Azimuth facts for kids
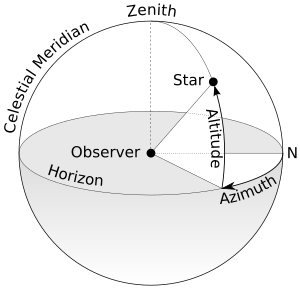
An azimuth is a way to measure direction using angles. Imagine you are standing in one spot, and you want to point to something far away, like a star or a landmark. Azimuth tells you the horizontal angle from a starting direction (usually north) to that object.
Think of it like a compass. If north is 0 degrees, then moving clockwise:
- East is 90 degrees.
- South is 180 degrees.
- West is 270 degrees.
Azimuth is usually measured in degrees (°). This idea is super useful in many areas, like finding your way around (navigation), studying stars (astronomy), building things (engineering), making maps, and even in mining.
Contents
What Does "Azimuth" Mean?
The word "azimuth" comes from an old Arabic word, al-sumūt, which means "the directions." People started using this word in Europe during the Middle Ages, especially when they were learning about astronomy and using tools like the astrolabe (an old tool for measuring the positions of stars).
The first time "azimuth" was written in English was in the 1390s by a famous writer named Geoffrey Chaucer.
Azimuth in Astronomy
In astronomy, azimuth helps us find objects in the sky, like stars or planets. It's one of two main measurements. The other is altitude, which tells you how high an object is above the horizon.
When astronomers talk about azimuth, they almost always measure it starting from true north. This system is also used when people install satellite dishes to make sure they point correctly at a satellite.
When you're finding your way on land, azimuth is a horizontal angle measured clockwise from a north line. This north line is often called a meridian. So, if you're facing north, that's 0 degrees. If you turn to your right (clockwise), the angle increases.
While true north is the most common starting point (0°), some navigation systems might use south as their starting point. The important thing is that everyone using the system knows exactly what the starting direction is.
Sometimes, people describe directions in a slightly different way, especially with a compass. They might say "South 30° East" (S30°E). This means you start facing south, then turn 30 degrees towards the east. This would be the same as 150 degrees clockwise from north (180° - 30° = 150°).
Common Azimuths from North
Here are some common directions and their azimuths when measured from north:
| Direction | Azimuth |
|---|---|
| North | 0° |
| North-northeast | 22.5° |
| Northeast | 45° |
| East-northeast | 67.5° |
| East | 90° |
| East-southeast | 112.5° |
| Southeast | 135° |
| South-southeast | 157.5° |
| South | 180° |
|---|---|
| South-southwest | 202.5° |
| Southwest | 225° |
| West-southwest | 247.5° |
| West | 270° |
| West-northwest | 292.5° |
| Northwest | 315° |
| North-northwest | 337.5° |
Azimuth in Mapping

When making maps, especially flat ones, we can calculate the azimuth between two points if we know their coordinates. This helps mapmakers and surveyors figure out directions accurately.
There are also many types of azimuthal map projections. These are special maps where the directions (azimuths) from a central point are always correct. This is very helpful for planning routes or understanding how different places relate to each other direction-wise.
Other Uses of Azimuth
- Magnetic Tape Drives: In old-fashioned magnetic tape drives (like those used for music cassettes or video tapes), "azimuth" refers to the angle between the tape and the reading/recording head. This angle needs to be just right for the sound or video to play clearly.
- Sound Localization: When scientists study how we figure out where sounds come from, "azimuth" describes the angle of a sound source compared to a straight line drawn from the front of your head.
- Shipbuilding: An azimuth thruster on a ship is a special propeller that can be rotated horizontally. This allows the ship to move in any direction without needing a rudder, making it very easy to steer and maneuver.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Acimut para niños
In Spanish: Acimut para niños
- Altitude (astronomy)
- Bearing (navigation)
- Clock position
- Course (navigation)
- Latitude
- Longitude
- Magnetic declination
- Relative bearing
- Solar azimuth angle
- Sound Localization
- Zenith