Karnataka facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Karnataka
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
From top, left to right:
Mysore Palace, Pattadakal, Brindavan Gardens, Hoysala Empire emblem, Shivanasamudra Falls and Virupaksha Temple, Hampi |
||
|
||
| Anthem: "Jaya Bharata Jananiya Tanujate" "(Victory To You Mother Karnataka)" |
||
Map of Karnataka
|
||
| Country | ||
| Formation | 1 November 1956 (as Mysore State) |
|
| Capital and largest city |
Bangalore (Bengaluru) | |
| Districts |
List
|
|
| Government | ||
| • Body | Government of Karnataka | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 191,791 km2 (74,051 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 7th | |
| Highest elevation | 1,925 m (6,316 ft) | |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) | |
| Population
(2011)
|
||
| • Total | 61,130,704 | |
| • Rank | 8th | |
| • Density | 318.7360/km2 (825.5226/sq mi) | |
| Demonym(s) | Kannadiga | |
| GDP (2018–19) | ||
| • Total | ₹14.08 lakh crore (US$240 billion) | |
| • Per capita | ₹174,551 (US$3,000) | |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) | |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-KA | |
| Vehicle registration | KA | |
| Official languages | Kannada | |
| HDI (2017) | ||
| Literacy (2011) | 75.36% | |
| Sex ratio (2011) | 973 ♀/1000 ♂ | |
| Symbols of Karnataka | ||
| Emblem | Gandaberunda | |
| Song | Jaya Bharata Jananiya Tanujate | |
| Animal | Indian elephant | |
| Bird | Indian Roller | |
| Flower | Lotus | |
| Tree | Sandalwood | |
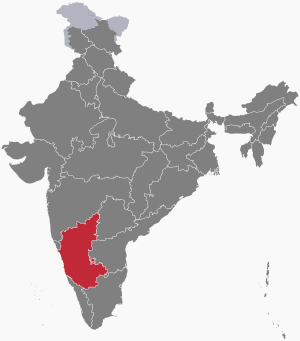
Karnataka is a state located in the southwestern part of India. It was created on November 1, 1956. At first, it was called the Mysore State. Later, in 1973, its name was changed to Karnataka. The state's capital and largest city is Bangalore, also known as Bengaluru.
Karnataka shares its borders with the Arabian Sea to the west. It is also next to Goa, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Kerala. The state covers an area of about 191,976 square kilometers. This is about 5.83% of India's total land area. It is the seventh largest state in India by size.
In 2011, Karnataka had over 61 million people. This makes it the eighth most populated state in India. It is divided into 30 districts. Kannada is the main and official language spoken here. It is one of India's classical languages.
Karnataka has a very old history, going back to the Stone Age. It has been home to many powerful empires throughout history. These empires supported thinkers and musicians. Their ideas and music are still important today. Karnataka has also greatly contributed to both major styles of Indian classical music: Carnatic and Hindustani.
Contents
Discovering Karnataka's Past
Karnataka's history began a very long time ago. Tools like hand axes found here show that people lived in this region during the Stone Age. Evidence of early farming and large stone monuments has also been found. Gold from Karnataka's mines was even found in Harappa. This suggests that ancient Karnataka traded with the Indus Valley Civilisation around 3300 BCE.
Before 300 BCE, most of Karnataka was part of the Nanda Empire. Then, it became part of the Mauryan empire under Emperor Ashoka. After that, the Satavahanas ruled for 400 years. They controlled large parts of Karnataka.
When the Satavahana power weakened, the first local kingdoms appeared. These were the Kadambas and the Western Gangas. This marked Karnataka's start as an independent political area. The Kadamba Dynasty was founded by Mayurasharma and had its capital at Banavasi. The Western Ganga dynasty had its capital at Talakad.
After India gained independence, the Maharaja, Jayachamarajendra Wodeyar, agreed for his kingdom to join India. In 1950, Mysore became an Indian state. The former Maharaja served as its head until 1975.
Many people wanted the Kannada-speaking regions to be united. So, in 1956, areas from Madras, Hyderabad, and Bombay states were added to Mysore. This happened because of the States Reorganisation Act. Seventeen years later, in 1973, the larger state was renamed Karnataka. In the early 1900s, people like Sir Mokshagundam Visvesvarayya helped build Karnataka's strong manufacturing and industrial base.
Karnataka's Thriving Economy
About 56% of the people in Karnataka work in farming. A huge area of land, about 12.31 million hectares, is used for farming. This is 64.6% of the state's total area. Most farming depends on the southwest monsoon rains. Only about 26.5% of the farmed land is irrigated.
Karnataka is a major manufacturing center for some of India's largest government-owned industries. Many of India's best science and technology research centers are also located here. The state is also investing a lot in solar power. The Pavagada Solar Park is a big project. By December 2017, the state had installed about 2.2 gigawatts of solar panels. In January 2018, it planned to generate another 1.2 gigawatts.
Since the 1980s, Karnataka has become a leader in information technology (IT) in India. In 2007, nearly 2,000 IT companies were working in Karnataka. The Nandi Hills area near Devanahalli is the site of a huge project. It's called the BIAL IT Investment Region. This $22 billion project covers 50 square kilometers. It is one of the biggest projects in Karnataka's history. Because of all this, Bangalore, the state capital, is often called the Silicon Valley of India.
Karnataka also leads India in biotechnology. The state produces 75% of India's floriculture (flower farming). This is a growing industry that sells flowers and ornamental plants worldwide.
Most of the silk industry in India is based in Karnataka. The state government plans to build a "Silk City" in Muddenahalli, close to the Bangalore International Airport.
Karnataka's Rich Culture
Karnataka holds a special place in the world of Indian classical music. Both Carnatic and Hindustani styles are popular here. Karnataka has produced many great musicians in both styles. The Haridasa movement in the 16th century helped develop Carnatic music as a performing art.
Gamaka is another classical music style. It is based on Carnatic music and is practiced in Karnataka.
The Mysore school of painting is an organization in Karnataka. It works to promote painting, especially in the Mysore painting style.
The Saree is the traditional dress for women in Karnataka. For men, the Dhoti, called Panche, is the traditional clothing. In cities, people also wear Shirts, Trousers, and Salwar kameez. The Mysore Peta is a traditional headgear in southern Karnataka. In the northern areas, people prefer the pagadi or pataga.
Rice and Ragi are staple foods in South Karnataka. In North Karnataka, Jolada rotti and Sorghum are common. For sweets, Mysore Pak, Karadantu from Gokak and Amingad, Belgaavi Kunda, and Dharwad pedha are very popular. Coastal Karnataka and Kodagu also have their own unique foods. Udupi cuisine from coastal Karnataka is famous across India.
Provincial Symbols of Karnataka
Exploring Karnataka: Top Tourist Spots
Karnataka has many interesting places for tourists. This is because of its diverse geography and long history. You can find ancient temples, modern cities, beautiful hills, forests, and beaches. Karnataka is ranked as the fourth most popular state for tourism in India. It has the second highest number of nationally protected monuments. Plus, 752 monuments are protected by the state.
The Western Ghats and southern parts of the state have popular eco-tourism spots. Karnataka has 25 wildlife sanctuaries and five national parks. Some famous ones are Bandipur National Park, Bannerghatta National Park, and Nagarhole National Park. The ancient ruins of the Vijayanagara Empire at Hampi and the monuments of Pattadakal are UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
The cave temples at Badami and the rock-cut temples at Aihole are also popular. These show the Badami Chalukyan style of architecture. The Hoysala temples at Belur and Halebidu are proposed UNESCO World Heritage sites. They were built using a soft stone called chloritic schist. The Gol Gumbaz and Ibrahim Rauza are great examples of Deccan Sultanate architecture. The huge statue of Gomateshwara Bahubali at Shravanabelagola is the tallest sculpted monolith in the world. Thousands of pilgrims visit it during the Mahamastakabhisheka festival.
Some people consider the waterfalls of Karnataka and Kudremukh to be among the "1001 Natural Wonders of the World." Jog Falls is India's tallest single-tiered waterfall. Other popular waterfalls include Gokak Falls, Unchalli Falls, Magod Falls, Abbey Falls, and Shivanasamudra Falls.
Many popular beaches are found along the coastline. Karnataka also has several important religious places. Many Hindu temples are in the northern parts of the state. Shravanabelagola, Mudabidri, and Karkala are famous for their Jain history and monuments. The Shettihalli Rosary Church near Shettihalli is a rare example of a Christian ruin. It shows French colonial Gothic architecture and is a popular tourist spot.
Recently, Karnataka has become a center for health care tourism. It has the highest number of approved health systems and alternative therapies in India. Along with some government hospitals, private hospitals offer international-quality services. This has made the health care industry grow a lot. Hospitals in Karnataka treat about 8,000 health tourists every year.
Images for kids
-
Infosys, a Bengaluru-headquartered information-technology company.
-
Vishnu image inside the Badami Cave Temple Complex number 3. The complex is an example of Indian rock-cut architecture.
-
Halmidi inscription (450 CE) is the earliest attested inscription in the Kannada language.
-
Indian Institute of Science is one of the premier institutes of India.
-
Anil Kumble, former captain of the Indian Test team and spin legend, is the highest wicket-taker for India in international cricket.
-
M. Chinnaswamy Stadium in Bangalore.
-
The state bird, Indian roller.
-
Bengal tigers at Bannerghatta National Park near Bangalore.
-
Chennakesava Temple is a model example of the Hoysala architecture, later repaired in the 16th century with financial support and grants by the Vijayanagara Emperors.
-
Gol Gumbaz at Bijapur has the second largest pre-modern dome in the world after the Byzantine Hagia Sophia.
-
Mysore Palace in the evening, the official residence and seat of the Wodeyar dynasty, the rulers of Mysore of the Mysore Kingdom, the royal family of Mysore.
See also
 In Spanish: Karnataka para niños
In Spanish: Karnataka para niños