Ventricular tachycardia facts for kids
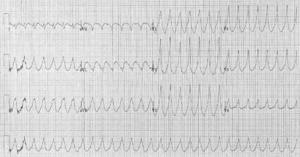
Ventricular tachycardia (often called V-tach or VT) is a type of very fast heart rate. Your heart has four main parts, like rooms. The top two are called the atria, and the bottom two are called the ventricles. Normally, electrical signals tell the top parts (atria) to squeeze first. This helps pump blood correctly. But with V-tach, the bottom parts (ventricles) squeeze first. This happens because the electrical signals are not working right.
V-tach is a serious medical emergency. When the heart beats too fast, it doesn't have enough time to fill with blood between beats. This means it can't pump enough blood to the rest of your body. Most people with V-tach have a heart rate of at least 170 beats per minute. This is much faster than a normal heart rate, which is usually 60 to 100 beats per minute.
If your heart can't pump enough blood, your blood pressure can drop very low. If blood pressure gets too low, important parts of your body, like your brain, won't get enough blood and oxygen. This can be very dangerous. V-tach can also lead to other serious heart problems, like your heart stopping suddenly.
Contents
What Are the Symptoms of V-tach?
The most common things people feel with ventricular tachycardia are feeling dizzy, feeling their heart pounding in their chest (called palpitations), having trouble breathing, or chest pain. Some people with V-tach might not feel anything at all, especially if the fast heart rate only lasts for a few seconds.
If a person's heart rate is very high, or if V-tach lasts for more than a few seconds, they might faint or become unconscious. This happens because their brain isn't getting enough blood and oxygen. In the worst situations, their heart might stop beating, which can lead to death.
How Do Doctors Diagnose V-tach?
A doctor can find out if someone has ventricular tachycardia by doing an electrocardiogram. This test is also known as an ECG or EKG. It's a simple test that shows the electrical activity of your heart. The doctor can see on the ECG that the electrical signals telling the top parts of the heart to squeeze first are not working correctly.
How Is V-tach Treated?
Ventricular tachycardia can be treated in different ways. The treatment depends on whether the person still has a pulse. If a person has "pulseless ventricular tachycardia," it means their heart is beating so fast that it can't pump any blood at all.
Cardioversion Treatment
If a person still has a pulse, doctors can usually stop V-tach with something called cardioversion. Cardioversion uses medication or a controlled electric shock to help the heart start beating normally again.
Defibrillation Treatment
If a person has pulseless ventricular tachycardia, they need to be shocked with a special machine called a defibrillator.
There are two main types of defibrillators. An external defibrillator is a machine that gives a shock through two sticky pads placed on the person's chest.
Some people who have already been diagnosed with V-tach might have surgery to put a defibrillator inside their chest. This is called an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). This special device can automatically shock the heart if it goes into V-tach again.
First Aid for V-tach
If someone suddenly goes into pulseless ventricular tachycardia, first aid is very important. You should call your local emergency telephone number (like 9-1-1 in the United States) right away. Then, if the person is unconscious and has no pulse, you should start cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) immediately. An emergency medical dispatcher can guide you on how to do CPR until an ambulance arrives.
What Causes V-tach?
Many different things can cause ventricular tachycardia. The most common reason is ischemic heart disease. This is a heart problem where the heart muscle doesn't get enough oxygen.
Other problems that can cause V-tach include:
- Cardiomyopathies: These are diseases that affect the heart muscle itself.
- Diseases like sarcoidosis and rheumatoid arthritis: These can affect the whole body, and sometimes they can attack the heart muscle.
- Problems with electrolytes: These are important chemicals in your body, like potassium, calcium, or magnesium. If you don't have enough of them, it can cause heart problems.
- Certain kinds of medications.
Sometimes, doctors cannot find a clear reason for ventricular tachycardia. When this happens, it is called idiopathic ventricular tachycardia.
What Is the Outlook for People with V-tach?
Ventricular tachycardia is a major cause of sudden heart-related deaths. In the United States, it causes about 300,000 deaths each year.
The chance of sudden death is highest for people who:
- Have ischemic cardiomyopathy (their heart muscle was damaged because it didn't get enough oxygen).
- Have V-tach that comes and goes.
The chance of sudden death is lowest for people with idiopathic ventricular tachycardia (where no cause is found).
Even for people at higher risk, treatments can help. Medications like beta blockers can be useful. Implantable cardio-defibrillators (ICDs) also greatly improve the outlook for many people.
Related pages
See also
 In Spanish: Taquicardia ventricular para niños
In Spanish: Taquicardia ventricular para niños

