Central forest–grasslands transition facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Central forest–grasslands transition |
|
|---|---|

|
|
 |
|
| Ecology | |
| Realm | Nearctic |
| Biome | Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands |
| Borders |
List
|
| Bird species | 234 |
| Mammal species | 81 |
| Geography | |
| Area | 407,000 km2 (157,000 sq mi) |
| Country | United States |
| States | Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, Missouri, Kansas, Oklahoma and Texas |
| Conservation | |
| Habitat loss | 67.6% |
| Protected | 2.09% |
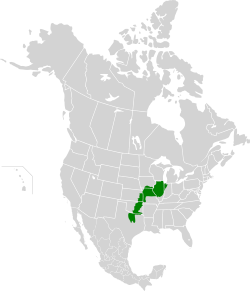
The Central Forest–Grasslands Transition is a special natural area in the central United States. It's like a big "in-between" zone where eastern forests meet the huge North American Great Plains. This area is a mix of prairie (grassy lands) and woodlands. The World Wildlife Fund helps us understand and protect places like this.
Contents
What is This Ecoregion Like?
This large natural area covers about 407,000 square kilometers (157,000 square miles). It stretches from northern Illinois through most of Missouri, eastern Kansas, Oklahoma, and into Texas.
A Mix of Habitats
This region was once a blend of woodlands and tall grass prairie. Tallgrass prairies have grasses that can grow taller than a person! The soil here is very rich and fertile. It's called mollisol, which is great for growing plants.
Weather and Location
Rainfall in this area ranges from about 600 to 1,040 millimeters (24 to 41 inches) each year. The region can sometimes have droughts (very dry periods) and fires. This ecoregion acts as a natural border. To its east are the Central U.S. hardwood forests. To its west are the mostly treeless Central and Southern mixed grasslands and Central tall grasslands.
Animals of the Ecoregion
This area is home to many different animals, especially reptiles, birds, and insects.
Birds and Reptiles
One interesting bird found here is the greater prairie chicken. These birds are known for their unique mating dances. Among the reptiles, you might find the Osage copperhead snake.
Protecting This Special Place
Sadly, most of this ecoregion has been changed into farmland. Farmers grow crops like corn and soybeans here because the soil is so good.
Remaining Natural Areas
Only small pieces of the original habitat are left. These remaining spots are very important for wildlife.
- The Emiquon National Wildlife Refuge in Illinois is a key stop for birds migrating (traveling) long distances.
- Other unspoiled prairie areas include Goose Lake Prairie State Natural Area and Midewin National Tallgrass Prairie in Illinois.
- The Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore in northwest Indiana also protects some of this habitat.
- In southern Kansas and central Oklahoma, you can find the Cross Timbers.
- The Osage Plains are in the southern part of the ecoregion.
Conservation Efforts
Even though these natural areas are spread out, many are protected. For example, Prairie State Park in Missouri helps preserve a piece of the prairie. There are also several small tallgrass prairie reservations in Cook County, Illinois. One of these is the National Natural Landmark, Gensburg-Markham Prairie. These protected areas are vital for keeping the plants and animals of this unique region safe.

