Borkum facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Borkum
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Borkum from the Borkum Great Light lighthouse
|
|||
|
|||
| Country | Germany | ||
| State | Lower Saxony | ||
| District | Leer | ||
| Elevation | 6 m (20 ft) | ||
| Population
(2022-12-31)
|
|||
| • Total | 5,171 | ||
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) | ||
| Postal codes |
26757
|
||
| Dialling codes | +49 4922 | ||
| Vehicle registration | LER | ||
| Website | www.stadt-borkum.de | ||
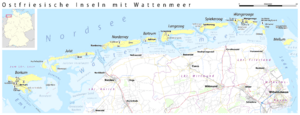
Borkum is a lovely island and a town in northwestern Germany. It is located in the Leer District of Lower Saxony. You can find it east of Rottumeroog and west of Juist.
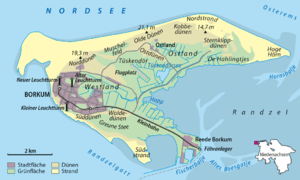
Geography of Borkum
Borkum is surrounded by water. To the west, it has the Westerems strait, which is a narrow waterway forming the border with the Netherlands. The Osterems strait is to its east. The North Sea is to the north, and the Wadden Sea is to the south.
Borkum is the biggest and westernmost of the East Frisian Islands. These islands are in the North Sea, just north of the Dutch province of Groningen. The island was actually formed in 1863. Before that, it was two separate islands. They were divided by shallow water. The area where these two parts joined is called Tüskendör. This means "through in between".
Borkum's Climate
Borkum is special because it's the only East Frisian island that feels the North Sea's influence all year. This is because it's about 30 km (19 mi) away from the mainland. The island has a maritime climate. This means its weather is shaped by the Gulf Stream and the west wind zone.
Because of this, Borkum has high humidity throughout the year. The weather changes often, with lots of sun and wind. Sometimes, there are also rain and showers. Compared to the mainland, Borkum has milder winters. Its summers are cooler, without very hot or very cold days. This is thanks to the sea, which warms up slowly in spring and summer. But it also holds onto that warmth longer in the autumn.
History of Borkum
Borkum was first mentioned as Burchana fabaria, which means "island of beans". This name was used by ancient writers like Strabo and Pliny the Elder. Around the time of Charlemagne, Borkum was part of a bigger island called Bant. This larger island included what are now Borkum, Juist, and the western part of Norderney.
In 1484, Bant became part of the land ruled by the Earls of East Frisia. They helped develop trade on the island. Borkum became known for piracy and whaling. However, strong storms in the 1700s broke Bant into three separate islands by 1781. As whaling became less common, the people on the island became poor. Many left, and the population dropped a lot.
Things started to get better in 1834. This is when the first tourists began to visit the island. Borkum then grew into a popular tourist spot. In 1910, two British officers, Captain Bernard Frederick Trench and Lieutenant Vivian H. Brandon, were arrested. They were caught taking photos of military buildings on the island.
Later, in 1934, something important happened on Borkum. On December 19 and 20, Wernher von Braun launched two early rocket prototypes. These rockets were named "Max" and "Moritz". They were part of the "A2" rocket program.
Getting Around Borkum
The island of Borkum is partly car-free. During the off-season, you can drive cars almost anywhere. But during busy times, there are special zones where cars are not allowed. The only town on the island is also called Borkum.
There is a small airfield in the Tüskendör area. You can reach Borkum by ferry from Emden, Germany. You can also take a ferry from Eemshaven in the Netherlands. Once you arrive, the Borkumer Kleinbahn is a narrow-gauge railway. It connects the harbor to the town of Borkum, making it easy to get around.
See also
 In Spanish: Borkum para niños
In Spanish: Borkum para niños