Colony collapse disorder facts for kids
Colony collapse disorder (CCD) is a problem where most of the adult worker bees in a hive suddenly disappear. They leave behind their queen, plenty of food, and a few young nurse bees to look after the baby bees and the queen. Bees disappearing has happened before throughout history, and it had different names.
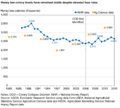
But in late 2006, this problem became much worse, especially for western honey bee colonies in North America. So, it was given the new name "colony collapse disorder." Beekeepers in Europe also saw similar problems, though not as bad. Some places like Northern Ireland reported more than half of their bee colonies disappearing.
Contents
Why Do Bee Colonies Collapse?
Scientists have suggested many reasons for CCD, but they don't all agree on one main cause. Some ideas include:
- Tiny mites like Varroa that attack bees.
- Bees not getting enough good food (malnutrition).
- Different kinds of pathogens (germs or diseases).
- Problems with bee genes.
- Bees having weak immune systems.
- Losing their natural homes (habitat destruction).
- Changes in how people care for bees (beekeeping practices).
- A mix of all these things.
Many people also think that a type of pesticide called neonicotinoids might be causing CCD.
This problem causes big money losses because many farm crops around the world need western honey bees to pollinate them. In 2005, the value of crops that honey bees pollinated was almost $200 billion. When there aren't enough bees, farmers in the U.S. have to pay more to rent bees for pollination, sometimes up to 20% more.
After bee numbers dropped a lot in 2013, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Department of Agriculture created a team to study the issue. In the six years before 2013, over 10 million beehives were lost, often because of CCD. This was almost twice the usual number of losses. However, the total number of beehives worldwide is still growing.
In 2013, the European Food Safety Authority said that three specific neonicotinoid pesticides were very risky for honeybees. Because of this, the European Commission (EC) suggested banning them for two years. Some scientists wondered why these chemicals were approved in the first place.
How Climate Change Affects Bees
Studies in Europe and North America show that bee colonies are decreasing a lot. The U.S. has lost 59% of its bee colonies since 1947, and Europe has lost over 25% since 1985. Finding out why bee colonies are collapsing is very important for the world's economy. This is because bee pollination helps with about 9.5% of all farming production globally, which is worth billions of dollars.
Research shows a connection between bee colony collapse and climate change. The changing weather itself harms bees. Also, climate change affects where bees can live and how much food they can find. It can stop flowers from growing well and making enough nectar. This directly impacts how much pollen bees can collect and how well their colonies can survive.
Signs of Colony Collapse Disorder
When a colony collapses due to CCD, you usually find that almost all the adult bees are gone. There are very few or no dead bees inside or outside the hive. A hive that has collapsed from CCD usually has all these things at the same time:
- There are still baby bees (capped brood) left in the abandoned hive.
- There is plenty of food, like honey and bee pollen.
- The queen bee is still there. If the queen is missing, the hive died for a different reason, not CCD.
Before a colony completely collapses, you might see these signs:
- Not enough worker bees to take care of the baby bees.
- The worker bees seem to be mostly young adult bees.
- The bees don't want to eat food given to them, like sugar syrup or protein supplements.
Renting Bees and Moving Hives
Since 1908, beekeepers in America have been moving their hives around the country for the winter. This practice, called migratory beekeeping, is now very common in the U.S. Renting bees for pollination is a very important part of U.S. farming. Without these rented bees, farms could not grow as much food as they do now. U.S. beekeepers actually earn more money from renting out their bees for pollination than they do from selling honey.
Scientists are worried that moving bee colonies across the country to pollinate crops can spread viruses and mites. This happens because bees from different places mix together. Also, constantly moving and resettling hives can be very stressful for the entire bee colony.
Impact on Economy and Nature
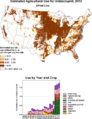
Honey bees are not originally from the Americas. So, in places like the U.S., they are mainly needed for farming and garden plants. CCD is especially important for crops like almonds in California. Honey bees are the main pollinators for almonds, and this crop was worth $3.6 billion in 2011.
In 2000, the total value of U.S. crops that completely depended on honey bee pollination was estimated to be over $15 billion. Because so many pollinators are needed, the cost of renting honey bees has gone up a lot. California's almond industry rents about 1.6 million honey bee colonies each spring to pollinate their crops. Around the world, honeybees provide about $200 billion worth of pollination services.
Honeybees help pollinate about one-third of the crops grown in the United States. These include crops like almonds, peaches, apples, pears, cherries, raspberries, blackberries, cranberries, watermelons, cantaloupes, cucumbers, and strawberries.
Honeybees help pollinate almost 75% of all plant species that humans eat worldwide. If we lost a lot of honeybees, it would have a huge impact. It's thought that seven out of the 60 main farm crops in North America could be lost, and this is just for one part of the world.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Problema de colapso de colonias para niños
In Spanish: Problema de colapso de colonias para niños