Altostratus cloud facts for kids
Altostratus clouds are middle-level clouds made of tiny water droplets, ice crystals, or a mix of both. They form when large amounts of warm, moist air rise into the sky, causing the water vapor to turn into visible clouds. Altostratus clouds usually look like flat, gray or bluish sheets. Sometimes, they can have wavy or banded patterns. You might be able to see the sun dimly through thinner altostratus clouds, but thicker ones can block the sun completely.
These clouds often tell us that a warm front is coming. When you see altostratus clouds, it usually means continuous rain or snow will arrive in the next 12 to 24 hours. Even though they predict wetter weather, altostratus clouds themselves don't usually produce much rain or snow. However, sometimes thunderstorms can be hidden within them, bringing showers.
Because altostratus clouds can contain ice crystals, they can create cool optical effects like iridescence (rainbow colors) and coronas (colorful rings around the sun or moon).
Contents
What are Altostratus Clouds Like?
Altostratus clouds are generally gray or slightly blue. They look like a smooth, uniform blanket covering the sky. They don't have many distinct features and usually don't cause heavy rain. The name "altostratus" comes from two Latin words: "altum," meaning "high," and "stratus," meaning "flat" or "spread out."
Sometimes, altostratus clouds can produce virga, which is rain or snow that falls from the cloud but evaporates before reaching the ground. This can make the bottom of the cloud look hazy. While they don't bring heavy downpours, altostratus clouds can cause light sprinkles or small rain showers. If they get thicker and lower, they can turn into nimbostratus clouds, which bring steady rain.
Altostratus clouds don't have many different "species" because they look so similar. However, they do come in five main types, called "varieties":
- Altostratus duplicatus: This is a rare type with two or more layers of cloud stacked on top of each other.
- Altostratus opacus: This variety is thick and opaque, meaning you can't see the sun or moon through it.
- Altostratus radiatus: Another rare type, these clouds have parallel bands that stretch across the sky towards the horizon.
- Altostratus translucidus: This type is translucent, so you can see the sun or moon dimly through the cloud.
- Altostratus undulatus: This variety has a wavy look, like ripples on the underside of the cloud.
Altostratus clouds are found at middle altitudes. In polar regions, they form about 2,000 to 4,000 meters (6,500 to 13,000 feet) above sea level. In temperate regions, they can be higher, from 2,000 to 7,000 meters (6,500 to 23,000 feet). In tropical regions, they can reach even higher, from 2,000 to 8,000 meters (6,500 to 26,000 feet). They can be 1,000 to 5,000 meters (3,300 to 16,400 feet) thick and cover huge areas of the Earth.
How Altostratus Clouds Form
Altostratus clouds form when a large mass of warm, moist air rises. As this air goes higher, the water vapor in it cools down and turns into tiny water droplets and ice crystals. These tiny particles then gather around small dust particles in the air, forming the cloud.
This often happens at the front edge of a warm front. Here, high-level cirrostratus clouds get thicker and lower, eventually turning into altostratus clouds. Sometimes, nimbostratus clouds can also thin out and become altostratus. Altostratus clouds can even form from the spreading top (called an "anvil cloud") or the middle part of a thunderstorm.
How Altostratus Clouds Help with Weather Forecasting
Altostratus clouds usually appear before warm fronts or occluded fronts arrive. These fronts bring warmer air to an area. An occluded front happens when a faster-moving cold front catches up to a warm front.
As a front gets closer, cirrostratus clouds will thicken and turn into altostratus clouds. Then, these altostratus clouds will gradually get even thicker and turn into nimbostratus clouds. If it's an occluded front, you might also see cumulonimbus clouds (thunderstorm clouds). Once you see altostratus clouds, rain or snow usually starts within the next 12 to 24 hours.
Sometimes, the atmosphere can be unstable, and thunderstorms can form within an altostratus cloud. However, altostratus clouds themselves don't create big storms.
How Altostratus Clouds Affect Climate
Clouds play a big role in Earth's climate. They reflect some of the sun's energy back into space, which helps cool the Earth. But they also trap some of the heat that the Earth gives off, which warms the planet. This is part of the greenhouse effect.
Altostratus clouds, along with cirrus clouds, are known to have a slight warming effect on Earth. This means they trap more heat than they reflect sunlight, contributing a little to the planet's warmth.
Cool Things You Can See with Altostratus Clouds
Altostratus clouds can create amazing optical effects:
- Halos: If you're looking down from an airplane, you might see bright halos around the sun or moon when flying near the top of altostratus clouds. These are rings, arcs, or spots of white or colored light. They form when sunlight or moonlight reflects and bends through ice crystals in the cloud. You usually can't see these halos from the ground.
- Coronas: Light bending through altostratus clouds can also create coronas. These are small, colorful rings of light that appear directly around the sun or moon. You can see coronas from the ground.
- Iridescence: Sometimes, altostratus clouds can look iridescent, showing bright, often parallel bands of rainbow colors. This effect is also visible from the ground.
How Altostratus Clouds Relate to Other Clouds
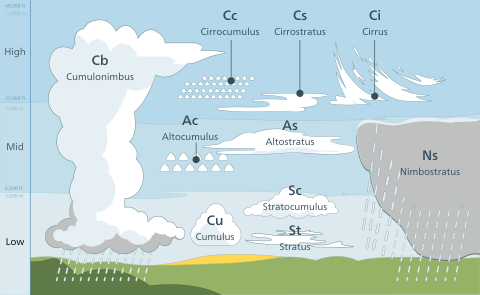
Clouds are grouped into three main levels based on their height in the sky:
- High-level clouds: These are the highest clouds, usually forming above 6,000 meters (20,000 feet). They have the prefix "cirro-" in their names. Examples include cirrus, cirrocumulus, and cirrostratus.
- Mid-level clouds: These clouds, like altostratus, usually form between 2,000 and 6,000 meters (6,500 and 20,000 feet). They have the prefix "alto-". The two main types are altostratus and altocumulus clouds. They can be made of ice crystals, supercooled water droplets, or liquid water droplets.
- Low-level clouds: These clouds usually form below 2,000 meters (6,500 feet) and don't have a special prefix. Examples include stratus and stratocumulus. They are mostly made of water droplets.
Some clouds, like cumulus, cumulonimbus, and nimbostratus, can grow vertically through different levels.
Cirrostratus Clouds
Cirrostratus clouds can look like a smooth, thin veil or a streaky sheet in the sky. They are sometimes similar to altostratus. The main way to tell them apart is that the sun or moon is always clearly visible through transparent cirrostratus clouds. Altostratus clouds, on the other hand, tend to be opaque or only translucent. Cirrostratus clouds often create halos around the sun or moon. They form when warm, moist air slowly rises to very high altitudes. As a warm front approaches, cirrostratus clouds get thicker and lower, turning into altostratus clouds. Rain usually starts 12 to 24 hours after this happens.
Altocumulus Clouds
Altocumulus clouds are small patches or heaps of white or light gray clouds. Like altostratus, they are mid-level clouds and can be made of water droplets, supercooled water droplets, and ice crystals. Even though they form at similar heights, altocumulus clouds form differently. They are created by rising air currents (convection), while altostratus usually forms from cirrostratus clouds getting lower and thicker.
Stratus Clouds
Stratus clouds are low-level clouds that often look very similar to altostratus. Stratus clouds come in two types: nebulosus, which is a mostly featureless flat gray cloud sheet, and fractus, which are broken fragments of cloud. It can be hard to tell thick altostratus clouds from stratus nebulosus just by looking. The World Meteorological Organization suggests one way to tell them apart is to see what clouds came before them. Altostratus clouds usually follow high-level cirrus clouds because they form from warm fronts. Stratus clouds often form from cooling air, especially at night, and usually don't have other cloud types before them.
Nimbostratus Clouds
Nimbostratus clouds are low-level clouds that bring rain. Unlike the light sprinkles from altostratus or stratus, nimbostratus clouds produce heavy, continuous rain or snow. These clouds are very thick and dark, so much so that they completely block out the sun. Like altostratus, nimbostratus clouds can be made of ice crystals, supercooled water droplets, or water droplets.
See Also
- List of cloud types
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |