Tilted Mountain facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tilted Mountain |
|
|---|---|

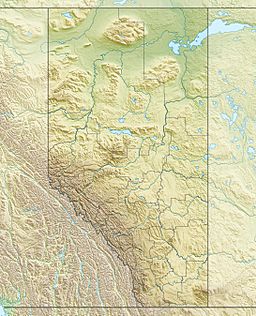
Tilted Mountain and Baker Lake from Deception Pass area
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 2,591 m (8,501 ft) |
| Parent peak | Lychnis Mountain (3124 m) |
| Listing | Mountains of Alberta |
| Geography | |
| Location | Alberta, Canada |
| Parent range | Sawback Range Canadian Rockies |
| Topo map | NTS 82O/05 Castle Mtn |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Cambrian |
| Type of rock | Sedimentary rock |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | Scrambling class 3 |
Tilted Mountain is a 2,591-metre (8,501-foot) mountain peak. It is found in Banff National Park, in the amazing Canadian Rockies of Alberta, Canada. This mountain is part of the Sawback Range. Its closest taller neighbor is Lychnis Mountain, which is about 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) to the east.
Mountain's Name: Why "Tilted"?
Tilted Mountain got its name in 1911. A person named James F. Porter gave it this name. He noticed that the layers of rock on the mountain looked like they were tilted or slanted. The name was officially accepted in 1924 by the Geographical Names Board of Canada.
How Tilted Mountain Was Formed
Like many mountains in Banff Park, Tilted Mountain is made of sedimentary rock. This type of rock forms from layers of sand, mud, and tiny bits of sea creatures that settle over millions of years. These rocks were laid down a very long time ago, from the Precambrian to the Jurassic periods.
- From Shallow Seas: The rocks that make up Tilted Mountain were first formed in shallow seas. Over time, these layers hardened into rock.
- Pushed Upwards: Later, during a major event called the Laramide orogeny, huge forces pushed these rock layers. This caused them to fold, break, and get pushed up and over younger rocks. This is why the mountain looks "tilted" today.
- Fossils Nearby: Close to Tilted Mountain, in an area called the Skoki Formation, you can find many fossils. These include ancient sea creatures like brachiopods, gastropods, and trilobites.
Weather at Tilted Mountain
Tilted Mountain is in a subarctic climate zone. This means it has very cold winters with lots of snow. The summers are usually mild. Temperatures can drop below −20 °C (which is -4 °F). With the wind, it can feel even colder, sometimes below −30 °C (-22 °F).