Banjul facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Banjul
ߓߊ߲߬ߖߎߟ Banjul
𞤄𞤢𞤲𞥆𞤶𞤵𞤤𞤵 Bannjulu |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Clockwise from top: King Fahad Mosque and Banjul skyline, Arch 22, Banjul Beach
|
|||
|
|||
 |
|||
| Country | The Gambia | ||
| Division | Banjul | ||
| Founded | 23 April 1816 as Bathurst | ||
| Area | |||
| • Capital city | 12 km2 (5 sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 93 km2 (36 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 0 m (0 ft) | ||
| Population
(2013 census)
|
|||
| • Capital city | 31,301 | ||
| • Density | 2,610/km2 (6,760/sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 413,397 | ||
| • Urban density | 4,445/km2 (11,510/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC±00:00 (GMT) | ||
| HDI (2017) | 0.552 medium |
||
Banjul, officially called the City of Banjul, is the capital city of The Gambia. It is the main city in its own administrative area. About 400,000 people live here, making it the largest and most crowded city area in The Gambia. Banjul is located on St Mary's Island, also known as Banjul Island. This island is where the Gambia River meets the Atlantic Ocean.
The city itself has a population of 31,301 people. However, the Greater Banjul Area, which includes Banjul and the Kanifing Municipal Council, has a population of 413,397 (based on the 2013 census). The island is connected to the mainland by bridges. There are also ferries that link Banjul to the other side of the river. From the 1800s until 1973, the city was known as Bathurst.
Contents
What's in a Name? The Story of Banjul
There are a few ideas about where the name 'Banjul' comes from. One old story says that a person named Bandjougou came to the island. He was running away from attacks in his home region. His name then became linked to the island, and over time, it changed to 'Bandjoulou'.
Another idea is that Banjul gets its name from Bang julo. This is a word from the Mandinka language. It means 'rope fibre'. The Mandinka people used to collect this fibre on the island.
Banjul's Past: A Look Back in Time
Early Days and British Arrival
In 1651, a European leader called the Duke of Courland and Semigallia rented Banjul. He rented it from the King of Kombo. This was part of a plan for Courland to set up colonies.
Later, on April 23, 1816, the King of Kombo gave Banjul Island to a British officer named Alexander Grant. In return, the King received 103 iron bars each year. Grant was sent by Charles MacCarthy to set up a military base. Grant founded Banjul as a trading post. He built homes and barracks to control the entrance to the Gambia River. This also helped stop the slave trade. The British renamed Banjul Island to St. Mary's Island. They called the new town Bathurst, after Henry Bathurst, who was an important government official. The streets were planned in a grid shape and named after famous generals. The town became the main center for British activities in the area.
Growing as a City
Soon after it was founded, people started moving to Bathurst. People from different parts of Africa came, along with people from the Middle East and Europe. Most people were Muslim, but there were many Christians too. The Wolof people were the largest African group. Their population grew a lot over the years. The Mandinka people were the second largest group.
Bathurst officially became the capital of the Gambia Protectorate in 1889. This made more people move there. Throughout the 1900s, it became even more popular. People came for jobs and social activities like cinemas. Young men from farms moved to work in government departments or at the docks. The town was also important during World War II. It served as a key naval and air base for the Allies. This caused the population to grow even more.
Changing to Banjul
After The Gambia became independent, the town's name was changed to Banjul in 1973. On July 22, 1994, Banjul saw a change in government leadership. To remember this event, Arch 22 was built as a special entrance to the capital. This gate is 35 meters tall. It stands in the middle of an open square. Inside, it has a textile museum.
Banjul's Weather
Banjul has hot weather all year round. It has a tropical wet and dry climate. This means it has a long dry season from November to May. Then, there's a shorter wet season for the other five months. During the wet season, Banjul gets a lot of rain. August is usually the rainiest month.
Scientists say that Banjul is at risk from rising sea levels. This is due to climate change and global warming. If sea levels rise by one meter, parts of Banjul could go underwater.
Parts of Banjul
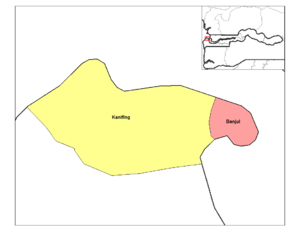
The Banjul Division, which is the Greater Banjul Area, is split into two main districts:
- Banjul
- Kanifing
Banjul's Economy
Banjul is the main economic and administrative center of The Gambia. The Central Bank of the Gambia is located here. Processing peanuts is the country's most important industry. Other products like beeswax, palm oil, and animal skins are also shipped from Banjul's port.
Banjul is also home to the Gambia Technical Training Institute. This institute works with a group called Power Up Gambia. They are creating a training program for solar energy.
Getting Around Banjul
You can reach Banjul by road. A highway connects Banjul to Serrekunda. This highway crosses the Denton Bridge. Ferries are another way to travel. Ferries regularly sail from Banjul across the Gambia River to Barra. The city also has its own airport, the Banjul International Airport. Banjul is part of the Trans–West African Coastal Highway. This highway connects it to cities like Dakar and Bissau. Eventually, it will link Banjul to 11 other countries in West Africa.
Culture and Fun in Banjul
There are many interesting places to visit in Banjul. These include the Gambian National Museum, the Albert Market, and the African Heritage Museum. You can also see the Banjul State House and the Banjul Court House.
Sports
Banjul is the finish line for the Plymouth-Banjul Challenge. This is a special road rally that raises money for charity.
Learning and Schools
The University of the Gambia was started in 1999. There are also several international schools in the Greater Banjul Area, such as:
- Banjul American Embassy School
- École Française de Banjul
- Maarif International School
- Marina International School
- SBEC International School
- British International School The Gambia
Places to Worship
Most places of worship in Banjul are Muslim mosques. There are also many Christian churches. These include the Roman Catholic Diocese of Banjul and churches from the Anglican Communion and Assemblies of God.
Famous People from Banjul
- Gambino Akuboy (born 1985), a singer, songwriter, actor, and screenwriter.
- Ebrima Darboe (Born 2001), a football player.
- Ibrahim Muhammadu Garba-Jahumpa (1912-1994), a trade union leader and politician.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Banjul para niños
In Spanish: Banjul para niños
 | Valerie Thomas |
 | Frederick McKinley Jones |
 | George Edward Alcorn Jr. |
 | Thomas Mensah |