Yonago facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Yonago
米子市
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Top left: Statue of Station Square, Top right: Kaike Spa and Kaike Coast, 2nd left: Yonago Castle Site, 2nd right: Yonago Takashimaya, 3rd left: Mugibandai ruins in Yodoe, 3rd right: Yonago Station
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
| Country | Japan | ||||||||||
| Region | Chūgoku (San'in) | ||||||||||
| Prefecture | Tottori | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| • Total | 132.42 km2 (51.13 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population
(December 31, 2022)
|
|||||||||||
| • Total | 146,139 | ||||||||||
| • Density | 1,103.60/km2 (2,858.32/sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) | ||||||||||
| City hall address | 1-1 Kamo-chō, Yonago-shi, Tottori-ken 683-8686 | ||||||||||
| Climate | Cfa | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
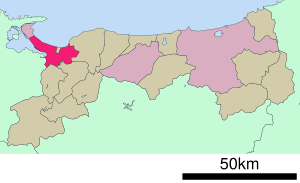
Yonago (米子市, Yonago-shi) is a city located in the western part of Tottori Prefecture, Japan. As of December 31, 2021, about 146,139 people lived here in 68,534 homes. The city covers an area of 132.42 square kilometers. Yonago is the second largest city in Tottori Prefecture, right after Tottori City. It's a very important business hub for the western part of the prefecture.
Contents
Exploring Yonago's Location
Yonago is located in the far west of Tottori Prefecture. It faces the Sea of Japan to the north and Lake Nakaumi to the northwest. The city is very close to Shimane Prefecture and sits across Lake Nakaumi from Matsue, which is Shimane's capital city.
Most of Yonago is flat land. The Hino River flows through the Yonago Plain, making the area fertile. In the southern part of the city, you'll find hills at the base of Mount Daisen. From the Yumigahama Peninsula in the northwest, you can see these mountains in the distance. There's also an irrigation canal called "Yonekawa" that brings water from the Hino River to Yonago and Sakaiminato City.
Neighboring Towns and Cities
Yonago shares its borders with several other places:
- In Tottori Prefecture:
- Sakaiminato
- Daisen
- Nanbu
- Hōki
- Hiezu
- In Shimane Prefecture:
- Yasugi
Yonago's Weather
Yonago has a humid subtropical climate. This means it has hot summers and cool winters. It rains quite a lot throughout the year, especially in July and September.
| Climate data for Yonago (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1939−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 20.0 (68.0) |
25.4 (77.7) |
27.5 (81.5) |
33.7 (92.7) |
33.8 (92.8) |
35.8 (96.4) |
38.3 (100.9) |
38.9 (102.0) |
37.1 (98.8) |
33.5 (92.3) |
27.3 (81.1) |
23.5 (74.3) |
38.9 (102.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.3 (46.9) |
9.2 (48.6) |
12.9 (55.2) |
18.4 (65.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
26.0 (78.8) |
30.3 (86.5) |
31.7 (89.1) |
27.1 (80.8) |
22.1 (71.8) |
16.8 (62.2) |
11.1 (52.0) |
19.8 (67.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.7 (40.5) |
5.1 (41.2) |
8.2 (46.8) |
13.2 (55.8) |
18.2 (64.8) |
21.8 (71.2) |
26.2 (79.2) |
27.3 (81.1) |
23.0 (73.4) |
17.5 (63.5) |
12.2 (54.0) |
7.1 (44.8) |
15.4 (59.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.3 (34.3) |
1.3 (34.3) |
3.5 (38.3) |
8.0 (46.4) |
13.3 (55.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
22.8 (73.0) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.3 (66.7) |
13.1 (55.6) |
7.9 (46.2) |
3.5 (38.3) |
11.3 (52.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −7.2 (19.0) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−3.1 (26.4) |
1.5 (34.7) |
5.9 (42.6) |
12.2 (54.0) |
13.7 (56.7) |
7.2 (45.0) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 151.7 (5.97) |
117.5 (4.63) |
128.2 (5.05) |
106.3 (4.19) |
119.1 (4.69) |
169.5 (6.67) |
227.2 (8.94) |
128.4 (5.06) |
214.3 (8.44) |
131.1 (5.16) |
118.1 (4.65) |
145.9 (5.74) |
1,757.2 (69.18) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 39 (15) |
32 (13) |
6 (2.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
19 (7.5) |
95 (37) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 17.5 | 14.5 | 13.4 | 10.2 | 9.1 | 10.5 | 11.9 | 9.6 | 11.3 | 10.0 | 12.4 | 16.5 | 146.9 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 1 cm) | 7.5 | 6.4 | 1.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.0 | 18.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 74 | 72 | 69 | 67 | 68 | 76 | 77 | 75 | 77 | 74 | 72 | 74 | 73 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 72.3 | 87.7 | 141.5 | 182.0 | 208.6 | 160.8 | 171.5 | 207.1 | 148.7 | 156.8 | 116.5 | 82.5 | 1,732.4 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
How Many People Live in Yonago?
The number of people living in Yonago has been slowly growing since the 1950s.
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1950 | 100,836 | — |
| 1960 | 108,583 | +7.7% |
| 1970 | 117,056 | +7.8% |
| 1980 | 136,053 | +16.2% |
| 1990 | 140,503 | +3.3% |
| 2000 | 147,837 | +5.2% |
| 2010 | 148,090 | +0.2% |
What Does the Name "Yonago" Mean?
The name "Yonago" comes from two Japanese characters. The first character, 米, means "rice." The second character, 子, means "child."
A Look at Yonago's Past
The area where Yonago is now was once part of an old region called Hōki Province. Ancient stories say that the tomb of the creator god Izanami is near Yonago's border. Many ancient items from the Yayoi period and Kofun period have been found in the city. These findings show that people lived here a very long time ago.
Yonago Castle and Its History
During the early Edo Period (a time in Japanese history), a powerful leader named Nakamura Kazutada became the ruler of the Yonago area. He rebuilt Yonago Castle. The modern city of Yonago grew up around this castle. After Nakamura died, the area became part of the Ikeda clan's lands. The Ikeda family kept Yonago Castle and had their trusted family members, the Arao clan, manage it until the Meiji restoration (a big change in Japan's government).
Becoming a City
The town of Yonago was officially created in October 1889. Over the years, it grew. A post office opened in 1872, a prison in 1877, and a courthouse in 1884. Train services started in 1902. Yonago officially became a city on April 1, 1927. Later, on March 31, 2005, Yonago joined with the town of Yodoe.
Yonago's Economy
Most people in Yonago work in the service industry, which means they provide services to others. Over 70% of the workers are in this sector.
Some big companies also have facilities here:
- Oji Paper has a factory in Yonago.
- Sharp Yonago makes Sharp-brand flat screen televisions.
Learning in Yonago
Yonago has many schools for students of all ages.
- There are 23 public elementary schools and 11 public junior high schools run by the city.
- There is also one private junior high school.
- For high school, there are six public high schools run by the Tottori Prefecture and one national public high school.
- There are also five private high schools.
- Tottori University has a campus in Yonago, where students can go for higher education.
- The prefecture also runs three special education schools for students with disabilities.
Getting Around Yonago
Air Travel
- Miho-Yonago Airport is located in the nearby city of Sakaiminato. You can catch flights here to and from Tokyo's Haneda Airport.
Train Travel
Yonago is connected by several train lines run by JR West.
- San'in Line: Yonago - Higashiyamakōen - Hōki-Daisen - Yodoe
- Hakubi Line: Hōki-Daisen
- Sakai Line: Yonago - Bakurōmachi - Fujimichō - Gotō - Sambommatsuguchi - Kawasakiguchi - Yumigahama - Wadahama - Ōshinozuchō
Road Travel
Major highways connect Yonago to other parts of Japan.
 Yonago Expressway
Yonago Expressway San'in Expressway
San'in Expressway National Route 9
National Route 9 National Route 180
National Route 180 National Route 181
National Route 181 National Route 183
National Route 183 National Route 431
National Route 431 National Route 482
National Route 482
Friendship Cities
Yonago has special "sister city" relationships with other cities around the world. These connections help promote cultural exchange and friendship.
Fun Places to Visit in Yonago
There are many interesting places to see in Yonago!
Important Historical Sites
- Yonago Castle - These are the ruins of an old castle, known as one of the Continued Top 100 Japanese Castles.
- Mukoeyama Kofun Cluster - A group of ancient burial mounds.
- Mukibanda Yayoi remains - An important archaeological site from the Yayoi period.
- Kamiyodo temple ruins - The remains of an old temple.
- Aoki Site - Another historical site.
- Fukuichi Site - An archaeological site.
- Tottori Domain Battery Sites - Old defense locations.
Other Cool Spots
- Odaka Castle - The ruins of a castle from the Sengoku period.
- Ōgamiyama Shrine - A beautiful traditional Japanese shrine.
- Yonago City Museum of Art - A great place to see local and national art.
- Kaike Onsen - This is a hot spring resort located along Miho Bay. It's famous for being the place where the sport of triathlon first started in Japan!
Famous People from Yonago
- Sena Irie - A Japanese boxer.
- Maika Yamamoto - A Japanese model and actress.
- Nobuko Otowa - A Japanese actress.
- Kihachi Okamoto - A Japanese film director.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Yonago (Tottori) para niños
In Spanish: Yonago (Tottori) para niños