Western Union (alliance) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Western Union
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1948–1954 | |||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| Status | Alliance | ||||||||
| Capital |
|
||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||
|
• Czechoslovak coup
|
21–25 February 1948 | ||||||||
|
• Treaty of Brussels
|
17 March 1948 | ||||||||
|
• WUDO established
|
28 September 1948 | ||||||||
|
• Korean War breaks out
|
25 June 1950 | ||||||||
|
• NATO absorbs WUDO
|
1951 | ||||||||
|
• Superseded by the WEU by the Modified Treaty of Brussels
|
23 October 1954 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Today part of |
|
||||||||
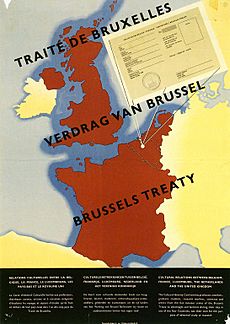
The Western Union (WU) was an important group of European countries. It was also known as the Brussels Treaty Organisation (BTO). This alliance was formed in September 1948. Its members were France, the United Kingdom (UK), and the three Benelux countries (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg).
They created this group to follow the rules of the Treaty of Brussels, which was signed earlier in March 1948. The countries involved, called the five powers, agreed to work together. They wanted to cooperate on defence, politics, money, and culture.
During the Korean War (1950–1953), the Western Union's defence part, called the Western Union Defence Organisation (WUDO), joined with a new group. This new group was the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). WUDO's plans and people became a key part of NATO's European command.
Later, in 1954, the Western Union changed. It became the Western European Union (WEU). Italy and West Germany also joined this new group. Today, the Western Union is seen as an early version of both NATO and the military side of the European Union (EU).
Contents
History of the Western Union
Why the Western Union Started

After World War II ended, people in Europe were worried. They feared that Germany might become aggressive again. To help prevent this, France and the United Kingdom signed the Treaty of Dunkirk on March 4, 1947. This treaty was an agreement to help each other if one was attacked.
On January 22, 1948, Ernest Bevin, the British Foreign Secretary, gave a speech. He suggested that the Treaty of Dunkirk should include the Benelux countries too. He wanted to create a stronger "Western Union." His goal was to unite Western Europe. This would also show the United States that Europe was serious about its defence. He also hoped Italy and West Germany would join later.
A meeting was held on March 4, 1948. This was right after some political changes in Prague. Because of this, the smaller countries convinced the others to agree. They decided to offer immediate help if any member was attacked. They also agreed to form a regional group, following the rules of the United Nations Charter. The Western Union was meant to protect Western Europe from the threat of communism. It aimed to bring more safety to the region.
Forming the Alliance
The Treaty of Brussels was signed on March 17, 1948. The countries that signed were Belgium, France, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom. This treaty expanded on the defence promise made in the Dunkirk Treaty from the year before.

The treaty talked about "cooperation" between the countries. This cooperation would happen through a "Consultative Council" and other groups. In practice, this agreement became known as the Western Union or the Brussels Treaty Organisation.
Changing into the Western European Union
The Western Union's main treaty, the Treaty of Brussels, was changed in 1954. This happened at the Paris Conference. It was because a plan for a European Defence Community (EDC) did not get approved by France.
There was a strong desire to include Germany in the defence plans for Western Europe. The new agreement, called the Modified Brussels Treaty (MBT), changed the Western Union. It became the Western European Union (WEU). At this point, Italy and Germany were allowed to join. Even though the WEU was not as powerful as the original Western Union, Germany's membership was enough. It meant that the Allied occupation of Germany could finally end.
Some parts of the Western Union that dealt with social and cultural issues were moved. They became part of the Council of Europe. This was done to avoid doing the same work in two different places. Since the end of World War II, sovereign European countries have entered into treaties and thereby co-operated and harmonised policies (or pooled sovereignty) in an increasing number of areas, in the European integration project or the construction of Europe (French: la construction européenne). The following timeline outlines the legal inception of the European Union (EU)—the principal framework for this unification. The EU inherited many of its present responsibilities from the European Communities (EC), which were founded in the 1950s in the spirit of the Schuman Declaration.
| Legend: S: signing F: entry into force T: termination E: expiry de facto supersession Rel. w/ EC/EU framework: de facto inside outside |
[Cont.] | ||||||||||||||||
| (Pillar I) | |||||||||||||||||
| European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom) | [Cont.] | ||||||||||||||||
| European Economic Community (EEC) | |||||||||||||||||
| Schengen Rules | European Community (EC) | ||||||||||||||||
| 'TREVI' | Justice and Home Affairs (JHA, pillar II) | ||||||||||||||||
| [Cont.] | Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters (PJCC, pillar II) | ||||||||||||||||
Anglo-French alliance |
[Defence arm handed to NATO] | European Political Co-operation (EPC) | Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP, pillar III) |
||||||||||||||
| [Tasks defined following the WEU's 1984 reactivation handed to the EU] | |||||||||||||||||
| [Social, cultural tasks handed to CoE] | [Cont.] | ||||||||||||||||
Cultural and Social Efforts
The Treaty of Brussels included plans for cultural and social cooperation. The idea was that working together would help stop the spread of communism.
Here are some examples of their cooperation:
- The Cultural Identity Card: The Western Union created this card. It helped students, teachers, and researchers from member states. The card allowed them to use cultural facilities in other member countries. It had a special stamp of the Brussels Town Hall. Later, the Council of Europe cultural identity Card replaced it.
- The 1951 Western Union International Guide for Young People: This guide helped young people from the member countries.
Defence Organisation
The member countries of the Western Union decided to create a military group. This group was called the Western Union Defence Organisation (WUDO). It was officially started on September 27–28, 1948.
WUDO's main goal was to coordinate defence among the five countries. This included military plans and supplies. They also studied how to best defend Western Europe. It provided a structure for a command organization if an emergency happened.
The Treaty of Brussels had a very important rule about defence. Article IV stated:
If any of the High Contracting Parties should be the object of an armed attack in Europe, the other High Contracting Parties will, in accordance with the provisions of Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations, afford the Party so attacked all the military and other aid and assistance in their power.
This meant that if one member country was attacked in Europe, the others would give all the military and other help they could.
Article V explained that members must work with the United Nations Security Council. This was to keep international peace and safety. Article VI said that members could not join any other treaties that went against the Treaty of Brussels.
See also
- Treaty establishing the European Defence Community
- Western European Union
- European Union
- Treaty of Brussels
- Common Security and Defence Policy
- History of the Common Security and Defence Policy
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization
- History of NATO
- Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe
- Supreme Allied Commander Europe
 | George Robert Carruthers |
 | Patricia Bath |
 | Jan Ernst Matzeliger |
 | Alexander Miles |