Ryanair facts for kids
A Boeing 737 MAX 8 of Ryanair
|
|
| Founded | 1984 |
|---|---|
| Operating bases |
List of bases
Agadir
Alicante Athens Barcelona Bari Beauvais Belfast–International Bergamo Berlin Billund Birmingham Bologna Bournemouth Bratislava Brindisi Bristol Bucharest–Otopeni Budapest Cagliari Catania Chania Charleroi Cologne/Bonn Copenhagen Corfu Cork Dublin (headquarters) Dubrovnik East Midlands Edinburgh Faro Fes Gdańsk Girona Glasgow–Prestwick Gothenburg Hahn Ibiza Karlsruhe/Baden-Baden Katowice Kaunas Kraków Lamezia Terme Leeds/Bradford Lisbon Liverpool London–Luton London–Stansted (largest base) Madrid Málaga |
| Subsidiaries |
|
| Fleet size | 624 |
| Destinations | 235 |
| Headquarters | Swords, County Dublin, Ireland |
| Key people |
|
| Revenue | |
| Operating income | |
| Net income | |
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
| Employees | 27,076 (2024) |
| Founded | 28 November 1984 |
|---|---|
| Commenced operations | 8 July 1985 |
| Parent company | Ryanair Holdings PLC |
| Headquarters | Swords, County Dublin, Ireland |
| Key people | Eddie Wilson (Ryanair DAC CEO) |
Ryanair is a large Irish airline group. It is known for offering very low-cost flights. Its main office is in Swords, County Dublin, Ireland. The group includes several airlines like Ryanair DAC, Malta Air, Buzz, Lauda Europe, and Ryanair UK. Ryanair DAC, the oldest airline in the group, started in 1984.
Ryanair grew very quickly after Europe made air travel rules simpler in 1997. Its business model focuses on keeping costs low. The group flies over 600 planes to more than 40 countries in Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. Its main bases are at Dublin, London Stansted, and Milan Bergamo. Ryanair is Ireland's biggest airline. In 2016, it became the world's largest airline for international passengers. Most of its planes are Boeing 737s.
The company has sometimes faced criticism for things like extra charges, customer service, and how it handles publicity.
Contents
How Ryanair Started and Grew
Since it began in 1984, Ryanair has grown from a small airline flying from Waterford to London Gatwick into Europe's largest airline. Over 19,000 people have worked for the company.
In 1997, the airline became a public company, meaning people could buy shares in it. The money raised helped Ryanair expand across Europe. Its income grew from €640 million in 2003 to €4.66 billion in 2010. Profits also increased a lot during this time.
Early Flights and New Ideas
Ryanair was founded in 1984 by Christopher Ryan, Liam Lonergan, and Tony Ryan. It was first called "Danren Enterprises" but soon changed to "Ryanair." Flights began in 1985 using a small 15-seat plane called an Embraer Bandeirante. It flew between Waterford and Gatwick Airport.
In 1986, Ryanair added a route from Dublin to Luton. This meant it was competing with bigger airlines like Aer Lingus and British Airways. The Irish government did not want this new route to protect Aer Lingus. However, the British government approved it. With two routes, Ryanair carried 82,000 passengers in one year.
In 1988, Michael O'Leary joined the company as its chief financial officer. In 1990, the company changed its business plan to focus on low fares, similar to Southwest Airlines. This new plan involved using only Boeing 737 planes, growing quickly, cutting costs, and teaching customers to prefer lower prices over extra services. The goal was to turn planes around in just 30 minutes to make more flights each day. Michael O'Leary believed that lower fares would attract new customers to flying, rather than just taking passengers from other airlines.
Growth and Changes (1992–2009)



In 1992, new rules in Europe allowed airlines from one EU country to fly between other EU countries. This was a big chance for Ryanair. After becoming a public company, Ryanair started flights to cities like Stockholm, Sandefjord (near Oslo), Beauvais (near Paris), and Charleroi (near Brussels). In 1998, with new money, the airline ordered 45 new Boeing 737-800 planes.
Michael O'Leary became the chief executive officer in 1994. In 2000, Ryanair launched its website, which quickly became the main way people booked flights. This helped cut costs by selling tickets directly to passengers.
In 2001, Ryanair opened a new base at Charleroi Airport. That same year, it ordered 155 new 737-800 planes from Boeing. In 2003, Ryanair bought another airline called Buzz from KLM.
The expansion of the European Union in 2004 allowed Ryanair to open even more new routes. This rapid growth made Ryanair one of the biggest airlines in Europe. By August 2005, Ryanair said it carried 20% more passengers within Europe than British Airways.
In 2006, Ryanair tried to buy another Irish airline, Aer Lingus, but Aer Lingus rejected the offer. Ryanair tried again in 2008, but this offer was also rejected.
In August 2007, Ryanair started charging passengers to check in at the airport. This was a change from its earlier policy. In October 2008, Ryanair closed its base in Valencia, Spain, for the first time.
By October 2009, Ryanair had stopped using check-in desks at airports. Passengers had to check in online and print their boarding passes.
Recent Developments (2010s and 2020s)



In April 2010, after flights were disrupted by a volcanic ash cloud from Iceland, Ryanair agreed to follow EU rules to pay back stranded passengers. In June 2010, Ryanair asked the Irish government to remove its tourist tax, saying it was hurting tourism.
In March 2011, Ryanair opened a new maintenance hangar at Glasgow Prestwick International Airport. This became its largest plane maintenance base.
In June 2012, Ryanair's CEO, Michael O'Leary, again tried to buy Aer Lingus, but this attempt was also blocked by the European Commission.
In October 2013, Ryanair announced improvements to its customer service. These included lower fees for reprinting boarding passes, free changes for small errors on bookings within 24 hours, and a free second small carry-on bag. Ryanair said these changes were based on customer feedback.
In January 2014, Ryanair moved into a new, larger head office in Dublin. In September 2014, Ryanair agreed to buy up to 200 Boeing 737 MAX 8 planes.
In November 2016, Ryanair launched "Ryanair Holidays," a new service offering flight, hotel, and transfer packages.
In April 2017, Ryanair started selling tickets for connecting flights. This meant if a connection was missed, the customer would be rebooked at no extra cost.
In 2017, Ryanair faced criticism for cancelling many flights due to pilot holiday schedules. The airline admitted it had "messed up" the holiday plans.
New Airlines in the Group
For many years, Ryanair operated as just one airline. However, starting in 2018, it began to add other airlines and operate under different licenses in various countries.

In 2017, Ryanair announced a new Polish airline called Ryanair Sun, which later became Buzz in 2019. This airline started by flying charter flights and later took over many of Ryanair's flights based in Poland.
In 2018, Ryanair also bought a share in an Austrian airline called Laudamotion, which was later renamed "Lauda." Ryanair fully bought this airline in December 2018.
Ryanair UK was created in December 2017 because of Brexit. Its first plane was moved from Ryanair DAC in 2018. By April 2023, Ryanair UK had 13 planes.
In early 2019, as the company changed its structure, each airline (Ryanair, Lauda, Buzz, and Ryanair UK) got its own CEO. Edward Wilson became the CEO of Ryanair, and Michael O'Leary became the Group CEO.
In June 2019, Ryanair announced a new airline with the Government of Malta called Malta Air. This airline would take over Ryanair's flights from Malta.
The 2020s and Beyond
The COVID-19 pandemic greatly affected Ryanair. In May 2020, the airline announced it would cut 3,000 jobs, mostly pilots and cabin crew. It also suspended most of its flights until June 2020. In July 2020, Ryanair reported a large financial loss. By the end of 2020, the airline saw an 83% drop in passengers compared to 2019.
In December 2020, Ryanair ordered 75 more Boeing 737 MAX 8 planes, bringing its total order to 210. These planes were to be delivered from early 2021 to December 2024.
In May 2023, Ryanair confirmed a large order with Boeing to buy 300 Boeing 737 MAX 10 planes. These planes are expected to be delivered between 2027 and 2033.
In November 2023, Ryanair announced it would start paying regular dividends to its shareholders for the first time. In December 2023, Ryanair briefly became the most valuable airline in the world outside the US.
Ryanair announced a big investment in Morocco for its Summer 2024 schedule. This included over 1,100 weekly flights on 175 routes, with 35 new ones. Ryanair also introduced very low fares on 11 domestic routes in Africa for the first time. This plan aimed to improve travel within Morocco and bring in over 5 million passengers. It also supported over 500 direct jobs.
In January 2025, Ryanair introduced five new routes to Sarajevo. These flights started in March and April 2025, connecting Sarajevo to cities like Paris, Karlsruhe, Stockholm, Weeze, and Girona. In June 2025, Ryanair also introduced four more new routes to Wroclaw, Cagliari, Valencia, and Kaunas.
How Ryanair Operates
Business Figures
Here are some key facts about the Ryanair Group's business over the years (ending March 31 each year):
| Income (€m) | Profit after tax (€m) | Number of employees | Number of passengers (m) |
Planes filled (%) |
Airports served | Countries served | Number of aircraft | Sources | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2,988 | 305 | 7,032 | 67 | 82 | 153 | 27 | 232 | |
| 2011 | 3,629 | 375 | 8,063 | 72 | 83 | 158 | 27 | 272 | |
| 2012 | 4,390 | 560 | 8,438 | 76 | 82 | 159 | 28 | 294 | |
| 2013 | 4,884 | 569 | 9,059 | 79 | 82 | 167 | 28 | 305 | |
| 2014 | 5,037 | 523 | 9,501 | 82 | 83 | 186 | 30 | 297 | |
| 2015 | 5,654 | 867 | 9,586 | 91 | 88 | 190 | 30 | 308 | |
| 2016 | 6,536 | 1,559 | 10,926 | 106 | 93 | 200 | 33 | 341 | |
| 2017 | 6,648 | 1,316 | 12,438 | 120 | 94 | 207 | 34 | 383 | |
| 2018 | 7,151 | 1,450 | 13,803 | 130 | 95 | 216 | 37 | 431 | |
| 2019 | 7,697 | 885 | 15,938 | 142 | 96 | 219 | 37 | 471 | |
| 2020 | 8,495 | 649 | 17,268 | 148 | 95 | 242 | 40 | 466 | |
| 2021 | 1,636 | −1,015 | 15,016 | 28 | 71 | 225 | 37 | 451 | |
| 2022 | 4,801 | −241 | 19,116 | 97 | 82 | 223 | 36 | 500 | |
| 2023 | 10,780 | 1,314 | 22,261 | 169 | 93 | 222 | 36 | 537 | |
| 2024 | 13,444 | 1,917 | 27,076 | 184 | 94 | 235 | 37 | 584 | |
| 2025 | 13,949 | 1,612 | 25,952 | 200 | 94 | 228 | 37 | 613 |
In 2023, the Ryanair group had about 6,600 pilots and 13,400 cabin crew. It also had 2,200 employees in other areas like IT and maintenance.
Main Office Location
Ryanair's main office has been in the Airside Business Park in Swords, County Dublin, Ireland, since 2014. Before that, from 2004, its office was located near Dublin Airport.
Customer Experience and Services
Extra Charges and Services
About 20% of Ryanair's income comes from extra charges, not just ticket prices. These are called "ancillary revenue." In 2009, these extra charges brought in €598 million.
Ryanair is known for charging for optional extras. As part of its low-cost model, it charges fees for things like checking in at the airport instead of online, or for checked-in luggage. It also sells food and drinks on board.
In 2009, Ryanair stopped airport check-in. Passengers had to check in online and print their boarding pass. If passengers arrived at the airport without a printed boarding pass, they had to pay a fee to get one re-issued.
Why Surcharges Exist
In 2011, a passenger sued Ryanair over a €40 charge for not printing a boarding pass. A court in Barcelona first ruled that the charge was unfair. However, an appeals court in Spain later said the charge was allowed under international law.
Simple Service Policy
New Ryanair planes have seats that do not recline and no seat-back pockets. Safety cards are stuck on the back of the seats, and life jackets are stored overhead. This helps the airline save money on plane costs and allows for faster cleaning between flights.
Ryanair has also thought about other ways to cut costs, like removing two toilets to add more seats or allowing passengers to stand. While the CEO, Michael O'Leary, joked about charging for toilets, he later said it was not possible.
Customer Service Feedback
Ryanair has received criticism for its customer service. Some people have said the airline treats passengers poorly. In January 2019, a survey found Ryanair was the least-liked short-haul airline in the UK for the sixth year in a row. Ryanair responded by saying its passenger numbers had grown a lot, which showed its popularity.
In 2002, a court ordered Ryanair to pay damages to a woman who was promised free travel as the airline's one millionth passenger but then had the prize taken away.
The airline has also faced criticism for how it treats passengers with disabilities. In 2002, it refused to provide wheelchairs at London Stansted Airport, saying it was the airport's job. A court later ruled that both the airline and airport were responsible. Ryanair then added a small fee to all its flight prices to cover these costs.
Ryanair has improved its customer service over time. It now offers a web form and live chat for customers to contact them.
Becoming More Family-Friendly
In June 2014, Ryanair announced a plan to become a more family-friendly airline. Michael O'Leary said the airline needed to "stop unnecessarily upsetting people." Ryanair wanted to attract more families, as they made up a large part of its customers. As part of this, the company launched a LiveChat service on its website. These changes quickly helped the company financially.
Afrikaans Language Test
In June 2022, Ryanair faced strong criticism for making South African passengers take a general knowledge test in the Afrikaans language. This was done to check if their passports were real before they could board flights to the UK. South Africa has 11 official languages, and Afrikaans is not understood by most people. Many also see it as a symbol of the past Apartheid era. Michael O'Leary later announced that the test was stopped due to the public outcry.
Publicity and Advertising
Eye-Catching Advertising

Ryanair's advertisements and Michael O'Leary's actions, like trying to create controversy for free publicity, have led to many complaints.
For example, in 2009, Michael O'Leary joked in a TV interview that Ryanair was thinking about charging passengers £1 to use the toilet on flights. This story made headlines for days and drew attention to Ryanair's plan to remove airport check-in desks. O'Leary later admitted it was a publicity stunt.
Ryanair often uses its ads to compare itself directly with other airlines. One ad used a picture of a famous Belgian statue, Manneken Pis, with the words: "Upset with Sabena's high fares? Low fares have arrived in Belgium." Sabena sued, and the court ruled the ads were misleading.
Another ad campaign called "Expensive BAstards!" compared Ryanair with British Airways. British Airways also took legal action, but the court sided with Ryanair.
In 2007, Ryanair used an ad for its new Belfast route that showed politicians Martin McGuinness and Gerry Adams with a speech bubble saying "Ryanair fares are so low even the British Army flew home." This caused some anger, but the Advertising Standards Authority said it would not cause widespread offense.
An advertisement showing a model dressed as a schoolgirl with the words "Hottest back to school fares" was banned in the UK. The Advertising Standards Authority said it linked teenage girls with inappropriate behavior. Ryanair disagreed but was told to remove the ad.
In late 2020, the airline was criticized for its "jab and go" advert, which was seen as insensitive during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Misleading Advertising Claims
In 2018, Ryanair was among the top 10 companies with the highest CO2 emissions in the EU. Its emissions had risen by 49% in five years. Environmental groups criticized the airline for this. In 2020, Ryanair was criticized for misleading ads claiming it was "Europe's… Lowest Emissions Airline." These claims used old data from 2011.
Ryanair has also been criticized for naming distant airports after major cities. For example, "Paris Beauvais" is 85 km from Paris, and "Frankfurt Hahn" is 102 km from Frankfurt. Critics say this is misleading.
In 2008, the UK Office of Fair Trading investigated Ryanair after many complaints about its ads. It was found to have broken advertising rules several times. Ryanair said the Advertising Standards Authority was not fair.
In July 2009, Ryanair agreed to make its website and ads clearer after talks with the Office of Fair Trading. Its website now states that "fares don't include optional fees/charges" and includes a table of fees.
In February 2020, the Advertising Standards Authority told Ryanair to stop claiming it was the lowest emissions airline in Europe. They said Ryanair did not have enough recent evidence to support this claim.
Safety Record
On March 21, 2008, Ryanair Flight 1216 skidded off the runway while landing in Limoges during bad weather. Passengers were evacuated using emergency slides.
On November 10, 2008, Ryanair Flight 4102 made an emergency landing in Rome–Ciampino Airport after birds hit both engines. The plane was damaged beyond repair.
On May 23, 2021, Ryanair Flight 4978 was forced to land in Minsk National Airport in Belarus due to a false bomb threat. A Belarusian journalist and his girlfriend were removed from the plane and arrested. This incident led to an investigation by international aviation authorities.
On October 3, 2024, a Ryanair plane caught fire while getting ready for take-off at Brindisi Airport. Passengers were evacuated, and the airport was closed for three hours. Italian lawmakers asked for an investigation into Ryanair's safety practices.
On June 4, 2025, Ryanair Flight 8 from Berlin to Milan experienced severe turbulence over Germany. Eight passengers and one crew member were injured, and the flight was diverted to Memmingen Airport.
Competitors
Ryanair has many low-cost competitors. Aer Lingus, which used to be a full-service airline, also moved to a low-fares strategy in 2002. This led to more competition with Ryanair on Irish routes.
Ryanair competes strongly with airlines that try to offer similar low fares. For example, when MyTravelLite started flying from Birmingham to Dublin in 2003, Ryanair started competing flights on some of MyTravelLite's routes until it stopped flying them.
In September 2004, Ryanair's biggest competitor, EasyJet, started flying to Ireland for the first time. EasyJet later stopped some of these routes.
In 2012, Ryanair also responded when another low-cost airline, Wizz Air, moved its flights from Warsaw Chopin Airport to the new low-cost Warsaw Modlin Airport. Ryanair then started many new routes from Modlin Airport, often the same ones offered by Wizz Air.
Where Ryanair Flies
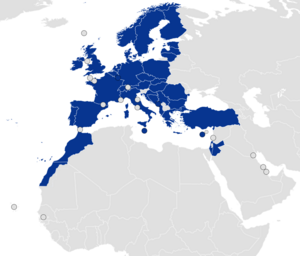
Ryanair's largest base is at London-Stansted. Its home base is at Dublin Airport. Ryanair has bases all over Europe, parts of the Middle East, and North Africa.
Ryanair usually prefers to fly to smaller or secondary airports. These airports are often outside major cities. This helps the company save money on landing fees and allows planes to turn around quickly. For example, Ryanair calls Bratislava Airport in Slovakia "Bratislava Vienna," even though Vienna is 80 km away in another country. However, some secondary airports are actually closer to the city than the main airport, like Rome Ciampino Airport.
Ryanair also flies to several major airports, including Amsterdam Schiphol, Stockholm Arlanda, Athens, Barcelona El Prat, and Berlin Brandenburg. More recently, Ryanair has been growing at primary airports to attract more business travelers. In 2014, it opened bases in Athens, Lisbon, and the main airports of Brussels and Rome.
Ryanair uses a "point-to-point" model. This means planes fly directly between two airports, rather than using a central "hub" where passengers change planes. In April 2017, Ryanair added connecting flights, starting with a new transfer hub at Rome Fiumicino Airport.
Ryanair's biggest country market is Italy, with fourteen bases. In February 2018, Ryanair cut many flights from Glasgow Airport and closed its base there because the Scottish Government did not reduce airport taxes. However, in April 2019, the airline brought back four of its routes from Glasgow. In 2022, Ryanair announced it would close its base at Frankfurt Airport due to disagreements over fees.
| Airport | IATA | Destinations |
|---|---|---|
| STN | 165 | |
| DUB | 135 | |
| CRL | 118 | |
| BGY | 112 | |
| AGP | 105 | |
| ALC | 101 | |
| MAN | 99 | |
| VIE | 85 | |
| PMI | 85 | |
| KRK | 81 | |
| OPO | 76 | |
| BVA | 76 | |
| BCN | 71 | |
| EDI | 68 | |
| MLA | 67 | |
| BLQ | 66 | |
| MRS | 63 | |
| MAD | 63 | |
| PSA | 59 | |
| BER | 57 | |
| WMI | 53 | |
| WRO | 45 | |
| PMO | 41 | |
| NRN | 41 | |
| GDN | 41 | |
| LIS | 40 | |
| CAG | 39 |
| City | destinations | retention |
|---|---|---|
| 185 | 73% | |
| 132 | 69% | |
| 124 | 65% | |
| 116 | 70% | |
| 112 | 35% | |
| 103 | 44% | |
| 97 | 45% | |
| 90 | 61% | |
| 86 | 57% | |
| 86 | 53% |
How Destinations are Chosen
When Ryanair talks with airports, it asks for very low fees for landing and handling planes. It also asks for money to help with marketing. If an airport does not agree to new deals, Ryanair might threaten to move its flights elsewhere.
Ryanair's growing popularity means it has more power when negotiating with airports and plane makers. This allows the airline to try new routes between low-cost airports, expecting that its presence alone will create demand for flights.
To further lower airport costs and speed up how quickly planes are ready for the next flight, Ryanair often has passengers board and leave the plane from both the front and back. This uses stairs instead of more expensive jet bridges.
Sometimes, Ryanair chooses to use large airports where it is not the main airline and pays the regular fees. Examples include Barcelona, Oslo, Copenhagen, and Manchester.
Ryanair's Fleet
Current Planes in the Group
As of March 2025, the Ryanair Group uses the following planes:
| Aircraft | In service | Orders | Passengers | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airbus A320-200 | 26 | — | 180 | Leased until 2028. Operated by Lauda Europe. |
| Boeing 737-700 | 1 | — | 148 | Operated by Buzz. |
| Boeing 737-800 | 410 | — | 189 | Largest operator. |
| Boeing 737 MAX 200 | 181 | 29 | 197 | Largest operator. Deliveries until 2025. |
| Boeing 737 MAX 10 | — | 300 | 228 | Order with 150 options. Deliveries from 2027 to 2034. |
| Bombardier Challenger 3500 | 2 | 2 | Used to quickly move engineers, parts and crew around the network when an aircraft needs repairs. | |
| Learjet 45 | 4 | Used to quickly move engineers, parts and crew around the network when an aircraft needs repairs. | ||
| Total | 624 | 331 | ||
Past Planes Used
Ryanair has used these types of planes in the past:
| Aircraft | Number | Introduced | Retired | Notes | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airbus A320-200 | 2 | 2015 | 2015 | One plane was moved to SmartLynx Airlines after a short lease with Ryanair. | |
| ATR 42-300 | 4 | 1989 | 1991 | One operated by Inter-Canadien | |
| BAC One-Eleven 500 | 16 | 1986 | 1994 | Including one plane leased from TAROM | |
| Convair 580 | 1 | 1988 | 1988 | Operated by Partnair. | |
| Boeing 737-200 | 21 | 1994 | 2005 | Replaced by Boeing 737-800. Ryanair sold its 737-200 planes in 2004 and 2005. |
|
| Boeing 737-300 | 7 | 2002 | 2004 | Replaced by Boeing 737-800. | |
| Boeing 737-400 | 1 | 2004 | 2005 | Leased for certain seasons from Air Atlanta Icelandic and AirExplore. | |
| Embraer EMB 110 Bandeirante | 1 | 1985 | 1989 | ||
| Hawker Siddeley HS 748 | 2 | 1986 | 1990 | ||
| Short S-25 Sunderland 5 | N/A | 1989 | 1989 | This plane was painted for a possible Ryanair sponsorship but it did not happen. |
How the Fleet Has Grown




After the grounding of all 737 MAX planes in 2019, Ryanair still showed confidence in the aircraft. It said it would be ready to order more once they were allowed to fly again.
When Boeing builds a plane for Ryanair, it gets a special code, "AS," in its name, like 737-8AS.
Ryanair's fleet reached 200 planes for the first time in September 2009. All planes in the Ryanair fleet have special parts called "winglets" that help them fly better and save fuel. Newer planes come with these already installed.
The company also owns four Learjet 45 business jets. These are used to quickly move engineers, parts, and crew around its network when a plane needs repairs.
In March 2013, Ryanair ordered 175 new Boeing 737-800s. In April 2014, Ryanair ordered five more planes. In September 2014, Ryanair agreed to order 100 new Boeing 737 MAX 8s. In December 2014, the airline finalized its order for up to 200 Boeing 737 MAX 200s. This made Ryanair the first airline to order this specific version of the 737 MAX 8, which can carry 200 passengers.
After delays due to the 737 MAX grounding, the first Boeing 737 MAX 200 was delivered to Ryanair in June 2021. Ryanair has been replacing its older leased 737s with these new MAX planes. In January 2023, the first Ryanair 737-800 was updated with new winglets that save 1.5% more fuel. All existing 737-800 planes in the fleet will get these updates.
In January 2023, Ryanair said it would extend the leases for its Airbus A320 planes until 2028.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ryanair para niños
In Spanish: Ryanair para niños