Biodiversity facts for kids
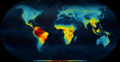
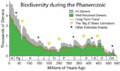
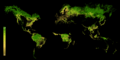
Biodiversity means the huge variety of life on Earth. It includes all the different kinds of species, from tiny microorganisms to giant trees and animals. We can see biodiversity in a small area, like a pond, or across the whole planet. It helps us understand how healthy our natural world is. It also warns us if too many species are in danger of becoming extinct. The United Nations even called 2011–2020 the "United Nations Decade on Biodiversity" to highlight its importance.
Contents
What is Biodiversity?
The full term, biological diversity, was first used by a scientist named Raymond F. Dasmann in 1968. He talked about it when discussing how to protect nature. However, the shorter word biodiversity became popular much later, in the 1980s.
The word biodiversity first appeared in a book title in 1988. This was when E. O. Wilson, an entomologist (someone who studies insects), used it. Since then, many people, including scientists, environmentalists, and leaders, use this term.
Levels of Biodiversity
Scientists often describe biodiversity as all the genes, species, and ecosystems in a certain area. This definition helps cover many different situations. There are three main ways we can look at the variety of life:
- Species diversity: This is about the number of different species in a place.
- Ecosystem diversity: This refers to the variety of different ecosystems, like forests, deserts, or oceans.
- Genetic diversity: This is the variety of genes within a single species.
Why is Biodiversity Important?
Biodiversity offers many benefits. Different groups of living things help each other in many ways.
Stronger Against Problems
When there is not enough biodiversity, it can cause big problems. For example, growing only one type of crop (called monoculture) has led to disasters. This happened during the Irish Potato Famine and a corn disease in the US in 1970.
More biodiversity also helps control the spread of diseases. If a virus has to adapt to many different species, it is harder for it to spread quickly.
Food and Drink for Humans
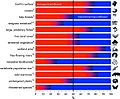
Biodiversity gives us most of our food. About 80% of the food we eat comes from only 20 types of plants. Humans use at least 40,000 different kinds of plants and animals every day. Even though we eat many animals, most of our meat comes from just a few species. Many people around the world rely on these species for their food, shelter, and clothes.
There are still many plants and animals we could use for food. But we need to stop the current high rate of species becoming extinct to discover these new possibilities.
Natural Medicines
Many medicines we use today come from nature. They are found in plants, animals, and tiny microorganisms. About 40% of the medicines used in the US come from natural sources. Often, these medicines cannot be made in a lab. Scientists have only studied a small part of all the plants for new drugs. Many medicines and antibiotics also come from microorganisms.
Materials for Industry
Many materials we use in industries come directly from nature. These include things like wood for building, fibers for clothes, dyes, glues, rubber, and oils. There is a huge chance to find even more useful materials from a wider variety of organisms. We need to make sure we use them in a way that protects nature.
Inspiration for Technology
Biodiversity has inspired many new technologies through a field called Bionics. By studying how living things work, scientists have created amazing inventions. For example, they might study how a bird flies to design better airplanes.
Better Crops for Farming
For important crops like food plants, we can use wild varieties of the same species. Mixing these wild types with farmed ones can create stronger, better crops. This has a huge economic impact. For example, the potato we eat today comes from only one variety brought from the Inca people. Wild potato types are in danger from climate change. A report by CGIAR shows how much money could be lost if these wild types disappear.
Rice, which humans have improved for thousands of years, can also get back some of its lost nutrition through this process. Projects are already working on this.
Other Natural Services
Biodiversity provides many important services that we often do not see. It helps control the chemistry of our atmosphere and our water supply. It also helps recycle nutrients and create fertile soils.
Experiments show that humans cannot easily build ecosystems that support our needs. For example, insect pollination (when insects help plants make seeds) cannot be copied by humans. This one activity alone is worth billions of dollars to us each year.
Fun, Culture, and Beauty
Many people enjoy biodiversity through fun activities. This includes walking in the countryside, watching birds, or watching nature shows on TV.
Biodiversity has also inspired artists like musicians, painters, and writers. Many cultures see themselves as part of the natural world. They show great respect for other living things.
Images for kids
-
A summer field in Belgium. The blue flowers are Centaurea cyanus and the red ones are Papaver rhoeas.
-
The amazing Amazon rainforest in South America.
-
Hiking at Eagle Creek, Oregon.
-
Cutting down forests and building more roads in the Amazon rainforest in Bolivia is a big worry. It means more people are moving into wild areas, taking more resources, and threatening biodiversity.
-
A male Lophura nycthemera (silver pheasant). This bird is from East Asia but has been brought to parts of Europe as an ornamental bird.
-
Polar bears on the sea ice near the North Pole. Climate change is starting to affect bear populations.
-
The melting of the Aletsch Glacier in the Swiss Alps (shown in 1979, 1991, and 2002). This is happening because of global warming.
-
A lot of effort is being made to protect the natural beauty of Hopetoun Falls, Australia, while still allowing visitors to enjoy it.
See also
 In Spanish: Biodiversidad para niños
In Spanish: Biodiversidad para niños