Staining facts for kids
Staining is a special trick used with microscopes. It helps scientists and doctors see tiny things like cells and tissues much more clearly. Imagine trying to see a ghost – staining makes it visible!
This method makes the tiny parts of a sample stand out. Stains and dyes are often used in biology and medicine. They help to highlight different structures in living things. This makes them easier to study under a microscope.
Staining can be done on living tissues. This is called in vivo staining. It can also be done on tissues that are no longer alive. This is known as in vitro staining.
Contents
Getting Samples Ready
When scientists want to study tissues that are not alive, they first need to "fix" them. Fixing stops the tissue from decaying or changing. It helps to keep its original shape and structure. After fixing, the tissue is often cut into very thin slices. These slices are then placed onto glass microscope slides. Sometimes, a special step is needed to open up cell membranes. This allows the colorful dye molecules to get inside the cells. Experts follow special rules for this, published in science journals.
How Staining Works
The simplest way to stain is to dip the slide with the sample into a dye solution. Then, it's rinsed and ready to be looked at under the microscope. The dyes used are very specific. They are tested and approved by special commissions to make sure they work well.
Staining Bacteria
Gram staining is a very important method used to sort bacteria into groups. It works by looking at what their cell walls are made of. This method uses a purple dye called crystal violet to stain the cell walls. It also uses iodine to help the dye stick. Finally, a different color is used to stain all bacteria, which helps to tell them apart.
Bacteria that stain dark blue or violet are called Gram-positive bacteria. Their cell wall is different from other bacteria. It does not have an outer membrane or a special layer called lipopolysaccharide.
Most Gram-stained samples show Gram-negative bacteria as red or pink. This color comes from the second dye used in the process.
Staining Tissues
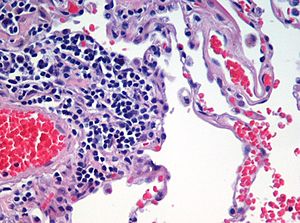
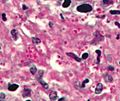
Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is very common in histology. Histology is the study of tissues. This method is used for thin slices of tissue. Haematoxylin makes the cell nuclei (the control centers of cells) look blue. On the other hand, eosin stains the cytoplasm (the jelly-like stuff inside cells), connective tissue, and other parts outside the cells pink or red.
Eosin is strongly absorbed by red blood cells, making them appear bright red. In a well-done H&E stain, red blood cells might look almost orange. Collagen and cytoplasm (especially in muscles) will show up in different shades of pink. Hematoxylin stains the cell nucleus and other parts that are acidic, like areas rich in RNA or cartilage, blue. Eosin, however, stains the cytoplasm and collagen pink.
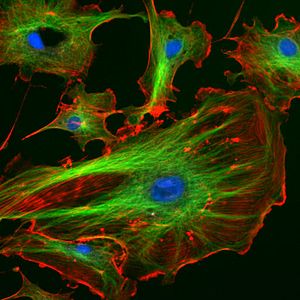
A quick and easy stain for blood samples or human cheek cells is methylene blue. This dye stains the cell nuclei. There are many other special stains too. Some of them even glow under special light, which is called fluorescence.
Images for kids
-
A stained histologic sample. It's held between a glass microscope slide.
-
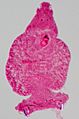
Carmine staining of a parasitic flatworm.
See also
 In Spanish: Tinción para niños
In Spanish: Tinción para niños