United States Department of Defense facts for kids

Seal of the Department of Defense
|
|
Logo for the Department of Defense
|
|
 An aerial view of the Pentagon |
|
| Agency overview | |
|---|---|
| Formed | 18 September 1947 (as National Military Establishment) |
| Preceding agencies | |
| Type | Executive department |
| Jurisdiction | U.S. federal government |
| Headquarters | The Pentagon Arlington County, Virginia, U.S. 38°52′16″N 77°3′21″W / 38.87111°N 77.05583°W |
| Employees |
|
| Annual budget | $842 billion FY2024 |
| Agency executives |
|
| Child agencies |
|
The United States Department of Defense (DoD) is a very important part of the U.S. government. Its main job is to manage and oversee the U.S. Armed Forces. These forces include the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, and sometimes the Coast Guard.
The DoD's headquarters is a famous building called The Pentagon. It is located in Arlington County, Virginia, near Washington, D.C.. The department's mission is to have strong military forces. This helps to prevent wars and keep the nation safe. The person in charge is the Secretary of Defense, currently Pete Hegseth.
The Secretary of Defense is a high-ranking official. They report directly to the president of the United States. The president is the Commander-in-Chief of all U.S. armed forces. The Department of Defense includes three main military departments. These are the Department of the Army, the Department of the Navy, and the Department of the Air Force.
The DoD also oversees several important intelligence agencies. These include the Defense Intelligence Agency, National Security Agency (NSA), National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency, and National Reconnaissance Office. Other agencies, like the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), help with research and development.
As of June 2024, the department has many employees. This includes over 1.2 million active-duty military personnel. It also supervises over 760,000 National Guard and reserve members. Plus, there are nearly 790,000 civilian employees. This brings the total to over 2.8 million people working for the DoD.
Contents
Understanding the Department's Name
The Department of Defense used to be called the Department of War. This name was used from 1789 until 1947. In 1947, it was reorganized and split into different parts. These parts joined with the Department of the Navy. Together, they formed the National Military Establishment (NME).
In 1949, the NME was renamed the Department of Defense. This new name better reflected its goal of protecting the nation. On September 5, 2025, President Donald Trump signed an order. This order allowed "Department of War" to be used as a secondary, unofficial title. However, "Department of Defense" remains the official and legal name.
A Brief Look at History
The idea of a national defense force started early in U.S. history. In 1774, the colonies began preparing for defense. This was due to growing tensions with the British government. In 1775, during the Revolutionary War, the Second Continental Congress created the Continental Army. They also formed the Continental Navy and Continental Marines later that year.
Early Military Departments
When the U.S. government was first set up, it created the War Department in 1789. This department handled all military matters. Later, in 1798, the Navy Department was created. This separated naval affairs from the War Department.
For many years, the leaders of these departments reported directly to the president. This changed after World War II.
Forming the Department of Defense

After World War II, President Harry Truman wanted to unite the military branches. He believed this would make them more efficient. In 1947, the National Security Act of 1947 was signed. This law created the National Military Establishment (NME). It also established the United States Air Force as a separate branch.
The NME began its work on September 18, 1947. James V. Forrestal became the first Secretary of Defense. In 1949, the NME was officially renamed the "Department of Defense." It brought the Army, Navy, and Air Force departments under one main leader.
Later, in 1958, the Department of Defense was further organized. This helped to make the chain of command clearer. It also created the Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). This agency focuses on new military technologies.
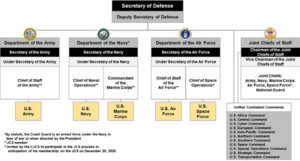
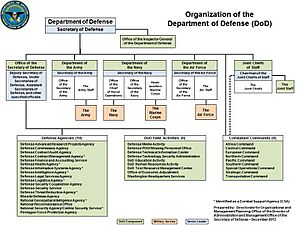
How the Department of Defense is Organized
The Secretary of Defense leads the Department of Defense. This person is chosen by the president and approved by the Senate. The Secretary is the president's main advisor on defense matters. They have authority over the entire department.
The Department of Defense has several key parts. These include the Office of the Secretary of Defense, the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and the military departments. It also includes various defense agencies and Combatant Commands.
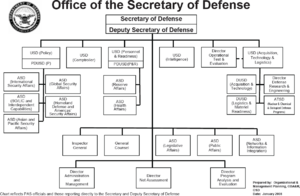
Office of the Secretary of Defense
The Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) is made up of the Secretary and their team. Most of these staff members are civilians. OSD helps the Secretary create policies, plan, and manage resources. They also work with other government agencies and foreign countries.
Important Defense Agencies
OSD oversees many specialized agencies. These agencies help the military in different ways. Some examples include:
- Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which develops new technologies.
- Defense Health Agency, which provides healthcare for military members.
- Defense Logistics Agency, which supplies equipment and services.
- Defense Commissary Agency, which runs grocery stores for military families.
- Space Development Agency, which focuses on space-related defense.
National Intelligence Agencies
Some defense agencies are part of the United States Intelligence Community. These agencies gather important information to protect the nation. They work under the Department of Defense. They also coordinate with other intelligence groups like the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA).
These agencies help national leaders and military planners. They collect information from various sources. This includes signals intelligence, geospatial intelligence, and satellite operations. The Under Secretary of Defense for Intelligence and Security oversees these agencies.
- National Intelligence Agencies under the Department of Defense
Joint Chiefs of Staff
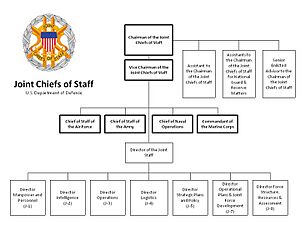
The Joint Chiefs of Staff are a group of top military leaders. They advise the Secretary of Defense and the president on military issues. This group includes the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff and leaders from each military service. These services are the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, and Space Force. The chief of the National Guard Bureau is also a member.
After a law called the Goldwater–Nichols Act in 1986, the Joint Chiefs of Staff became advisors. They no longer directly command troops. The Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is the main military advisor to the president and Secretary of Defense. The chain of command for military operations goes from the president to the Secretary of Defense, then to the commanders of the Combatant Commands.
The Joint Staff is a team at the Pentagon. It includes personnel from all military services. They help the Chairman and Vice Chairman with their duties.
Military Departments and Services
The Department of Defense has three main military departments:
- The Department of the Army, which organizes the United States Army.
- The Department of the Navy, which organizes the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps.
- The Department of the Air Force, which organizes the United States Air Force and United States Space Force.
Each department is led by its own Secretary. These Secretaries are appointed by the president. They manage the training, equipment, and administration of their forces. However, they report to the Secretary of Defense.
- Military Departments of the Department of Defense
- Military Services of the Department of Defense
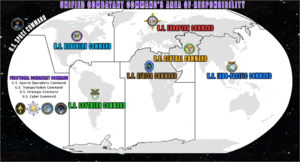
Unified Combatant Commands
A unified combatant command is a military group with a big, ongoing mission. It includes personnel and equipment from at least two military departments. These commands are responsible for leading military operations. Most U.S. forces are under the authority of a Unified Command.
The chain of command for military operations is clear. It goes from the president to the Secretary of Defense. Then it goes to the commanders of these Combatant Commands.
As of 2019, there are eleven Combatant Commands. Some cover specific geographical areas. Others focus on global functions. Examples include:
- U.S. Northern Command (USNORTHCOM)
- U.S. Southern Command (USSOUTHCOM)
- U.S. European Command (USEUCOM)
- U.S. Indo-Pacific Command (USINDOPACOM)
- U.S. Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM)
- U.S. Cyber Command (USCYBERCOM)
- U.S. Space Command (USSPACECOM)
How the Department of Defense is Funded
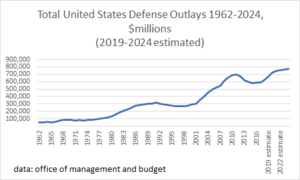
The Department of Defense needs a large budget to operate. This money pays for military personnel, equipment, and operations. For the fiscal year 2024, the DoD's budget was $842 billion. This funding helps ensure the U.S. military can protect the country.
The DoD's budget is a significant part of the U.S. federal budget. It covers many expenses. These include salaries for service members and buying new technologies. It also funds training exercises and maintaining military bases. Other defense-related costs, like nuclear weapons research, are handled by different departments.
See also
 In Spanish: Departamento de Defensa de los Estados Unidos para niños
In Spanish: Departamento de Defensa de los Estados Unidos para niños
- Arms industry
- Energy usage of the United States military
- List of United States military bases
- Nuclear weapons
- United States Department of Homeland Security
- United States Department of Veterans Affairs