Spanish Virgin Islands facts for kids
|
Spanish: Islas Vírgenes de Puerto Rico / Islas Vírgenes Españolas
|
|
|---|---|
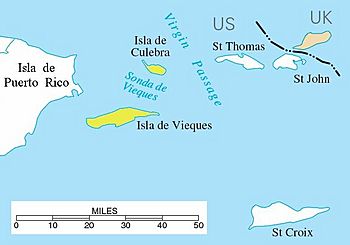
Location of the Spanish Virgin Islands (yellow) between Puerto Rico (left) and Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands
|
|
| Geography | |
| Coordinates | 18°13′36.27″N 65°20′18.38″W / 18.2267417°N 65.3384389°W |
| Archipelago | Virgin Islands |
| Adjacent bodies of water | Caribbean Sea |
| Area | 165.1 km2 (63.7 sq mi) |
| Administration | |
| Commonwealth | Puerto Rico |
| Municipality | Culebra and Vieques |
| Largest settlement | Isabel II barrio-pueblo (pop. 1,459) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 11,119 |
| Pop. density | 67.35 /km2 (174.44 /sq mi) |
The Spanish Virgin Islands are a group of islands that belong to Puerto Rico. They are also known as the Puerto Rican Virgin Islands. These islands are found east of the main island of Puerto Rico in the Caribbean Sea. The two main islands in this group are Culebra and Vieques.
Contents
History of the Islands
Early Inhabitants and European Arrival
Long ago, around 1,500 years before Christopher Columbus arrived, people lived on the island of Vieques. These early groups came from South America. They were related to the Taino people who lived on the main island of Puerto Rico. The Tainos of Vieques tried to stop the Spanish from taking over and enslaving them.
Christopher Columbus is believed to have found Culebra Island in 1493 during his second trip to America. The first people on Culebra were likely the Taino Indians, followed by the Caribs. Culebra also became a safe place for many Taino Indians who were defeated in a rebellion against the Spanish in 1511.
Conflicts and Colonization Attempts
Throughout the 1600s and 1700s, English settlers from nearby British colonies like Tortola and Anguilla tried to settle Vieques. In 1688 and again in 1717, they tried to build towns, a fort, and farms. However, the Spanish Governor in Puerto Rico sent soldiers. These soldiers successfully removed the English settlers, making sure Spain kept control of Vieques.
In 1875, the Spanish government wanted to populate Culebra Island. But it wasn't until 1880 that people started to settle there. This began with the founding of a town called San Idelfonso de la Culebra.
Changing Hands: Spain to the United States
Like Puerto Rico, these islands belonged to Spain until 1898. On September 19, 1898, the United States took control of the islands. This happened after an agreement was signed, ending the Spanish–American War. The islands, along with Puerto Rico and other smaller islands, were officially given by Spain to the United States. This was part of the Treaty of Paris, signed on December 10, 1898.
In 1903, the U.S. government set aside all public lands on Culebra Island for the U.S. Navy. The U.S. military took full control of the San Ildefonso de la Culebra community. They moved the people living there to a small area called Dewey, named after an American general.
On March 17, 1941, a law was passed to spend $35 million to build a Navy base on Vieques. Later that year, another law allowed the U.S. Navy to take over land in Vieques right away. This process meant the Navy eventually controlled 26,000 out of 33,000 acres of Vieques by the end of the 1940s.
During World War II, Culebra Island became the main area for the U.S. Navy to practice artillery and bombing. The Navy continued to use Culebra for this purpose until 1975.
Geography of the Spanish Virgin Islands
Even though tourist guides call them the Spanish Virgin Islands, most maps don't show them as part of the main Virgin Islands group. People in Puerto Rico often call Vieques "Isla Nena," which means "Little Girl Island." Since 1898, these islands have been controlled by the United States. Before that, they belonged to Spain.
Spanish is the main language spoken here, but English is also very common.
Main Islands and Smaller Islets
The two main islands in this group are Culebra and Vieques. There are also many smaller islands and islets nearby. Some islands close to Puerto Rico's shore include Icacos Island, Cayo Lobo, Cayo Diablo, Palomino Island, Palominito Island, Isla de Ramos, Isla Pineiro, and Cayo Lobo. Near Culebra, you can find Cayo Luis Peña.
Natural Features
Culebra has an uneven landscape with a very detailed coastline. The island is about 11 by 8 kilometers (about 7 by 5 miles). Its coast has cliffs, coral sand beaches, and mangrove forests. The highest point on Culebra is Mount Resaca, which is about 190 meters (623 feet) tall. The island has many lagoons, like Laguna Flamenco and Laguna Zoní. It also has several bays, such as Ensenada Honda and Bahía de Tamarindo, and small creeks.
A smaller island near Culebra, called Cayo Norte, is part of the Culebra National Wildlife Refuge. A large part of Vieques is also a wildlife refuge, called the Vieques National Wildlife Refuge. This area used to be a facility for the U.S. Navy.
See also
 In Spanish: Islas Vírgenes Españolas para niños
In Spanish: Islas Vírgenes Españolas para niños