Schengen Area facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Schengen Area
|
|
|---|---|
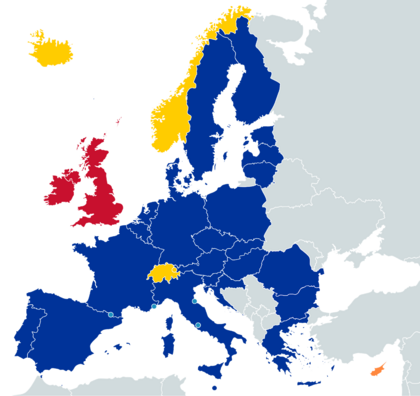
Map of the Schengen Area
Schengen Area Countries with open borders to the Schengen area Member of the EU committed by treaty to join the Schengen Area in the future |
|
| Type | Open border area of the European Union |
| Members | |
| Establishment | 26 March 1995 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
4,595,131 km2 (1,774,190 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• 2021 estimate
|
453,324,255 |
|
• Density
|
98.7/km2 (255.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
The Schengen Area is a special zone in Europe. It includes 29 countries that have removed their border checks with each other. This means you can travel between these countries without showing your passport at every border. It's like traveling between states in one country!
This area is part of a bigger plan by the European Union (EU) to make travel and security easier. It also has a shared visa policy for people visiting from outside the area. The Schengen Area got its name from two agreements signed in 1985 and 1990 in a town called Schengen, in Luxembourg.
Most of the 27 EU countries are part of the Schengen Area. Only Cyprus and Ireland are not. Cyprus is working to join soon. Ireland has chosen to keep its own border rules.
Besides EU countries, four countries from the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) are also part of Schengen: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. Also, four tiny countries—Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City—are included because they are so small and close to Schengen countries.
More than 450 million people live in the Schengen Area. It covers about 4.6 million square kilometers. Every day, about 1.7 million people cross a border to go to work. This free movement helps trade and makes travel much easier for everyone.
Contents
- History of the Schengen Area
- Countries in the Schengen Area
- Future Members of Schengen
- Parts of Schengen Countries Outside the Area
- European Microstates and Gibraltar
- Opt-Outs from Schengen
- Economics of Schengen
- Rules for Internal Borders
- Rules for External Borders
- Police and Justice Cooperation
- See also
History of the Schengen Area
How European Borders Changed
Before World War I, it was much easier to travel between countries. There were not many strict border checks. Wealthy people often went on long educational trips called the Grand Tour.
After World War I, countries started requiring visas and had more border controls. But after World War II, European countries began working together more closely. Some groups of countries, like the Nordic Passport Union (in 1954) and Benelux (in 1960), removed border checks between themselves. The European Communities (which later became the EU) also started in the 1950s to help countries work together on economic matters. However, they did not deal with border controls at first.
The Schengen Agreement Begins
The idea of removing border controls for all EU countries started on June 14, 1985. Five countries from the European Economic Community (EEC)—Belgium, Luxembourg, Netherlands (the Benelux countries), France, and West Germany—signed the first Schengen Agreement. They did this on their own because not all EEC countries agreed at the time.
In 1990, they added the Schengen Convention. This agreement planned to remove internal border checks and create a shared visa policy. The Schengen Area officially began on March 26, 1995.
As more EU countries joined, everyone agreed to make the Schengen rules part of EU law. This happened in 1997 with the Amsterdam Treaty, which started in 1999. This meant that any changes to Schengen rules would be made through EU laws. Countries not in the EU, like Norway and Iceland, do not get to vote on these changes.
The United Kingdom (UK) and Ireland had their own travel agreement called the Common Travel Area since 1923. The UK did not want to remove its border controls with other countries, so it opted out of Schengen. Ireland also chose not to join to keep its open border with Northern Ireland (part of the UK).
The Schengen Area has a common visa policy. This means people from certain countries can enter the Schengen Area without a visa for up to 90 days within a 180-day period. This applies whether they arrive by air, land, or sea. People from other countries need a visa to enter or even to pass through.
Countries in the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area has 29 countries. Most are members of the European Union. Four countries are not EU members: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. Iceland and Norway were already part of the Nordic Passport Union. Switzerland joined in 2008, and Liechtenstein in 2011.
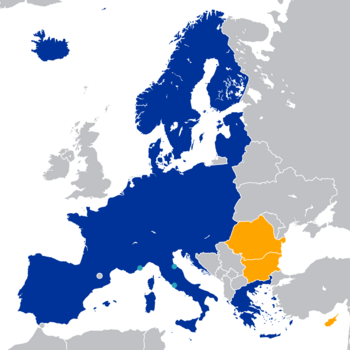
Romania and Bulgaria are the newest members. Border checks for air and sea travel ended on March 31, 2024. Land border checks are set to end on January 1, 2025. This happened more than 17 years after they joined the EU. Some countries had concerns about crime and corruption, but these issues were worked out.
Four tiny European countries are also included in the Schengen Area in practice: Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City. They have open or mostly open borders with the Schengen countries around them.
Ireland chose not to join Schengen. It still has border controls with other EU countries. However, it is part of the open-border Common Travel Area with the United Kingdom and its associated islands.
Future Members of Schengen
The process to join the Schengen Area involves checking if a country meets certain rules. These rules cover border control, data protection, visas, and police cooperation. If the checks are positive, all current Schengen members must agree to let the new country join.
Cyprus's Journey to Schengen
Cyprus, an EU member since 2004, is required to join the Schengen Area eventually. However, its entry has been delayed because of the Cyprus dispute. This dispute involves the northern part of Cyprus, which has been occupied by Turkey since 1974. Managing borders there under Schengen rules is complicated.
In November 2019, Cyprus officially started the process to join. By July 2023, Cyprus joined the Schengen Information System (SIS). This system helps countries share information about crime and security. Cyprus expects to be ready to join the Schengen Area by the end of 2025.
Parts of Schengen Countries Outside the Area
Some areas that belong to Schengen member countries are not part of the Schengen Area. These include the Faroe Islands and Svalbard, which are part of Denmark and Norway, respectively.
French Territories
France has several overseas territories that are part of the EU but not the Schengen Area. These include French Guiana, Guadeloupe, Martinique, Mayotte, Réunion, and Saint Martin. This means you cannot travel there with a Schengen visa. Each territory has its own visa rules for non-European visitors.
Dutch Territories
Only the European part of the Netherlands is in the Schengen Area. Six Dutch territories in the Caribbean are not. These include Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, Saba, Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten. They have their own visa rules. People traveling between these islands and the Schengen Area must go through full border checks.
Norwegian Territories
Svalbard is part of Norway but not the Schengen Area. It has special international rules. There are no visa requirements to enter Svalbard. However, it is hard to get there without passing through the Schengen Area. Since 2011, Norway has checked passports for everyone entering and leaving Svalbard.
Danish Territories
The Faroe Islands and Greenland are Danish territories. They are not part of the EU or the Schengen Area. Visas for Denmark are not automatically valid there. However, they do not have border controls for arrivals from the Schengen Area. Airlines and ferries are responsible for checking documents before boarding.
European Microstates and Gibraltar
Four tiny European countries—Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City—are not officially part of the Schengen Area. However, they are treated as if they are, because they have open or mostly open borders with the Schengen countries around them. They do not have regular border checks.
In 2015, Andorra, Monaco, and San Marino started talking about closer ties with the EU. Monaco left these talks in 2023. Andorra and San Marino are still working on an agreement. On May 30, 2024, the EU agreed to start talks to make sure there are no border controls between these countries and the Schengen Area.
Andorra
Andorra is a country surrounded by land. It does not have an airport or seaport. You can only enter by road or helicopter through France or Spain. Andorra does not have regular border checks with France or Spain. However, customs checks happen because Andorra has lower taxes. If you need a visa to enter the Schengen Area, you will need a multiple-entry visa to visit Andorra. This is because entering Andorra means leaving the Schengen Area. In June 2024, Germany's foreign ministry confirmed Andorra has an open border with Spain and France.
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein is also landlocked and has no international airport. It joined the Schengen Area in 2011. There are no border checks at its heliport, as flights must be from within the Schengen Area. Liechtenstein does not issue visas. Visitors are advised to get a visa from another Schengen country.
Monaco
Monaco has an open border with France. Schengen rules apply there because of agreements with France. Schengen visas are accepted. French and Monegasque officials do check at Monaco's seaport and heliport.
San Marino
San Marino has an open border with Italy. However, Italy's police and San Marino's police sometimes do random checks.
Vatican City
The Vatican City has an open border with Italy. There are no customs checks between them. Regular border controls would not work due to its small size and many visitors. In 2006, Vatican City showed interest in joining the Schengen agreement to share information.
Gibraltar
After Brexit, Gibraltar left the EU on January 31, 2020. It was never part of the Schengen Area. On December 31, 2020, Spain and the UK agreed on a plan for Gibraltar's future. This plan aims to make Gibraltar's port and airport entry points to the Schengen Area. Border checks there will be managed by Frontex, the EU's border agency.
Gibraltar residents are expected to have free movement to the Schengen Area. UK citizens who do not live in Gibraltar will have checks when entering Gibraltar. An agreement was reached on June 11, 2025, to apply Schengen rules to Gibraltar once ratified.
Opt-Outs from Schengen
When the Schengen Agreement became part of EU law, two current members and one former member chose not to follow all its rules.
Denmark
Denmark has a special opt-out from some EU policies, but it has adopted the Schengen rules. Its territories of Greenland and the Faroe Islands are not included. Because of this opt-out, Denmark does not have voting rights on new Schengen measures.
Ireland
Ireland chose not to join Schengen to keep its Common Travel Area with the UK. This agreement allows free travel between Ireland and the UK. Ireland joined the law enforcement part of the Schengen Information System (SIS II) on January 1, 2021. It checks identity documents against SIS II at airports and ports. Ireland is likely to keep its open land border with the UK, so it probably will not join the Schengen Area soon.
Economics of Schengen
Trade between any two Schengen countries increases by about 0.1% each year. Removing border controls is like removing a 0.7% tax on trade. This saves money and makes trade easier. Countries outside the Schengen Area also benefit from this.
Movement of People
About 1.7 million people cross a European border for work every day. In some areas, these commuters make up a third of the workforce. For example, 2.1% of workers in Hungary work in another country, mostly Austria and Slovakia. Each year, there are 1.3 billion crossings of Schengen borders. This includes 57 million crossings for goods transport by road, worth €2.8 trillion.
Rules for Internal Borders

Before Schengen, most European borders had many checkpoints to check travelers. Now, these border posts between Schengen countries have been removed.
The Schengen rules say that all barriers to free travel at internal borders must be removed. This means road, rail, and air travelers do not have their identity checked by border guards when moving between Schengen countries. However, security checks by airlines or train companies are still allowed. EU guidelines suggest all EU citizens carry a passport or national ID card.
Passport stamps are never given when traveling between Schengen countries, even if temporary border controls are put back in place.
Checks Inside Countries
Even though there are no border checks, most Schengen countries require people to carry identity documents. You might need to show these to an authorized person if asked. Different rules apply to non-EU citizens. Everyone traveling in the area must have a valid ID accepted by other Schengen states.
Hotels and other places to stay must register all foreign visitors, including those from other Schengen countries. They need to fill out a form and show a valid ID.
Temporary Border Controls
A Schengen country can bring back border controls with another Schengen country for a short time. This can happen if there is a serious threat to public safety or if external border control is not working well. If the threat is expected, the country must tell the European Commission beforehand.
The European Court of Justice clarified in April 2022 that temporary internal border controls cannot last longer than six months for the same threat. A country can only start new controls if there is a new serious threat.
Many countries put temporary border controls in place during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. Almost all Schengen countries closed their borders to non-essential travel. By July 2020, most of these borders had reopened.
In September 2024, Germany announced it would temporarily check all its land borders for six months to deal with irregular migration.
Internal Border Controls Since 2015
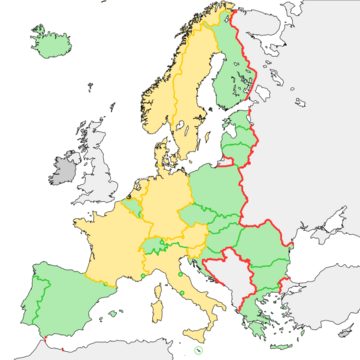
Several Schengen countries have had temporary border controls in place since 2015. These were often due to the European migrant crisis or security concerns like terrorism. For example, Austria, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Norway, Slovenia, and Sweden have had controls at various internal borders.
Rules for External Borders
Countries in the Schengen Area must check travelers entering and leaving the area very carefully. These checks are coordinated by Frontex, the EU's border agency. The rules for border checks are detailed in the Schengen Borders Code.
Temporary Travel Restrictions
During the COVID-19 pandemic, starting March 16, 2020, the European Commission suggested a temporary ban on non-essential travel into the Schengen Area for people from outside the EU. This ban did not apply to EU citizens, their families, or people with essential jobs like healthcare workers. The ban was extended several times and most restrictions were lifted by July 2020.
Border Checks
Everyone crossing an external border (entering or leaving) must be checked by a border guard. Before April 2017, EU citizens had quicker "minimum checks." But after the November 2015 Paris attacks, systematic checks were introduced for everyone, including EU citizens. This means all travel documents are checked against databases.
These checks can sometimes cause long waiting times at borders. For example, in April 2017, travelers entering Slovenia from Croatia faced hours of waiting. Border guards must respect travelers' dignity and not discriminate based on sex, race, religion, disability, age, or sexual orientation.
External border controls are found at roads, airports, seaports, and on trains. Some land borders have fences, like the one between Lithuania and Belarus. Surveillance cameras are also used in critical areas.

Many external border points have special lanes for EU citizens and other lanes for all travelers. Some checkpoints are only for certain travelers, like residents of nearby countries. Automated border control systems are also used in some airports.
ETIAS Travel Authorization
The European Travel Information and Authorisation System (ETIAS) is a new electronic travel authorization system. It is planned to start in 2026. People from countries that do not need a visa to enter the Schengen Area will need to apply online for ETIAS before their trip. This system is similar to those in the United States and Canada. It will cost €7, but children will not have to pay.
Entry/Exit System (EES)
In October 2025, the EU plans to launch the Entry/Exit System (EES). This automated system will record when travelers from outside the EU enter and leave the Schengen Area. It will use facial recognition and fingerprint scans instead of passport stamps.
Carrier's Responsibility
Airlines and other transport companies must check that passengers have the correct travel documents and visas before they board a flight or ferry to the Schengen Area. If they transport someone without the right documents, they can be fined. This rule helps prevent illegal immigration.
Short-Stay and Transit Visas
The rules for short-term visas to the Schengen Area are set by EU laws. There are lists of countries whose citizens need a visa and those who do not.
If you need a Schengen visa, you should apply at the embassy or consulate of the country you plan to visit most. If you are visiting several countries, apply at the embassy of the first Schengen country you will enter.
The standard fee for a Schengen visa is €80. For children aged 6 to 12, it is €40. Children under 6 do not pay a fee. This fee is not refunded, even if your application is denied.
Entry Rules for Non-EU Citizens
A Schengen visa does not guarantee entry. Non-EU citizens must meet certain requirements to be allowed into the Schengen Area for up to 90 days in any 180-day period:
- They must have a valid travel document (like a passport).
- The travel document must be valid for at least three months after their planned departure and issued within the last 10 years.
- They must have a valid visa or residence permit if required.
- They must explain their reason for visiting and show they have enough money for their stay and return trip.
- They must not be flagged in the Schengen Information System as a threat.
- They must not be considered a threat to public safety or international relations.
Even if someone does not meet all these rules, they might still be allowed entry for humanitarian reasons or national interests.
Passport Stamps
Until the EES system is fully working, some travelers get a passport stamp when they enter and leave the Schengen Area. All 29 Schengen countries use stamps with a similar design. These stamps help border officials track how long non-EU citizens have stayed.
There are no immigration checks or passport stamps when traveling between Schengen countries.
When traveling to or from a country outside the Schengen Area, rules for stamping passports are as follows:
- Stamps are given to: Non-EU citizens (unless exempt) and family members of EU citizens who do not have a special residence card and are not traveling with their EU family member.
- Stamps are NOT given to: EU citizens, citizens of Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Switzerland, and non-EU citizens with a residence permit from a Schengen country. Also, citizens of Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City do not get stamps.
Border officials must stamp passports of non-EU citizens who are required to get one. If a stamp is missing, officials might assume the person has overstayed, unless they can prove otherwise with tickets or receipts.
- Uniform design of Schengen member states' passport stamps
-
Entry stamp for air travel, issued at Sandefjord Airport in Norway
-
Entry stamp for rail travel, issued at Nickelsdorf at Austro-Hungarian border before Hungary joined the Schengen Area
-
Entry stamp for ferry travel, issued at the port of Amsterdam IJmond in Netherlands
-
Exit stamp for air travel, issued at Prague Ruzyně Airport in Czech Republic
Stays Longer Than 90 Days
For stays longer than 90 days in the Schengen Area, non-EU citizens usually need a long-stay visa or a residence permit. A long-stay visa is for up to one year. If someone wants to stay longer, they need a residence permit.
People with a long-stay visa or residence permit can travel freely within other Schengen countries for up to three months in any six-month period.
Entry for Families of EU Citizens
Non-EU citizens who are family members of EU citizens and have a special residence card from their EU host country can visit other Schengen countries without a visa for up to three months. This applies if they are traveling with or joining their EU family member.
Police and Justice Cooperation

To help fight crime and illegal immigration after removing border controls, Schengen countries use the Schengen Information System (SIS). This is a large database used by all EU and Schengen states. It helps police track missing persons, stolen items, and people who are not allowed to enter the Schengen Area.
The Schengen Agreement also allows police officers to follow suspects across borders and work together on criminal cases.
|
See also
 In Spanish: Espacio Schengen para niños
In Spanish: Espacio Schengen para niños
 | Mary Eliza Mahoney |
 | Susie King Taylor |
 | Ida Gray |
 | Eliza Ann Grier |