Tulu language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tulu |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ತುಳು തുളു |
||||
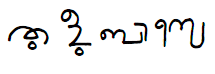
Tulu Baase written in Tigalari script
|
||||
| Native to | India | |||
| Region | Tulu Nadu region (Dakshina Kannada and Udupi District of Karnataka and a part of Kasaragod district of Kerala) |
|||
| Ethnicity | Tuluvas | |||
| Native speakers | 1.85 million (2011 census) | |||
| Language family |
Dravidian
|
|||
| Writing system | Tigalari script Kannada script |
|||
| Official status | ||||
| Recognised minority language in | ||||
| Regulated by | Karnataka Tulu Sahitya Academy Kerala Tulu Academy |
|||
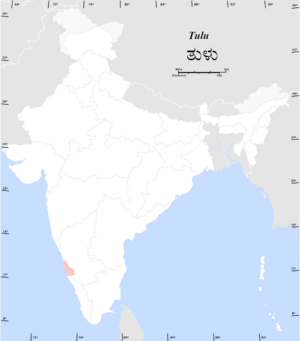
Distribution of native Tulu speakers in India
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
||||
Tulu (called Tulu bāse by its speakers) is an old language from the Dravidian language family. It is spoken mainly in two coastal areas of Karnataka in southwestern India. You can also find Tulu speakers in parts of the Kasaragod district in Kerala.
People who speak Tulu as their first language are called Tuluva or Tulu people. The area where they live is often called Tulu Nadu.
In 2011, about 1.85 million people in India spoke Tulu. Some experts believe that between 3 to 5 million people worldwide speak Tulu. It can be tricky to count Tulu speakers who have moved away from their home region. This is because they are sometimes counted as Kannada speakers in official reports.
Tulu separated from other South Dravidian languages a long time ago. Because of this, it has some special features not found in languages like Tamil or Kannada. For example, Tulu can show actions that happened before another past action, similar to how French or Spanish do it. But Tulu does this without needing an extra helping verb.
Tulu is the main language spoken in Tulu Nadu. This region includes the Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts of Karnataka. It also covers part of the Kasaragod district in Kerala. Many Tulu speakers also live in the Kalasa and Mudigere areas of the Chikkamagaluru district.
People who live in Tulu Nadu but do not speak Tulu as their first language might speak other languages. These include Beary, Havyaka, and Gowda dialects of Kannada. They might also speak Konkani or Koraga.
Many Tulu-speaking people have moved to other places. You can find large groups of them in Maharashtra, Bangalore, and Chennai in India. They also live in countries where English is spoken and in the Gulf countries.
Tulu Writing and Literature
Old writings from the 15th century show that Tulu used its own script, called the Tulu script. Two long poems, or epics, from the 17th century were also written in this script. These epics were called Sri Bhagavato and Kaveri.
Today, Tulu is mostly written using the Kannada script. Tulu is also famous for its oral literature. This means stories and poems passed down by speaking, not writing. These include long epic poems called Paddana. Famous examples are the Epic of Siri and the story of Koti and Chennayya.
Tulu Dialects
Tulu has several different ways of being spoken, called dialects. Here are some of the main ones:
- Brahmin dialect: This is spoken by Tulu Brahmin people.
- Jain dialect: This is spoken by Jain people in the northern part of Tulu Nadu.
- Common dialect: Most people in Tulu Nadu speak this dialect. It is used for business, entertainment, and art.
- Tribal dialect: This is spoken by tribal groups. It is quite similar to the Common dialect.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma tulu para niños
In Spanish: Idioma tulu para niños