War of the Third Coalition facts for kids
Quick facts for kids War of the Third Coalition |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Napoleonic Wars and the Coalition Wars | |||||||
 Napoléon at the Battle of Austerlitz, by François Pascal Simon, Baron Gérard |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
Third Coalition: |
|||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
160,000
|
62,050
|
||||||
The War of the Third Coalition was a major European conflict from 1803 to 1806. It was part of the larger Napoleonic Wars. During this war, France and its allied countries, led by Emperor Napoleon I, fought against an alliance called the Third Coalition. This alliance included the Holy Roman Empire, Russia, and Great Britain.
The main battles in Central Europe ended when Napoleon won the Battle of Austerlitz in 1805. However, fighting continued in Italy for a while longer. Napoleon's victory changed the map of Europe.
Contents
What Was the Third Coalition?
The Third Coalition was an alliance of European countries. They joined forces to try and stop the growing power of Napoleon's France. Great Britain was already at war with France since 1803. Other countries like Russia and Austria (part of the Holy Roman Empire) joined later. They were worried about France's control over other parts of Europe.
Who Fought in the War?
On one side was the Third Coalition. This included:
- The Holy Roman Empire (mainly Austria)
- The Russian Empire
- The United Kingdom
- The Kingdom of Naples and Sicily
- Sweden
On the other side was the French Empire. France had many allies, sometimes called "satellite states." These were countries that France had conquered or strongly influenced. They included:
Key Events of the War
The war had several important parts. It started with Great Britain and France already fighting. Then, other countries formed the Third Coalition.
The Trafalgar Campaign
This part of the war was fought at sea. It happened from March to November 1805. France and Spain wanted to invade Great Britain. To do this, they needed to control the sea.
The most famous battle was the Battle of Trafalgar. It took place on October 21, 1805. The British navy, led by Admiral Horatio Nelson, fought against the combined French and Spanish fleets.
- Outcome: The British won a huge victory. They destroyed many French and Spanish ships. This battle made sure that Napoleon could not invade Great Britain. Sadly, Admiral Nelson was killed during the battle.
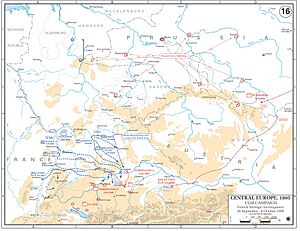
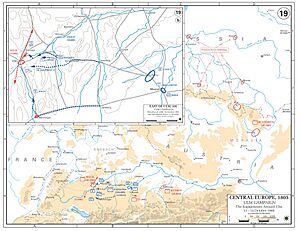
The Ulm Campaign
While the sea battle was happening, Napoleon moved his army, called the Grande Armée, across Europe. This land campaign took place in September and October 1805. Napoleon's goal was to defeat the Austrian army before the Russian army could join them.
- Strategy: Napoleon used a clever plan. He marched his army very quickly. They surrounded the Austrian army near the city of Ulm in Germany. The Austrians were surprised and trapped.
- Outcome: The Austrian army, led by General Karl Mack von Leiberich, was forced to surrender at Ulm. This was a big victory for Napoleon without a major battle. About 70,000 Austrian soldiers were captured.

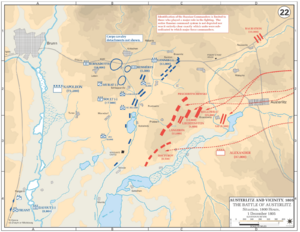
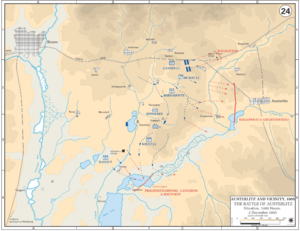
The Battle of Austerlitz
After Ulm, Napoleon continued to advance. The main battle of the war happened on December 2, 1805. This was the Battle of Austerlitz, also known as the "Battle of the Three Emperors." Napoleon fought against the combined armies of Austria (led by Emperor Francis II) and Russia (led by Tsar Alexander I).
- Location: The battle took place near Austerlitz (in what is now the Czech Republic).
- Napoleon's Plan: Napoleon pretended his army was weaker than it was. He made the Allied forces attack his right flank. When they did, he launched a surprise attack through the center of their lines.
- Outcome: Napoleon won a brilliant victory. The Allied armies were badly defeated. This battle is considered one of Napoleon's greatest military successes.
Invasion of Naples
Even after Austerlitz, fighting continued in Italy. In February 1806, French forces invaded the Kingdom of Naples. This was because Naples had joined the Third Coalition against France.
- Outcome: The French quickly conquered Naples. Napoleon's brother, Joseph Bonaparte, was made the new King of Naples.
Results of the War
The War of the Third Coalition ended with a clear victory for France.
- Treaty of Pressburg: After Austerlitz, Austria signed the Treaty of Pressburg on December 22, 1805. Austria had to give up a lot of land to France and its allies.
- French Empire Grows: Napoleon's power in Europe became much stronger. The French Empire expanded.
- Confederation of the Rhine: In July 1806, Napoleon created the Confederation of the Rhine. This was a group of German states allied with France. It replaced the old Holy Roman Empire, which was officially dissolved.
- New Coalitions: Even though France won, other European powers were still worried about Napoleon. A few months later, a new alliance, the Fourth Coalition, was formed to fight against France again.
Images for kids
-
In The Plumb-pudding in danger (1805), James Gillray drew a cartoon about Napoleon's attempts to make peace with Britain in January 1805.
-
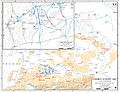
The situation from October 7 to 9. With Kutuzov's army too far away, the Austrians were in a difficult spot.
-
The Battle of Caldiero, 1805
See also
 In Spanish: Tercera Coalición para niños
In Spanish: Tercera Coalición para niños