Sharptooth houndshark facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Sharptooth houndshark |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Order: | Carcharhiniformes |
| Family: | Triakidae |
| Genus: | Triakis |
| Species: |
T. megalopterus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Triakis megalopterus (A. Smith, 1839)
|
|
 |
|
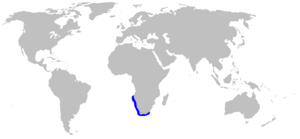
| Range of the sharptooth houndshark | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Mustelus megalopterus Smith, 1839 |
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The sharptooth houndshark (Triakis megalopterus) is a type of houndshark. It lives in shallow coastal waters. You can find it from southern Angola to South Africa. This shark likes sandy areas near rocky reefs and gullies. It swims actively and usually stays close to the bottom.
This strong shark can grow up to 1.7 m (5.6 ft) long. It has large, rounded fins. Its pectoral fins, which are like arms, are wide and curved in adult sharks. It also has a short, blunt nose and long grooves around its mouth. The sharptooth houndshark is gray or bronze on top. It often has black spots.
This shark is mostly active at night. It eats crustaceans like crabs, bony fishes, and cephalopods like octopus. During summer, these sharks gather in groups in shallow water. This might be for mating. Females give birth to 6–12 pups between late May and August. They reproduce every 2 or 3 years. The sharptooth houndshark is often caught by people fishing for fun. Some are also caught by commercial fishing boats. Because it lives in a small area and grows slowly, it is sensitive to too much fishing. However, the International Union for Conservation of Nature says it is of "least concern" for now.
Contents
About the Sharptooth Houndshark's Name
A Scottish zoologist named Andrew Smith first described this shark. He did this in 1839 in his book Illustrations of the Zoology of South Africa. He based his description on two sharks caught near the Cape of Good Hope, South Africa.
Smith named the shark megalopterus. This name comes from two Greek words: mega meaning "large" and pteron meaning "wing." This name refers to the shark's big fins. Another common name for this shark is "sweet William."
Later, scientists moved the sharptooth houndshark into the Triakis group. It is part of a smaller group called Cazon. Other sharks in this group include the sharpfin houndshark and the spotted houndshark.
What Does the Sharptooth Houndshark Look Like?
The sharptooth houndshark has a strong body. Its snout (nose) is short, thick, and blunt. Its nostrils are far apart. They have small skin flaps in front of them. The shark's eyes are oval-shaped and have a special eyelid called a nictitating membrane.
Its large mouth has long, deep grooves at the corners. The grooves on the lower jaw almost meet in the middle. The shark's teeth are small and packed together. They form a flat, pavement-like surface. Each tooth has a rounded base, like a molar, and a sharp point. It has five pairs of gill slits.
The fins of this shark are noticeably large and rounded. The pectoral fins of adult sharks are wide and curved like a sickle. The dorsal fins (on its back) have straight back edges. The first dorsal fin starts above the back tips of the pectoral fins. The second dorsal fin is about three-quarters as tall as the first.
The anal fin is much smaller than the second dorsal fin. It starts behind it. The shark has a short, thick tail base. The caudal fin (tail fin) has a small lower part and a longer upper part. The skin often feels loose. This shark is dark gray to bronze on top and white underneath. Young sharks usually have no spots. Adult sharks can have no spots or many irregular black spots. It can grow up to 1.7 m (5.6 ft) long and weigh 40 kg (88 lb). Female sharks grow larger than males.
Where Sharptooth Houndsharks Live
The sharptooth houndshark lives only in the coastal waters of southern Africa. Its range goes from southern Angola to the Eastern Cape in South Africa. Sometimes, it is seen in KwaZulu-Natal. This shark is common in its area.
It lives in sandy habitats like bays. It can be found from the surf zone (where waves break) down to 50 m (160 ft) deep. However, most are found no deeper than 10 m (33 ft). It usually swims just above the bottom. It prefers flat areas near rocky reefs or gullies. It rarely swims in open water.
Sharptooth Houndshark Life and Diet
The sharptooth houndshark is a very active shark. Sometimes, it rests inside rocky cracks. It mainly hunts at night. It has even been seen chasing prey almost onto the shore. Its pointed teeth help it grab slippery prey. Its wide teeth bases help it crush hard-shelled prey.
This shark eats many different things. It eats crustaceans like crabs, slipper lobsters, and spiny lobsters. It also eats bony fishes like morwongs and sea catfishes. Cephalopods, especially Octopus vulgaris, are also on its menu. Larger sharks sometimes eat other sharks and rays or their egg capsules. Off South Africa, the most important food is the crab Plagusia chabrus.
What the shark eats changes as it gets older. Young sharks under 1.0 m (3.3 ft) long eat mostly crabs. Larger sharks eat more bony fishes and cephalopods. They also eat a wider variety of prey. This shark has been seen hunting during the day to eat chokka squid when they gather to lay eggs. The broadnose sevengill shark is known to hunt the sharptooth houndshark.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
During the summer, sharptooth houndsharks form groups in shallow water. These groups are often seen in False Bay. They might be for reproduction, as many pregnant females are present. This shark gives birth to live young. The baby sharks grow inside the mother and get their food mainly from a yolk.
Female sharks have one working ovary and two working uteri. They give birth to 6–12 pups between late May and August. The pregnancy lasts about 20 months. Larger females tend to have more pups. The pups are born at a length of about 30–44 cm (12–17 in). Pups in the same litter can be different sizes.
Females seem to reproduce every two or three years. This depends on whether they have eggs developing during pregnancy. This would allow them to mate again soon after giving birth. The sharptooth houndshark grows slowly. Males become ready to reproduce at 1.2–1.4 m (3.9–4.6 ft) long and 11–13 years old. Females mature at 1.3–1.5 m (4.3–4.9 ft) long and 15–16 years old. They can live for at least 25 years.
Sharptooth Houndsharks and People
The sharptooth houndshark is harmless to humans. It does well in aquariums and has been shown in public aquariums. People often catch it when fishing for fun from shore or from boats. It can be eaten but is not often used for food.
A small number are also caught by accident by commercial fishing boats. These boats use longlines to catch other sharks, like the school shark. This happens in the Gansbaai and False Bay areas. The meat from these sharks is sometimes made into biltong or jerky and sold locally. It can also be sent fresh or frozen to Italy and Taiwan.
In South Africa, the sharptooth houndshark is not supposed to be caught for commercial use. However, fishers often mistake it for the common smooth-hound. The International Union for Conservation of Nature says this species is of "least concern." But it is very sensitive to fishing. This is because it lives in a small area, grows slowly, and does not have many babies. It is also a worry that most sharks caught by fishers are still young.
See also
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |





