Brain injury facts for kids
A brain injury happens when your brain gets hurt. Many different things can cause this. For example, some brain injuries can happen even before a baby is born. These are called congenital brain injuries.
Your brain can also be hurt by a physical injury, like hitting your head in a car accident. These are known as traumatic brain injuries. Also, certain medical problems can injure the brain. For instance, if the brain does not get enough oxygen, like during a stroke, it can be damaged.
Every brain injury is unique. Some are mild, meaning not very serious. Others are severe, which means they are very serious. Some injuries get better quickly, while others improve slowly over time, or might not fully heal. Since the brain controls everything in your body, the symptoms of a brain injury can be very different for each person. This depends on which part of the brain was hurt and how badly.
Contents
Types of Brain Injuries
Traumatic Brain Injuries
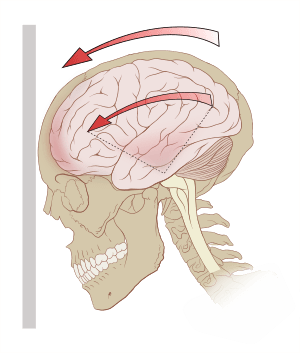
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) happen when there is a physical injury to the brain. This can occur if your head suddenly hits something very hard, like in a car crash. It can also happen if an object, such as a bullet or knife, goes through your head and into the brain.
Traumatic brain injury is one of the most common causes of disability around the world. It is more common in developing countries. About 10 million people worldwide are affected by TBI every year.
Experts believe the most common causes of TBI globally are:
- Injuries from road traffic accidents (about 60% of all TBI)
- Falls (about 20%-30%)
- Violence (10%)
- Injuries from working or playing sports (10%)
In some parts of the world, like Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, and the Middle East, War and violence are much more common causes of TBI.
TBI has become a very common injury for soldiers serving in places like Iraq and Afghanistan. The United States Department of Defense reports that 22% of all injuries from these wars are traumatic brain injuries.
Some traumatic brain injuries are mild and can heal over time, like a concussion. Others are more serious, especially if they cause bleeding or swelling inside the brain.
Other Brain Injuries
Another main type of brain injury is a hypoxic brain injury. This happens when the brain does not get enough oxygen. This can occur for several reasons, such as:
- Cardiac arrest (when the heart stops)
- Drowning
- Stroke
- Shock (when the body doesn't get enough blood flow)
Many other things can also injure the brain. Some examples include:
- Infections like encephalitis (brain swelling) and meningitis (swelling around the brain and spinal cord)
- Seizures
- Brain cancer
- Exposure to certain harmful substances or Poisons, like lead
Signs and Symptoms of Brain Injury
The signs and symptoms of a brain injury depend on many things.
Diffuse or Focal Injuries
A diffuse injury affects the entire brain. For example, if a person is drowning and cannot breathe, their whole brain will not get oxygen. If this lasts long enough, the entire brain will be injured due to lack of oxygen.
A focal injury hurts only a specific part of the brain. For instance, in some strokes, a blood clot blocks blood flow to just one area of the brain. If the person gets good medical treatment, only that part of their brain might be injured.
This difference is important because different parts of the brain control different things. When someone has a focal brain injury, their symptoms will depend on which part of the brain was hurt. For example, if the part of the brain that controls speech was injured, the person might have trouble speaking.
How Serious the Injury Is
A brain injury's symptoms can also depend on how serious the injury was.
For example, brain injuries can cause changes or problems in a person's thinking, senses, feelings, or ability to move. However, some people might have mild problems in these areas, while others might have more serious problems:
- Thinking problems
- Mild symptoms: Getting distracted easily; feeling confused sometimes; forgetting things easily.
- Severe symptoms: Unable to concentrate; getting very confused; unable to remember important things, people, or parts of life; intellectual disability.
- Problems with the senses
- Changes in feelings
- Mild symptoms: Mood changes; depression; anxiety.
- Severe symptoms: Long-lasting depression or anxiety; severe, sudden mood changes or aggression; changes in personality.
- Trouble moving
Recovery from Brain Injury
There are many different treatments that can help people with brain injuries. For example:
- Physical therapy can help people re-learn how to move, walk, and balance themselves.
- Occupational therapy can help people practice how to do everyday things, like getting dressed and making meals.
- Speech therapy can help people who are having trouble speaking after their brain injury.
- Psychotherapy can help with depression, anxiety, mood changes, and stress.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lesión cerebral para niños
In Spanish: Lesión cerebral para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |