Big hairy armadillo facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Big hairy armadillo |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Chaetophractus
|
| Species: |
villosus
|
 |
|
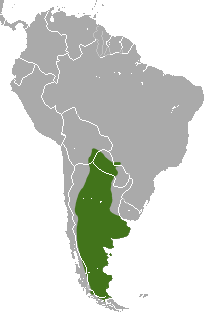
| Big hairy armadillo range | |
The big hairy armadillo (Chaetophractus villosus) is one of the largest and most common armadillos in South America. You can find it from sea level up to 1,300 meters high. It lives in grasslands, forests, and savannahs. It has even started living in farm areas.
This armadillo is a great digger. It spends most of its time underground. It digs both short-term and long-term burrows. This depends on where it finds its food. Armadillos have thin, bony plates on their heads and backs. These plates protect them from animals that want to eat them.
Big hairy armadillos become adults at about 9 months old. They can live for over 30 years if they are cared for by humans. Even though some people hunt this animal for its meat or shell, its numbers are still strong. There are no special rules to protect this armadillo right now. But it does live in many protected natural areas. Scientists also like to study this armadillo. It adapts well to labs and handles stress easily.
Contents
- What does the big hairy armadillo look like?
- What other armadillos are like the big hairy armadillo?
- How can you tell the difference between hairy armadillos?
- Where did armadillos come from?
- Where do big hairy armadillos live?
- How do big hairy armadillos survive in their environment?
- What is the big hairy armadillo's daily life like?
- Are big hairy armadillos in danger?
- See also
What does the big hairy armadillo look like?
The big hairy armadillo is the most common armadillo in Argentina. Its head and body are covered with bony plates. The head plate is very noticeable. Flexible bands around its body allow its armor to bend. This helps the armadillo move.
The underside of this armadillo has lots of hair. This is how it got its name! Long, rough hairs also stick out from its bony plates. This makes it much hairier than other armadillos. An average big hairy armadillo is about 26 to 34 centimeters (10 to 13 inches) long. Some can be up to 40 centimeters (16 inches). It usually weighs about 2 kilograms (4.4 pounds). Its tail is about 9 to 17 centimeters (3.5 to 6.7 inches) long.
This armadillo has strong front claws. It uses them to dig for food and to escape predators. It also has a special way to breathe underground. It can get oxygen from the air between soil particles. This means it does not breathe in the soil itself.
What other armadillos are like the big hairy armadillo?
The Chaetophractus group includes two or three species. These are the screaming hairy armadillo (C. vellerosus), the Andean hairy armadillo (C. nationi), and the big hairy armadillo (C. villosus). The Andean hairy armadillo might actually be a type of screaming hairy armadillo.
These species are known for having a lot of hair. The hair is especially thick on their undersides. Scientists tell these species apart by their body size, where they live, and how they behave.
How can you tell the difference between hairy armadillos?
There are a few clear ways to tell these armadillo species apart. The main difference is their size. The big hairy armadillo (C. villosus) is much larger. It can grow up to 34 centimeters (13 inches) long. The screaming hairy armadillo (C. vellerosus) is much smaller. It can fit in your hand when fully grown. It usually weighs only about 1 kilogram (2.2 pounds).
Both species have much more hair than other armadillos. The hair grows mostly on their undersides or between their bony plates. The smaller screaming hairy armadillo often lives in higher places. Its smaller size and slower body processes help it survive where there is less food.
Where did armadillos come from?
Armadillos have unique bony plates called osteoderms. These plates are often found in fossils. This helps scientists learn about ancient armadillos. The earliest known fossils of the big hairy armadillo were found in the Pampean region. This suggests that the species started there.
Fossils show that these armadillos then moved into Patagonia. This likely happened after the ice ages. Scientists believe the first armadillos appeared around the time the Cretaceous period ended. This was about 66 million years ago.
Where do big hairy armadillos live?
The big hairy armadillo lives in the Pampas and Patagonia regions. You can find it as far south as Santa Cruz, Argentina, and Magallanes, Chile. It also lives in the Gran Chaco Province of Bolivia, Paraguay, and Argentina. It is even starting to move south into the Tierra del Fuego province of Argentina.
You can also find it in the Biobío province and south to Aisén Province in eastern Chile. It seems that Climate change and the armadillo's ability to adapt are helping it live in more places. Unlike some other armadillos, the big hairy armadillo has not seen big changes in its home area. It has not moved as far north as some other species.
How do big hairy armadillos survive in their environment?
Big hairy armadillos have special features that help them survive. Their bony plates cover their heads and backs. These plates protect them from predators. This species also has an amazing way to breathe when its nose is covered in soil. It can still breathe by using the air between soil particles. It does not breathe in the soil itself.
This, along with its strong digging claws, helps it live underground. Living underground helps the armadillo avoid very hot or cold temperatures. It also helps them hide from predators.
What is the big hairy armadillo's daily life like?
The big hairy armadillo spends most of its time digging in the ground. It looks for insects or worms to eat. Its strong front claws and snout help it dig through the soil easily.
When an armadillo senses danger, it runs to the nearest burrow. It then wedges itself in using its legs. Only its bony plates are exposed to the predator. If it cannot get to a burrow, it will lie flat on the ground. This helps protect its softer underside.
Most of this armadillo's activity happens from dusk into the night. But you might see it active during the day if it cannot find enough food at night. It uses its sense of smell to find prey. Then it shovels soil away to reach it.
Most big hairy armadillos breed in late winter or spring. But in captivity, they can have babies all year. After being pregnant for 60 to 75 days, the female usually gives birth to one or two young. The young drink milk for another 50 to 80 days.
Big hairy armadillos can dig through most types of soil. But they tend to avoid rocky areas. They often dig into the side of a hill instead of on flat ground. Their temporary burrows, used for finding food or safety, are usually shallow. Their home burrows are much deeper and can be very complex. They often have many escape tunnels and dens. The way they dig their burrows depends on the wind direction. This helps them live well in dry desert areas.
Are big hairy armadillos in danger?
The big hairy armadillo is listed as a "least concern" species. This means it is not currently in danger. This is because it has a large population and lives in many different places. It also has a great ability to adapt to changing environments. Its population seems to be growing. It is not expected to become threatened any time soon.
See also
 In Spanish: Armadillo peludo para niños
In Spanish: Armadillo peludo para niños



