World Wide Web facts for kids
The World Wide Web ("WWW" or "The Web") is the part of the Internet that contains websites and webpages. Think of it like a giant library or a massive interconnected collection of documents and resources that you can access using your computer or phone. It was created to make sharing information over the Internet easy for everyone.
It is a fascinating system that has changed how billions of people around the world find information, communicate, and interact. It's built on clever ideas and technologies that work together to bring websites and online content right to your screen.
Contents
How the Web works: The basics
Imagine you want to visit a website, like your favorite online game or a page for school research. Here's a simplified look at what happens:
You type a web address (like www.example.com) into your web browser or click on a link. This address is called a Uniform Resource Locator (URL). Your computer needs to find where that website lives on the Internet. It uses a system called the Domain Name System (DNS) to translate the easy-to-remember web address (like example.com) into a numerical address (like 203.0.113.4) that computers understand.
Your web browser then sends a request across the Internet to a special computer called a web server at that numerical address. This request uses a set of rules called the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). If the website is secure (like for online shopping or banking), it uses HTTPS, which adds an extra layer of protection by encrypting the information.
The web server receives your request. If it finds the page you asked for, it sends the information back to your browser using HTTP or HTTPS.
Your web browser receives the information, which is usually written in a language called Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). The browser reads the HTML and figures out how to display the text, pictures, videos, and other parts of the web page on your screen.
This whole process happens incredibly fast, often in just a fraction of a second!
Key parts
The World Wide Web is made up of several important components that work together:
- Web pages: These are the individual documents you see when you visit a website. They are usually created using HTML and can contain text, images, videos, and links to other pages.
- Websites: A website is a collection of related web pages and other resources (like images or videos) that are usually grouped under a common web address (domain name). For example, wikipedia.org is a website with millions of web pages.
- Web servers: These are powerful computers that store websites and send web pages to your browser when you request them. A single server can host many websites.
- Web browsers: This is the software you use to access and view the Web, like Chrome, Safari, Edge, or Firefox. Browsers are like the windows through which you look at the online world.
- Hyperlinks: These are the clickable words, phrases, or images that take you from one web page to another. They are what connect all the pages on the Web, allowing you to "surf" or "navigate" from one piece of information to another.
- URLs (Uniform Resource Locators): These are the unique addresses for every resource on the Web, like https://www.example.com/about.html. They tell your browser exactly where to find a specific page or file.
- HTTP/HTTPS: These are the rules (protocols) that computers use to communicate and transfer information on the Web. HTTPS is the secure version, important for protecting private information.
- HTML (Hypertext Markup Language): This is the main language used to create web pages. It tells the browser how to structure and display the content.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): This language works with HTML to control how web pages look – the colors, fonts, layout, and design.
- JavaScript: This is a programming language that adds interactive features to web pages, like games, animations, or forms that respond to what you do.
Brief History
The World Wide Web was invented by a brilliant English computer scientist named Tim Berners-Lee while he was working at a research organization called CERN in Switzerland.
Tim Berners-Lee came up with the idea for the Web in March 1989. He wanted a better way for scientists to share documents and information easily, no matter where they were located or what kind of computer they used. He imagined a system where documents could be linked together using "hypertext" – clickable connections that let you jump from one document to another.
By the end of 1990, Tim Berners-Lee had built the first web server, the first web browser (which he also called "WorldWideWeb"), and defined the basic rules (HTTP) and language (HTML) that the Web uses.
The technology was first shared with other research institutions in 1991. Then, on August 23, 1991, it was made available to everyone on the Internet. This date is sometimes called "Internaut Day."
In 1993, CERN made the Web technology completely free for anyone to use, which was a huge step. This allowed the Web to grow incredibly fast.
Early Browsers and Growth (Mid-1990s)
The release of graphical web browsers like Mosaic (in 1993) and Netscape Navigator (in 1994) made the Web much easier and more fun to use for regular people. Suddenly, you could see images right on the web page. This led to a massive increase in the number of websites and users.
Standardization
As the Web grew, it was important to have common rules so that websites would work correctly on different browsers and devices. Tim Berners-Lee founded the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) in 1994 to create and maintain these standards for web technologies like HTML and CSS.
Today the World Wide Web is an essential part of modern life. Billions of people use it daily for everything from learning and working to entertainment and connecting with friends. It continues to evolve with new technologies and ways of interacting.
Understanding Web Content
Web pages aren't all the same. They can be:
- Static Pages: These pages show the exact same information to everyone who visits them. They are like a printed page that doesn't change unless someone manually updates the file on the server.
- Dynamic Pages: These pages can show different information depending on who is viewing them, what they are doing, or what is happening in real-time. Examples include online banking sites (showing your specific account information), social media feeds (showing posts relevant to you), or online stores (showing your shopping cart). These pages are often created "on the fly" by programs running on the web server or in your browser using languages like JavaScript.
Deep Web and Search Engines
When you use a search engine like Google or Bing, you are searching the Surface Web. This is the part of the Web that search engines can easily find and index by following links.
However, there's also the Deep Web. This includes parts of the Web that standard search engines don't index.
Keeping Things Fast: Caching
To make the Web faster, computers use something called caching. When your browser downloads a web page, it can save a copy of some of the files (like images or CSS styles) on your computer. The next time you visit that page, your browser can use the saved copy instead of downloading it again from the server. This makes the page load much quicker. Web servers and Internet providers also use caching to speed things up for many users.
Privacy and Security
Because the Web involves sending and receiving information, it's important to think about privacy and security.
- IP Addresses: When you visit a website, the server knows your computer's IP address, which is like its unique online number. Servers often keep logs of these visits.
- Cookies: Websites can store small pieces of information called cookies on your computer. Cookies help websites remember things about you, like if you're logged in, items in your shopping cart, or your preferences. Some cookies are used by advertisers or other companies to track your browsing activity across different websites. This is why you often see ads related to things you've recently looked at online. Many websites now ask for your permission before using certain types of cookies.
- HTTPS: Using websites with HTTPS (look for the padlock symbol in the browser address bar) helps protect the information you send and receive, like passwords or credit card details, by encrypting it.
- Being Careful: It's always a good idea to be mindful of the information you share online, especially on social media. Think about who might see it and how it could be used. Using strong passwords and being cautious about clicking on suspicious links are also important steps to stay safe online.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The NeXT Computer used by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN
-
The CERN data centre in 2010 housing some WWW servers
-
Robert Cailliau, Jean-François Abramatic, and Tim Berners-Lee at the tenth anniversary of the World Wide Web Consortium
-
The World Wide Web functions as an application layer protocol that is run "on top of" (figuratively) the Internet, helping to make it more functional. The advent of the Mosaic web browser helped to make the web much more usable, to include the display of images and moving images (GIFs).
-
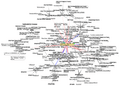
Graphic representation of a minute fraction of the WWW, demonstrating hyperlinks
-
Multiple web servers may be used for a high traffic website; here, Dell servers are installed together to be used for the Wikimedia Foundation.
See also
 In Spanish: World Wide Web para niños
In Spanish: World Wide Web para niños