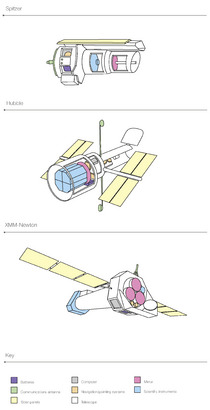
Space telescope facts for kids
A space telescope or space observatory is like a giant eye floating in outer space. It's a special telescope that helps us look at stars, planets, and other amazing things far away in the universe.
Scientists first thought about putting telescopes in space back in 1946. The very first ones that actually worked were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory (called OAO-2) launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope in 1971.
Space telescopes are super helpful because they avoid problems that telescopes on Earth have. Earth's air can make things look blurry or twinkle, and city lights can make the sky too bright. Telescopes in space don't have these problems!
There are two main kinds of space telescopes:
- Some map the whole sky, like making a giant cosmic map.
- Others focus on specific objects or small parts of the sky to study them closely.
It's important to know that space telescopes are different from satellites that look down at Earth. Those satellites are used for things like checking the weather, spying, or gathering other information about our planet.
Contents
Why do we need telescopes in space?
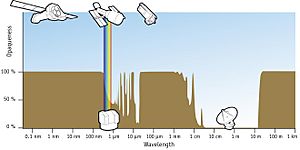
Looking at space from Earth is tricky because of our atmosphere. The air around Earth can block or distort the light and other signals coming from space. This is why stars seem to twinkle!
A telescope orbiting Earth, outside the atmosphere, doesn't have these issues. It gets a much clearer view. This means space telescopes can see much finer details than a similar telescope on the ground. Even though some big Earth telescopes use special technology to reduce air effects, space is still the best place for a clear view.
Space telescopes are especially important for seeing types of light that our atmosphere blocks completely. For example, X-ray astronomy is almost impossible from Earth. That's why telescopes like the Chandra X-ray Observatory and XMM-Newton are so important. They let us see X-rays from space. The atmosphere also largely blocks infrared and ultraviolet light, so space telescopes are crucial for studying those too.
How did space telescopes begin?
People have dreamed about observatories in space for a long time. Back in 1837, two scientists, Wilhelm Beer and Johann Heinrich Mädler, even talked about putting an observatory on the Moon!
In 1946, an American scientist named Lyman Spitzer suggested building a telescope in space. He wanted a big telescope that wouldn't be bothered by Earth's atmosphere. After many years of hard work and planning, Spitzer's idea finally came true. The famous Hubble Space Telescope was launched on April 24, 1990, by the Space Shuttle Discovery.
The first space telescopes to actually work were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory (OAO-2), launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope, which flew on the Salyut 1 space station in 1971.
What are the challenges of space telescopes?
Space telescopes are amazing, but they are also very expensive to build. Plus, because they are so far away in space, they are extremely hard to fix if something goes wrong. The Hubble Space Telescope was special because astronauts could visit it using the Space Shuttle to make repairs. However, most other space telescopes cannot be serviced at all.
What's next for space observatories?
Many countries and space agencies, like NASA (USA), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and CNSA (China), have launched and operated space telescopes.
Some space observatories have finished their missions, while others are still working even after their planned time. The future of space telescopes depends a lot on getting enough money to build them. Scientists sometimes worry there might be "gaps" in coverage. This means there could be periods where no new telescope is available to continue important research. For example, people worried about a gap between the Hubble Space Telescope and the newer James Webb Space Telescope.
NASA has announced plans for several future space telescope programs. These include the Great Observatory Technology Maturation Program (GOMAP), the Habitable Worlds Observatory, and other New Great Observatories. These new projects aim to continue exploring the universe and finding amazing discoveries.
Images for kids
-
The Hubble Space Telescope, one of the Great Observatories
See also
 In Spanish: Observatorio espacial para niños
In Spanish: Observatorio espacial para niños
- Airborne observatory
- Earth observation satellite
- List of telescope types
- Observatory
- Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes
- Timeline of telescopes, observatories, and observing technology
- Ultraviolet astronomy
- X-ray astronomy satellite