Banja Luka facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Banja Luka
Бања Лука (Serbian)
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| Grad Banja Luka Град Бања Лука City of Banja Luka |
|||
|
Panoramic view of Banja Luka
Ferhat Pasha Mosque
Cathedral of Christ the Saviour
Mariastern Abbey
Kastel Fortress
|
|||
|
|||
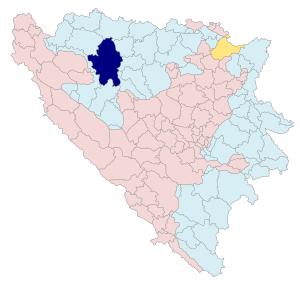
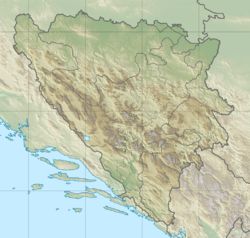
Location within Republika Srpska / Bosnia and Herzegovina
|
|||
| Country | |||
| Entity | |||
| Geographical region | Bosanska Krajina | ||
| Government | |||
| • Body | City Assembly of Banja Luka | ||
| Area | |||
| • City | 1,238.91 km2 (478.35 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 163 m (535 ft) | ||
| Population
(2013 census)
|
|||
| • City | 185,042 | ||
| • Urban | 138,963 | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | ||
| Postal code |
78000
|
||
| Area code(s) | +387 51 | ||
Banja Luka is the second largest city in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is the main city in the Bosanska Krajina region, which is known for its many forests. In 2013, the city itself had about 139,000 people. The wider area of Banja Luka had over 185,000 people.
The city is home to the University of Banja Luka and a large hospital. Many important government offices for Republika Srpska and Bosnia and Herzegovina are also here. Banja Luka is located on the Vrbas River. It is famous for its tree-lined streets, parks, and gardens. In 2018, Banja Luka was named the European City of Sport.
Contents
What's in a Name?
The name Banja Luka was first written down in a document in 1494. It means 'Ban's meadow'. A "ban" was a special noble title in medieval times. Luka means 'valley' or 'meadow'.
Some people think the name comes from banja ('bath' or 'spa') or bajna ('marvelous'). Others think it comes from the Hungarian name Lukácsbánya, which means 'Luke's Mine'. Today, the name is sometimes said and written as one word, Banjaluka.
Exploring Banja Luka's Geography
City Location and Rivers
Banja Luka covers about 96 square kilometers (37 square miles) in Bosnia and Herzegovina. It sits on both sides of the Vrbas River. The city center is about 163 meters (535 feet) above sea level.
The Vrbas River starts about 90 kilometers (56 miles) south of the city. Smaller rivers like the Suturlija, Crkvena, and Vrbanja flow into the Vrbas within the city. There are also many natural springs nearby.
Mountains Around the City
The area around Banja Luka has many forests and fields. Further from the city, especially to the south, you can find several mountains. These include Ponir (743 m), Osmača (950 m), Manjača (1,214 m), Čemernica (1,338 m), and Tisovac (1,173 m). All these mountains are part of the Dinaric Alps.
Banja Luka's Climate
Banja Luka has a climate with mild winters and warm summers. It doesn't get very cold, and frosts are not common. July is the warmest month, with an average temperature of 22.5°C (72.5°F). January is the coldest, with an average of 1.3°C (34.3°F).
The city gets about 1047.5 millimeters (41.2 inches) of rain each year. It rains about 104 days a year. Snow falls almost every winter. Strong winds usually come from the north and northeast. Sometimes, warm air from the Adriatic Sea blows in from the south.
The highest temperature ever recorded was 41.8°C (107.2°F) on August 10, 2017. The lowest was -23.5°C (-10.3°F) on January 15, 2003.
| Climate data for Banja Luka (1991-2020, extremes 1973-2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.3 (72.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
29.0 (84.2) |
31.8 (89.2) |
35.2 (95.4) |
37.9 (100.2) |
41.6 (106.9) |
41.8 (107.2) |
40.2 (104.4) |
30.9 (87.6) |
29.1 (84.4) |
23.2 (73.8) |
41.8 (107.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 6.1 (43.0) |
8.9 (48.0) |
14.0 (57.2) |
19.0 (66.2) |
23.4 (74.1) |
27.3 (81.1) |
29.5 (85.1) |
29.8 (85.6) |
24.0 (75.2) |
18.6 (65.5) |
12.4 (54.3) |
6.7 (44.1) |
18.3 (65.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.3 (34.3) |
3.0 (37.4) |
7.4 (45.3) |
12.1 (53.8) |
16.7 (62.1) |
20.8 (69.4) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.1 (71.8) |
16.7 (62.1) |
11.9 (53.4) |
7.1 (44.8) |
2.3 (36.1) |
12.0 (53.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −2.5 (27.5) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
1.8 (35.2) |
5.9 (42.6) |
10.3 (50.5) |
14.2 (57.6) |
15.8 (60.4) |
15.6 (60.1) |
11.3 (52.3) |
7.0 (44.6) |
3.1 (37.6) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
6.6 (43.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −23.5 (−10.3) |
−21.5 (−6.7) |
−18.2 (−0.8) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
3.0 (37.4) |
6.2 (43.2) |
5.6 (42.1) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−18.8 (−1.8) |
−23.5 (−10.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 73.3 (2.89) |
68.4 (2.69) |
80.0 (3.15) |
88.9 (3.50) |
104.0 (4.09) |
101.8 (4.01) |
81.0 (3.19) |
75.4 (2.97) |
107.9 (4.25) |
84.8 (3.34) |
90.3 (3.56) |
91.7 (3.61) |
1,047.5 (41.25) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 9 | 9 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 10.5 | 9.2 | 8.2 | 6.5 | 9 | 8.3 | 9.4 | 10.2 | 109.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 82 | 80 | 73 | 69 | 71 | 71 | 70 | 73 | 78 | 82 | 84 | 83 | 76 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 67.2 | 90 | 140.9 | 175 | 222.7 | 253.7 | 285.9 | 264.6 | 181.6 | 136.3 | 75.1 | 55.3 | 1,948.3 |
| Source 1: NOAA NCEI | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Deutscher Wetterdienst (extremes 1973–2016, humidity, 1973–1991) | |||||||||||||
Banja Luka's Past: A Quick Look

From Roman Times to the Middle Ages
People have lived in the Banja Luka area for a very long time. The Romans were here in the first few centuries AD. You can still see parts of their old fort, "Kastel," in the city center. This fort was called Castra by the Romans.
Later, in the 6th century, Slavs settled in the Balkans. During the Middle Ages, several fortresses were built near Banja Luka. One document from 1494 mentions a leader named Juraj Mikulasić as the castellan (commander) of Banja Luka.
Under Ottoman Rule

Banja Luka became part of the Ottoman Empire in 1527. It grew into an important center. A leader named Ferhad Pasha Sokolović built over 200 buildings here, including shops, baths, and mosques. This helped Banja Luka become a major trading and political city in Bosnia.
In 1688, the Austrian army burned the city, but it quickly recovered. Later, military buildings were added, making Banja Luka a key military spot. In the 1800s, Orthodox churches and monasteries were built. Also, Sephardic Jews and Trappists (a type of monk) came to the city. They helped start factories for things like mills, breweries, and textiles. The Trappist monastery even gave its name to a neighborhood and is known for its special cheese and beer.
Austro-Hungarian and Yugoslav Eras
After the Ottomans, the Austro-Hungarian Empire took over in the late 1800s. They brought many modern changes to Banja Luka. Railroads, schools, factories, and new buildings made it a modern city.
After World War I, Banja Luka became the capital of a region called Vrbas Banovina within the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The city grew quickly thanks to its first leader, Svetislav Milosavljević. Many important buildings were constructed, like the Banski dvor (a palace) and the Serbian Orthodox Church of the Holy Trinity. Schools were improved, and a city bridge and park were built.
World War II and Its Impact
During World War II, Banja Luka was occupied. Many people faced difficult times, and important buildings were damaged or destroyed. The city's Cathedral of Christ the Saviour and the Orthodox Church of the Holy Trinity were completely ruined. A bishop named Platon Jovanović was arrested and killed. The city was finally freed in 1945.
The 1969 Earthquake
On October 26 and 27, 1969, two strong earthquakes hit Banja Luka. Many buildings were damaged, and some people lost their lives. A large building called Titanik in the city center was completely destroyed. People from all over Yugoslavia helped to repair and rebuild Banja Luka. After the earthquake, many Serbs moved to the city from nearby villages and other areas.
Who Lives in Banja Luka?
According to the 2013 census, Banja Luka city had 138,963 people. Most of them were Serbs.
City Population Over Time
| Population of Banja Luka city | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1879 | 1885 | 1895 | 1910 | 1921 | 1931 | 1948 | 1953 | 1961 | 1971 | 1981 | 1991 | 2013 | |
| Banja Luka | 9,560 | 11,357 | 13,566 | 14,800 | 18,001 | 22,165 | 31,223 | 38,135 | 50,650 | 90,831 | 123,937 | 143,079 | 138,963 |
City Ethnic Groups
| Ethnic composition – Banja Luka city | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 1991 | |||||||
| Total | 138,963 (100%) | 143,079 (100%) | ||||||
| Serbs | 121,185 (87.2%) | 70,155 (49.0%) | ||||||
| Bosniaks | 7,573 (5.5%) | 27,689 (19.4%) | ||||||
| Croats | 4,205 (3.0%) | 15,700 (11.0%) | ||||||
| Yugoslavs | 615 (0.4%) | 22,645 (15.8%) | ||||||
| Others | 4,830 (3.9%) | 7,400 (4.8%) | ||||||
Banja Luka's Economy
Even though the city was not directly in the war in the early 1990s, its economy was affected. Technology companies faced challenges, and the economy slowed down. However, in recent years, financial services have become very important.
In 2002, the Banja Luka Stock Exchange started trading. More companies are now listed, and more people are investing. Big companies like Telekom Srpske and Banjalučka Pivara (a brewery) are traded here. Investors come from many countries, including Slovenia, Croatia, Serbia, and even Japan and China.
Banja Luka is now a major financial center in Bosnia. Many financial offices, like the Securities Commission and the Banking Agency, are located here.
Jobs in Banja Luka
The table below shows the main types of jobs people have in Banja Luka (as of 2018):
| Activity | Total | % |
|---|---|---|
| Wholesale and retail trade, repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles | 12,579 | 18% |
| Public administration and defense; compulsory social security | 9,162 | 13% |
| Manufacturing | 8,972 | 13% |
| Human health and social work activities | 5,948 | 9% |
| Education | 5,301 | 8% |
| Transportation and storage | 2,747 | 4% |
| Professional, scientific and technical activities | 3,900 | 6% |
| Information and communication | 3,567 | 5% |
| Financial and insurance activities | 3,212 | 5% |
| Construction | 3,241 | 5% |
| Accommodation and food services | 3,564 | 5% |
| Arts, entertainment and recreation | 1,760 | 3% |
| Other service activities | 1,968 | 3% |
| Administrative and support service activities | 1,368 | 2% |
| Water supply; sewerage, waste management and remediation activities | 788 | 1% |
| Electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply | 817 | 1% |
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | 586 | 1% |
| Real estate activities | 318 | 0% |
| Mining and quarrying | 25 | 0% |
| Total | 69,283 | 100% |
Culture in Banja Luka
The Museum of Republika Srpska started as an Ethnographic Museum in 1930. Now, it has collections of old artifacts, history, art, and nature. The Museum of Modern Art of Republika Srpska shows art from both local and international artists.
Banja Luka has a National Theatre and a National Library, both built in the early 1900s. There are also many other theaters. The main office for the Archives of Republika Srpska is in a building called Carska kuća (Imperial House), built around 1880. It has been used by the public longer than any other building in the city.
One of the most famous cultural places is the "Banski Dvor" (Halls of the Ban). It was built in the 1930s as a home for the regional governors.
Many cultural and artistic groups exist in the city. The oldest one is CAA "Pelagić," started in 1927. It is one of the oldest groups of its kind in Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Sports in Banja Luka
Banja Luka has a large football stadium and several indoor sports halls. The local teams for handball, basketball, and football are all named Borac, which means fighter. There are sixteen football clubs in the city. The most famous is FK Borac Banja Luka, which has won many trophies. They have even played in big European competitions like the UEFA Champions League and UEFA Europa League.
The city has a long history with handball. The team RK Borac Banja Luka won the European Championship in 1976.
Banja Luka also hosts a professional tennis tournament called the Banja Luka Challenger. It is part of the ATP tour. In 2023, the city hosted the 2023 Srpska Open tournament.
Since 2015, the city has hosted the Banjaluka Half-marathon. In 2005 and 2019, the European Championships in Rafting were held on the Vrbas River. Banja Luka was named the European City of Sport in 2018.
Getting Around Banja Luka
Public Transportation
Banja Luka mainly uses buses for public transport. There are 23 bus lines that connect the city center to other parts of the city and its suburbs. Taxis are also easy to find.
An expressway (E-661) goes north from Banja Luka to Croatia. You can also find many bus services to other towns in Bosnia and Herzegovina, and to countries like Austria, Germany, Italy, and Serbia.
Banja Luka is a small hub for the railway services in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Trains go to most northern Bosnian towns. There are also modern 'Talgo' trains that go to Sarajevo every day.
The Banja Luka International Airport is about 23 kilometers (14 miles) north of the city. Airlines like Air Serbia and Ryanair fly from here to cities like Belgrade, Berlin, and Vienna. There is also a small airstrip called Banja Luka Zalužani Airfield.
Bus Lines in the City
Banja Luka mostly uses buses for public transport. Here are some of the bus lines:
- 1 - Mađir - Ortopedija - Nova bolnica
- 3 - Centar (Vodovod) - Vrbanja - Zeleni vir
- 7 - Lauš - Paprikovac - Centar - Obilićevo (TO Bema)
- 9 - Česma - Centar - Desna novoselija
- 13A - Nova bolnica - Centar - Zalužani
- 14 - Starčevica - Centar - Starčevica
- 17 - Obilićevo - Nova bolnica
A single bus ticket costs 2.3 convertible marks. A day ticket, which lets you ride as much as you want, costs 7.1 marks. People over 65 and pensioners can ride for free.
Banja Luka Around the World
Sister Cities
Banja Luka has special connections with other cities around the world. These are called "sister cities":
 Belgrade, Serbia
Belgrade, Serbia Patras, Greece
Patras, Greece Moscow, Russia
Moscow, Russia Kaiserslautern, Germany
Kaiserslautern, Germany Kranj, Slovenia
Kranj, Slovenia Campobasso, Italy
Campobasso, Italy Bari, Italy
Bari, Italy Bitonto, Italy
Bitonto, Italy Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut, Israel
Modi'in-Maccabim-Re'ut, Israel Graz, Austria
Graz, Austria Västerås, Sweden
Västerås, Sweden Focșani, Romania
Focșani, Romania
Partner Cities
Banja Luka also has a "partner city":
 Novi Sad, Serbia
Novi Sad, Serbia
Famous People from Banja Luka
Many well-known people come from Banja Luka, including:
- Srđan Babić, a Serbian footballer who won the World U-20 championship.
- Marijan Beneš, a famous Serbian boxer.
- Saša Čađo, a Serbian basketball player who won an Olympic bronze medal.
- Anton Josipović, a Serbian boxer and Olympic champion.
- Petar Kočić, a famous Serbian writer.
- Ivan Ljubičić, a Croatian tennis player who was once ranked World No. 3.
- Mustafa Nadarević, a well-known actor.
- Marija Šestić, a Serbian singer.
- Neven Subotić, a Serbian footballer.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bania Luka para niños
In Spanish: Bania Luka para niños
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |