sines, which helps solve problems with triangles. Many Arabic mathematicians, like Al-Khwārizmī and Muhammad ibn Jābir al-Harrānī al-Battānī, created tables of these functions. These tables helped people calculate angles and distances.
How the Names Came About
The word sine comes from the Sanskrit word jyā, which means 'bow-string'. This is because a bow and its string look a bit like a circle's arc and its chord. When this word was translated into Arabic, it became jība. Later, when Arabic texts were translated into Medieval Latin, jība was mistaken for the Arabic word jayb, meaning 'bosom' or 'fold'. So, the Latin word sinus (which also means 'fold' or 'bay') was used. This is where our English word sine comes from!
The word cosine is shorter for the Latin phrase complementi sinus. This means 'sine of the complementary angle'. A complementary angle is what you add to an angle to make 90 degrees.
Sine and Cosine in Computers
Computers and calculators use sine and cosine all the time. There isn't just one way for a computer to figure out these values. Different methods might be faster or more accurate, especially for very large numbers.
A common trick, especially in 3D graphics, is to have a table of sine values already saved. Instead of calculating sine every time, the computer just looks up the closest value in the table. This can make things faster.
Most programming languages, like Python and C, have built-in functions for sine and cosine. You just give them an angle, and they give you the sine or cosine value back.
Images for kids
See also
- Euler's formula
- Hyperbolic function
- Law of sines
- List of trigonometric identities
- Sinc function
- Sine wave
- SOH-CAH-TOA
- Trigonometric functions
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |