White-lined broad-nosed bat facts for kids
Quick facts for kids White-lined broad-nosed bat |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Phyllostomidae |
| Genus: | Platyrrhinus |
| Species: |
P. lineatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Platyrrhinus lineatus Geoffroy, 1810
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
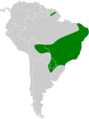
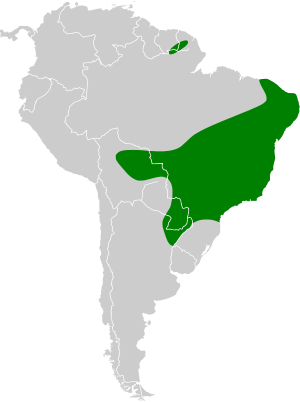
The white-lined broad-nosed bat (Platyrrhinus lineatus) is a fascinating type of bat that lives in parts of South America. You can find these bats in countries like southern and eastern Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay, northern Argentina, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, French Guiana, and Suriname. They are known for the distinct white lines on their faces and backs.
Template:TOC limit=3
Contents
Discovering the White-Lined Broad-Nosed Bat
This bat got its scientific name, Platyrrhinus lineatus, from a scientist named Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire in 1810. The name Platyrrhinus means "flat nose," which describes their unique nose shape. The word lineatus refers to the white lines they have.
Where Do These Bats Live?
White-lined broad-nosed bats prefer to live in warm, moist places. They are often found in tropical and subtropical forests. These bats can live in different types of habitats, from dense forests to more open areas. They need places with plenty of fruit to eat and safe spots to rest during the day.
What Does This Bat Look Like?
The white-lined broad-nosed bat is a medium-sized bat. It has soft, brownish fur. The most noticeable features are the two bright white stripes that run down its back. It also has white stripes on its face, above and below its eyes. These markings help it blend in with its surroundings or might help other bats recognize it. Like all bats, it has large wings made of skin stretched between its long fingers and body.
Nose Leaf and Ears
This bat has a special nose structure called a "nose leaf." This is a small, fleshy growth on its nose. Scientists believe the nose leaf helps the bat direct the sounds it makes for echolocation. Echolocation is how bats "see" in the dark by sending out sound waves and listening for the echoes. Their ears are also quite large, which helps them hear these echoes and find their way around.
Bat Behavior and Diet
White-lined broad-nosed bats are nocturnal, meaning they are active at night. During the day, they rest in safe places like hollow trees, caves, or dense foliage. They often roost in small groups, which can help them stay warm and safe from predators.
What Do White-Lined Broad-Nosed Bats Eat?
These bats are primarily frugivores, which means they love to eat fruit. They play an important role in their ecosystem by spreading seeds from the fruits they eat. This helps new plants grow in the forest. They might also eat some insects, but fruit is their main food source.
How Do They Find Food?
At night, these bats use their excellent sense of smell and echolocation to find ripe fruits. They fly through the forest, using sound to create a map of their surroundings. Once they find a fruit, they might pick it up and carry it to a safe spot to eat.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Like other mammals, white-lined broad-nosed bats give birth to live young. The female bat usually gives birth to one baby at a time. The baby bat is called a pup.
Raising Bat Pups
Bat pups are born tiny and helpless. They rely completely on their mother for milk and protection. The mother bat cares for her pup, often carrying it with her when she flies. As the pup grows, it learns to fly and hunt for food on its own. It will eventually leave its mother to live independently.
Conservation Status
The white-lined broad-nosed bat is currently listed as "Least Concern" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that its population is stable, and it is not considered to be at high risk of extinction right now. However, like many animals, their habitats can be threatened by deforestation and human activities. Protecting their forest homes is important for their future.
Images for kids
See also

- In Spanish: Falso vampiro listado para niños