War of the Austrian Succession facts for kids
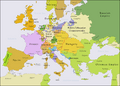
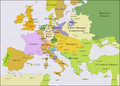
The War of the Austrian Succession was a major conflict in Europe that lasted from 1740 to 1748. Many countries were involved. The main reason for the war was about who would become the ruler of the Habsburg Monarchy. This was the powerful family that ruled Austria.
The war started because Maria Theresa wanted to take over her father's crowns. Her father was Emperor Charles VI. However, an old rule called Salic law said that a woman could not inherit the crown. This gave countries like France and Prussia a chance to challenge Austria's power. They were joined by Bavaria.
Maria Theresa had strong supporters. These included Britain, the Dutch Republic, Sardinia, and Saxony. Spain also joined the war. Spain had been fighting Britain since 1739 over colonies and trade. Spain wanted to regain its influence in northern Italy. Austria had taken control of this area earlier in the 18th century.
The war ended with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1748. Maria Theresa was confirmed as the ruler of Austria and Hungary. However, Prussia kept control of a region called Silesia. This peace did not last long. Austria wanted Silesia back, and new political changes in Europe led to the Seven Years' War (1756–1763).
Contents
What Caused the War of Austrian Succession?
The main cause of the war was the question of who would rule the Habsburg lands. Emperor Charles VI had no sons. He wanted his daughter, Maria Theresa, to inherit his titles. He created a document called the Pragmatic Sanction. This document aimed to make sure other European powers would accept Maria Theresa as his heir.
However, when Charles VI died in 1740, several countries did not respect the Pragmatic Sanction. They saw an opportunity to gain land or power from the Habsburgs.
The Role of Salic Law
Salic law was an old rule. It prevented women from inheriting royal titles or land. While it wasn't strictly applied to all Habsburg lands, it was used as an excuse by some rulers. They argued that Maria Theresa could not legally become the ruler.
Prussia's Ambitions in Silesia
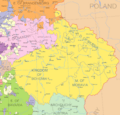
Frederick II, the new King of Prussia, was especially quick to act. He invaded Silesia in December 1740. Silesia was a rich and important region belonging to Austria. Frederick wanted to expand Prussia's territory and power. This invasion officially started the conflict.
Who Fought in the War?
The war involved two main groups of countries.
Maria Theresa's Supporters
- Austria: Led by Maria Theresa.
- Great Britain: Provided financial support and troops.
- Dutch Republic: Also known as the Netherlands.
- Sardinia: A kingdom in Italy.
- Saxony: A German state.
Challengers to Habsburg Power
- Prussia: Led by Frederick the Great.
- France: A major European power.
- Bavaria: A German state.
- Spain: Joined to regain influence in Italy.
Key Events and Battles
The War of the Austrian Succession was fought across many different parts of the world.
Fighting in Europe
- Silesian Wars: Prussia's invasion of Silesia led to two separate wars within the larger conflict. Prussia won both and kept Silesia.
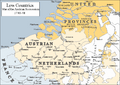
- Battles in the Low Countries: French forces fought against British, Dutch, and Austrian armies. A famous battle was the Battle of Fontenoy in 1745.
- Italian Campaigns: Spain and France fought against Austria and Sardinia for control of northern Italy.
- Jacobite Rising in Scotland: In 1745, a rebellion supported by France tried to put a new king on the British throne. This forced Britain to send troops home from Europe.
Conflicts Around the World
- War of Jenkins' Ear: This conflict between Britain and Spain started in 1739. It was mainly fought in the Americas and at sea.
- King George's War: This was the North American part of the war. It involved British and French colonies.
- First Carnatic War: This was fought in India. It involved British and French trading companies.
How Did the War End?
The war ended with the signing of the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1748.
Terms of the Treaty
- Maria Theresa's Rule Confirmed: The treaty officially recognized Maria Theresa as the ruler of Austria and Hungary.
- Prussia Keeps Silesia: Prussia was allowed to keep the rich region of Silesia. This was a big win for Prussia.
- Territorial Changes: Some territories were exchanged, but generally, the map of Europe did not change drastically.
- Return of Conquests: Most lands captured during the war were returned to their original owners.
The Aftermath and Future Conflicts
Even though the war ended, the peace did not last long. Austria was still determined to get Silesia back from Prussia. This desire, combined with new alliances forming in Europe, led to another major conflict just a few years later. This was the Seven Years' War (1756–1763), which was even bigger and involved more countries.
Images for kids
-
Maria Theresa, Queen of Hungary and Bohemia and Archduchess of Austria
-
Frederick the Great of Prussia
-
Maria Theresa's husband, Francis I
-
Victory at Fontenoy in May 1745
-
Philip V of Spain's family
-
The Franco-Spanish fleet near Toulon in 1744
-
King George II at the Battle of Dettingen, 1743
-
The Duke of Lorraine and Imperial troops crossing the Rhine before Strasbourg, 1744
-
The British fleet bombarding Bastia in 1745
-
The Battle of Fontenoy, 11 May 1745
-
The Battle of Rocoux in 1746
-
The Battle of Cape Finisterre, 1747
-
Marshal Maurice de Saxe at the Battle of Lauffeld, 1747
-
Taking of the fortress of Bergen-op-Zoom in 1747
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra de sucesión austríaca para niños
In Spanish: Guerra de sucesión austríaca para niños