Arecibo Telescope facts for kids

Arecibo Observatory, aerial view, 2012
|
|
| Alternative names | Arecibo Telescope |
|---|---|
| Named after | William E. Gordon, James Gregory |
| Location(s) | Esperanza, Arecibo, Puerto Rico, Caribbean |
| Coordinates | 18°20′39″N 66°45′10″W / 18.3442°N 66.7528°W |
| Organization | University of Central Florida |
| Altitude | 498 m (1,634 ft) |
| Wavelength | 3 cm (10.0 GHz)–1 m (300 MHz) |
| First light | November 1, 1963 |
| Decommissioned | Announced November 19, 2020 Collapsed December 1, 2020 |
| Diameter | 304.8 m (1,000 ft 0 in) |
| Secondary diameter | 27 m (88 ft 7 in) |
| Illuminated diameter | 221 m (725 ft 1 in) |
| Collecting area | 73,000 m2 (790,000 sq ft) |
| Focal length | 132.6 m (435 ft 0 in) |
| Website | www |
|
Arecibo Telescope
|
|
|
U.S. Historic district
Contributing property |
|
| Part of | National Astronomy and Ionosphere Center (ID07000525) |
| Designated CP | December 22, 2015 |
| |
|
The Arecibo Telescope was a giant radio telescope located in Arecibo, Puerto Rico. It was built inside a natural sinkhole and had a huge dish, about 305 meters (1,000 feet) wide. For 53 years, it was the largest single telescope of its kind in the world!
This amazing telescope helped scientists study space, Earth's atmosphere, and even search for signs of life beyond our planet. It was used for radio astronomy, atmospheric science, and radar astronomy. Scientists from all over the world sent ideas to use it for their research. NASA also used it to find objects near Earth.
The Arecibo Telescope was famous for its unique look. It appeared in movies like the James Bond film GoldenEye and Contact. It was even one of the 116 pictures sent into space on the Voyager Golden Record to show what Earth is like. The telescope was recognized as a historic place in the U.S. in 2008.
Sadly, the telescope faced challenges. It was damaged by Hurricane Maria in 2017 and by earthquakes in 2019 and 2020. Then, two important support cables broke in 2020. Because it became too dangerous to repair, the telescope was set to be taken apart. However, before that could happen, more cables failed, and the entire structure collapsed on December 1, 2020. In 2022, it was decided that the telescope would not be rebuilt.
Contents
How the Arecibo Telescope Worked
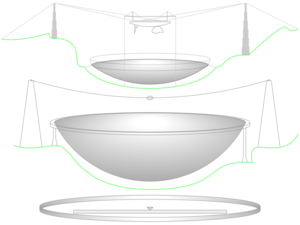
The Arecibo Telescope's main dish was shaped like a giant bowl, 305 meters (1,000 feet) across. It was built into a natural sinkhole in the ground. The dish surface was made of nearly 39,000 aluminum panels. These panels were supported by a network of steel cables.
The telescope had powerful radar transmitters. These could send out signals at different frequencies. The dish itself stayed still. Instead, special receivers and transmitters moved above the dish to focus on different parts of the sky.
Imagine a giant mirror that collects radio waves. Because the dish was spherical, its focus wasn't a single point. Instead, it was a line. So, special "line feeds" were used to collect the signals.
The Hanging Platform
The most striking part was a 900-ton (about 816,000 kg) platform. This platform hung 150 meters (490 feet) above the dish. It was held up by 18 strong cables. These cables ran from three tall concrete towers around the sinkhole.
The platform had a rotating arm, 93 meters (305 feet) long. This arm carried the antennas and reflectors. This design allowed the telescope to look at a wide area of the sky. Because Puerto Rico is near the equator, the telescope could observe planets in the northern part of their orbits.
Building the Giant Telescope
Designing the Telescope
The idea for the Arecibo Telescope started in the late 1950s. Scientists wanted to understand Earth's upper atmosphere, called the ionosphere. This was important for defense and for understanding how radio waves travel.
William E. Gordon from Cornell University led the design. He noticed the natural sinkholes in Puerto Rico. These deep, bowl-shaped holes were perfect for building a huge dish.
At first, they thought about a fixed dish that always pointed in one direction. But this would limit its use for studying planets and stars. So, they needed a way to aim the telescope.
A Clever Suspension System
The solution was to suspend the equipment above the dish. George and Helias Doundoulakis helped design this clever system. Instead of a tower in the middle, they proposed hanging a platform from cables. This platform could move and aim the receivers.
Helias Doundoulakis designed the strong cable system that was eventually used. The final design had three towers holding up the suspended platform.
Construction began in 1960. The telescope officially opened on November 1, 1963.

Telescope Upgrades Over Time
Over the years, the Arecibo Telescope received many improvements.
- In 1973, the original wire mesh surface was replaced. It got 38,000 precise aluminum panels. This allowed it to work at higher frequencies.
- In 1997, a new system called a Gregorian reflector was added. This used secondary and tertiary mirrors to focus radio waves better. It also allowed for more receivers to be used.
- More cables were added to support the heavier platform after this upgrade.
- In 2013, a new facility was added to study the ionosphere.
The Telescope's Final Years
Funding Challenges
For many years, the National Science Foundation (NSF) and NASA helped pay for the Arecibo Observatory. However, starting in the mid-2000s, the NSF began to reduce its funding. This made it harder to keep the observatory running.
Scientists and supporters worked hard to find new funding. They showed how important the telescope was for discoveries. The government of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Congress provided some extra money for maintenance and upgrades.
In 2011, the University of Central Florida (UCF) and other partners took over managing the observatory. NASA also increased its support for studying objects near Earth.
Damage and Collapse
The telescope faced several natural disasters.
- In 2017, Hurricane Maria damaged some of the aluminum panels on the dish.
- Earthquakes in 2019 and 2020 also affected the structure.
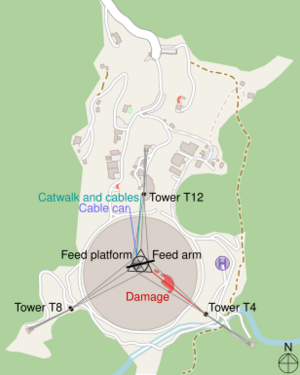
Then, in August 2020, an auxiliary support cable broke. It tore a 30-meter (100-foot) gash in the dish. Engineers began to assess the damage and plan repairs. They found that some cable connections might have been corroded over time.
Before repairs could begin, a second main support cable snapped on November 7, 2020. This caused more damage to the dish. Engineers realized that the remaining cables might also be weak. It became too risky to try and repair the structure.
On November 19, 2020, the NSF announced that the telescope would be safely taken apart. However, on December 1, 2020, before decommissioning could start, several more cables failed. The entire receiver platform and its support structure crashed into the dish. This completely destroyed the telescope. No one was hurt in the collapse.
After the Collapse
After the collapse, the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST) in China, which was inspired by Arecibo, opened its doors to international researchers.
Puerto Rico's governor signed an order for $8 million to clear the debris and plan a new observatory. The goal was to rebuild something new at the site. Scientists also managed to save all 3 petabytes of data collected by the telescope since the 1960s. This data is still used for research.
Scientists suggested a "Next Generation Arecibo Telescope." This idea involved many smaller telescopes in the sinkhole. It would have been much more powerful than the original. However, in October 2022, the NSF decided not to build a new telescope. Instead, the site is becoming a STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) educational center. Some parts of the original telescope were saved for their historical importance.
Amazing Discoveries from Arecibo

The Arecibo Telescope helped make many important scientific discoveries:
- In 1964, it showed that the planet Mercury spins much faster than previously thought.
- In 1968, it helped discover the first solid evidence of neutron stars by finding the regular pulses from the Crab Pulsar.
- In 1974, scientists Hulse and Taylor discovered the first binary pulsar. This discovery earned them a Nobel Prize!
- In 1982, the fastest-spinning pulsar at the time, PSR B1937+21, was found. It spun 642 times per second!
- Arecibo made the first radar observation of a comet in 1980.
- In 1989, it took the first direct image of an asteroid, 4769 Castalia.
- In 1990, Polish astronomer Aleksander Wolszczan discovered the first extrasolar planets (planets outside our solar system) orbiting a pulsar.
- In 1994, it mapped ice at the poles of Mercury.
- In 2008, it detected molecules that are building blocks for life in a distant galaxy.
- In 2010-2011, it detected radio bursts from a cool brown dwarf star, showing it had a strong magnetic field.
The Arecibo Message
In 1974, a special message was sent from the Arecibo Telescope. This was called the Arecibo message. It was an attempt to communicate with any intelligent life that might exist in space. The message was a pattern of 1s and 0s that formed a picture. This picture showed numbers, stick figures, chemical formulas, and a simple image of the telescope itself. It was aimed at a star cluster called Messier 13, about 25,000 light-years away.
Searching for Alien Life
The Arecibo Telescope was also a key part of the Search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). SETI projects listen for signals from other civilizations in our galaxy. Arecibo's data was used by projects like SETI@home, where many people used their home computers to help analyze the signals.
Sometimes, scientists also send messages into space, which is called METI (messaging to extraterrestrial intelligence).
Other Uses of the Telescope
- Arecibo helped study Earth's upper atmosphere for NASA.
- It even had early military uses, like detecting signals from Soviet radar stations by bouncing them off the Moon.
- Amateur radio operators sometimes used the telescope for "Moon bounce" communication. They would send radio signals to the Moon and receive them back on Earth.
A Cultural Icon
The Arecibo Telescope's unique design made it famous in popular culture.
- It was a key location in the James Bond film GoldenEye (1995).
- It also appeared in the movies Species (1995) and Contact (1997).
- The TV show The X-Files featured it in an episode.
- A video game, Battlefield 4, had a map inspired by the telescope.
- Artists Jennifer Allora and Guillermo Calzadilla, with writer Ted Chiang, created an art piece called The Great Silence about the telescope and the search for alien life.
An asteroid discovered in space was named 4337 Arecibo in honor of the observatory's contributions to science.
See also
 In Spanish: Radiotelescopio de Arecibo para niños
In Spanish: Radiotelescopio de Arecibo para niños
 | William L. Dawson |
 | W. E. B. Du Bois |
 | Harry Belafonte |