Datong facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Datong
大同市
Tatung
|
|
|---|---|
|
Prefecture-level city
|
|
|
From top down, left to right: Datong panorama; Shanhua Temple; Huayan Temple; Yungang Grottoes; Tower at Lingyan Temple; Temple of Confucius (Wenmiao); Guandi Temple; Yinghui Gate of the City Wall
|
|
Location of Datong City jurisdiction in Shanxi
|
|
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Shanxi |
| Municipal seat | Pingcheng District |
| Government | |
| • Type | Prefecture-level city |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 14,068 km2 (5,432 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 3,563 km2 (1,376 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 976 km2 (377 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,042 m (3,419 ft) |
| Population
(2020 census)
|
|
| • Prefecture-level city | 3,105,591 |
| • Density | 220.756/km2 (571.755/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,030,203 |
| • Urban density | 569.80/km2 (1,475.78/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,790,452 |
| • Metro density | 1,834.5/km2 (4,751.3/sq mi) |
| GDP | |
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 137 billion US$ 21.5 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 44,110 US$ 7,058 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code |
037000
|
| Area code(s) | 0352 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-SX-02 |
| License Plates | 晋B |
| Administrative division code | 140200 |
| Datong | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 大同 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Great Unity Great Togetherness |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Former names | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pingcheng | |||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 平城縣 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 平城县 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Peaceful City County Pacified City County |
||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Xijing | |||||||||
| Chinese | 西京 | ||||||||
| Literal meaning | Western Capital | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
Datong is a large city in northern Shanxi Province, China. It sits in the Datong Basin at a high elevation of about 1,040 meters (3,412 feet). The city shares borders with Inner Mongolia to the north and west, and Hebei to the east.
As of 2020, Datong had a population of over 3.1 million people. About 1.79 million of these people live in the main city area. This area includes two of its four urban districts, Pingcheng and Yungang.
Contents
Datong's Long History
The land where Datong is today has a very old history. It was once near the ancient state of Dai, which was taken over in 457 BC. This area was a borderland between Chinese farmers and nomadic groups from the Great Steppe. It was well-known for trading horses.
Early Settlements and Dynasties
During the Qin dynasty, the area was called Pingcheng County. It was part of the Qin empire. Later, under the Han dynasty, a settlement was built here in 200 BC. This happened after a victory against the Xiongnu nomads.
Pingcheng was located near a pass in the Great Wall of China. It became a busy stop for camel caravans traveling between China and Mongolia. The city grew important but was later damaged at the end of the Eastern Han dynasty.
From 398 to 494 AD, Pingcheng became the capital of the Northern Wei dynasty. During this time, the famous Yungang Grottoes were carved (460–494 AD). Later, during the Tang dynasty, the city was called Yunzhou, and the original Guandi temple was built.
Datong's Name and Later Periods
The city was renamed Datong in 1048. It was known as Xijing (meaning "Western Capital") during the Jurchen Jin dynasty. However, it was later attacked by the Mongols.
Datong then came under the control of the Ming dynasty. It became a very important military base for the Ming against the Mongols in the north. Many famous buildings in Datong, like the Drum Tower and the Nine-Dragon Wall, were built during the Ming period. The city was damaged again in 1649 but was quickly rebuilt in 1652.
Modern Changes in Datong
In 1982, Datong was recognized as a National Famous Historical and Cultural City because parts of its old city walls still stood. Around 2008, the city's mayor decided to rebuild much of the old city center. This project aimed to restore historical areas.
The reconstruction was a big effort. It involved rebuilding old structures and changing parts of the city. While the project aimed to bring back history, it also meant many people had to move.
Where is Datong Located?
Datong is the northernmost city in Shanxi province. It is located in the Datong Basin. The city's administrative area stretches from 39° 03' to 40° 44' North latitude and 112° 34' to 114° 33' East longitude.
The urban area of Datong is surrounded by mountains on three sides. There are passes only to the east and southwest. Generally, the land gets higher as you go from the southeast to the northwest. Datong is about 250 kilometers (155 miles) west of Beijing.
Datong's Weather
Datong has a steppe climate, which means it's quite dry. It has long, cold, and very dry winters. Summers are very warm.
- Temperatures: The average temperature in January is about -10.5°C (13.1°F). In July, it's around 22.6°C (72.7°F). The average temperature for the whole year is about 7.33°C (45.2°F).
- Daily Temperature Swings: Because it's dry and at a high elevation, the temperature can change a lot between day and night.
- Rainfall: There's hardly any rain in winter. Most of the rain, more than three-quarters of the yearly total, falls from June to September.
- Sunshine: Datong gets a lot of sunshine all year, about 2,671 hours per year.
| Climate data for Datong, elevation 1,053 m (3,455 ft), (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1951–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 11.2 (52.2) |
19.2 (66.6) |
25.3 (77.5) |
35.4 (95.7) |
36.1 (97.0) |
39.0 (102.2) |
39.2 (102.6) |
35.9 (96.6) |
34.7 (94.5) |
27.5 (81.5) |
21.9 (71.4) |
15.8 (60.4) |
39.2 (102.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −2.9 (26.8) |
2.1 (35.8) |
9.2 (48.6) |
17.4 (63.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.8 (82.0) |
28.9 (84.0) |
27.2 (81.0) |
22.4 (72.3) |
15.3 (59.5) |
6.2 (43.2) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
14.7 (58.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −10.5 (13.1) |
−5.8 (21.6) |
1.5 (34.7) |
9.7 (49.5) |
16.5 (61.7) |
21.0 (69.8) |
22.7 (72.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
15.2 (59.4) |
7.7 (45.9) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
7.5 (45.4) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −16.6 (2.1) |
−12.4 (9.7) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
2.1 (35.8) |
8.7 (47.7) |
14.0 (57.2) |
16.7 (62.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
8.8 (47.8) |
1.4 (34.5) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−14.1 (6.6) |
0.9 (33.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −31.1 (−24.0) |
−27.6 (−17.7) |
−20.9 (−5.6) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
−5.8 (21.6) |
2.9 (37.2) |
7.8 (46.0) |
2.8 (37.0) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−11.5 (11.3) |
−24.0 (−11.2) |
−31.9 (−25.4) |
−31.9 (−25.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 2.1 (0.08) |
3.6 (0.14) |
8.9 (0.35) |
21.0 (0.83) |
32.8 (1.29) |
53.1 (2.09) |
96.9 (3.81) |
76.1 (3.00) |
60.2 (2.37) |
23.3 (0.92) |
8.3 (0.33) |
1.8 (0.07) |
388.1 (15.28) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 1.8 | 2.2 | 3.6 | 4.3 | 6.6 | 11.2 | 12.5 | 11.1 | 8.8 | 5.5 | 3.1 | 1.7 | 72.4 |
| Average snowy days | 3.3 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 1.7 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 3.4 | 3.2 | 20.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 53 | 46 | 42 | 38 | 40 | 50 | 64 | 68 | 64 | 57 | 54 | 52 | 52 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 192.0 | 200.7 | 236.7 | 255.0 | 278.4 | 256.6 | 249.6 | 243.8 | 225.1 | 225.9 | 189.0 | 182.2 | 2,735 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 64 | 66 | 64 | 64 | 62 | 57 | 55 | 58 | 61 | 66 | 64 | 63 | 62 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administrationall-time extreme temperature | |||||||||||||
Exploring Datong's Divisions
Datong is divided into several smaller areas. These include four districts and six counties. Each area has its own population and size.
| Map | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
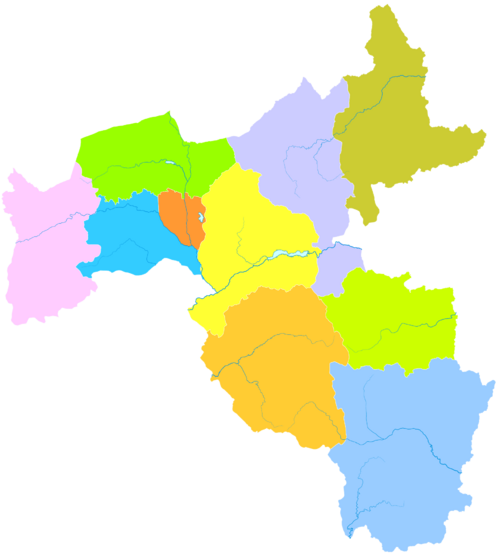
Pingcheng
Yungang
Xinrong
Yunzhou
Yanggao
County Tianzhen
County Guangling
County Lingqiu
County Hunyuan
County Zuoyun
County |
||||||
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Pinyin | Population (2003 est.) |
Area (km²) | Density (/km²) |
|
| Pingcheng District | 平城区 | Píngchéng Qū | 580,000 | 246 | 2,358 | |
| Yungang District | 云冈区 | Yúngāng Qū | 280,000 | 684 | 409 | |
| Xinrong District | 新荣区 | Xīnróng Qū | 110,000 | 1,102 | 109 | |
| Yunzhou District | 云州区 | Yúnzhōu Qū | 170,000 | 1,501 | 113 | |
| Yanggao County | 阳高县 | Yánggāo Xiàn | 290,000 | 1,678 | 173 | |
| Tianzhen County | 天镇县 | Tiānzhèn Xiàn | 210,000 | 1,635 | 128 | |
| Guangling County | 广灵县 | Guǎnglíng Xiàn | 180,000 | 1,283 | 140 | |
| Lingqiu County | 灵丘县 | Língqiū Xiàn | 230,000 | 2,720 | 85 | |
| Hunyuan County | 浑源县 | Húnyuán Xiàn | 350,000 | 1,965 | 178 | |
| Zuoyun County | 左云县 | Zuǒyún Xiàn | 140,000 | 1,314 | 107 | |
Things to See and Do in Datong
Datong is a great place to visit with many historical sites.
Ancient Wonders: Yungang Grottoes
The Yungang Grottoes are a must-see. They are a collection of shallow caves located about 16 kilometers (10 miles) west of Datong. Inside these caves, you'll find over 50,000 carved images and statues of Buddhas. These carvings range from tiny 4-centimeter figures to huge 7-meter tall statues. Most of them are around 1,500 years old.
Historical Sites Within the City
Within Datong city, there are several old sites worth exploring:
- The Nine-Dragon Wall: A beautiful and colorful wall with nine dragons.
- The Huayan Monastery (Huáyán Sì): A large and historic Buddhist temple.
- The Shanhua Temple: Another important ancient temple.
Unique Temples and Walls
Further from the city, you can find the amazing Hanging Temple. This temple is built right into a cliff face near Mount Heng. Most historical sites in this area are from the Liao, Jin, and Ming dynasties. However, the Hanging Temple is even older, dating back to the Northern Wei dynasty (386–534 AD).
In 2010, work began to rebuild Datong's 14th-century Ming dynasty defensive wall. This project aimed to restore the city's ancient defenses.
Datong's Culture and Food
Datong is famous for its delicious knife-cut noodles. These noodles are a special local dish.
Datong's Economy and Industries
Datong's economy has long been linked to coal mining. The city sits on large reserves of coal. The Datong Coal Mining Group, one of China's biggest coal companies, is based here.
Moving Beyond Coal
Because of its coal industry, Datong has faced challenges with pollution. However, the city is working to change this. It wants to rely less on coal and use cleaner mining methods. Datong is also developing new industries, like:
- Machinery manufacturing
- Tourism
- Logistics and warehousing services
The city's economy is growing. Datong is also a pilot city for environmental cleanup and restoration. It is working with other cities worldwide to learn how to improve its environment. For example, there are plans to develop tourism around old steam engine technology.
Key Businesses in Datong
Some of the main companies in Datong include:
- Datong Coal Mine Group (a major coal company)
- Datong Electric Locomotive Co., Ltd. (DELC) (a large electric locomotive company)
- Shanxi Diesel Engine Industries Corporation, Ltd.
- Shanxi Synthetic Rubber Group Co., Ltd.
Getting Around Datong
Datong has good transportation links:
- Highways: China National Highway 109 and China National Highway 208 pass through the city. There are also expressways like G55 Erenhot–Guangzhou Expressway and G5501 Datong Ring Expressway.
- Trains: You can travel by train from Datong railway station and Datong South railway station.
- Airport: The city has its own airport, Datong Yungang Airport.
Learning in Datong
Datong has several educational institutions:
Colleges and Universities
- Datong University (大同大学)
Major Schools
- Datong No.1 Middle School (大同市第一中学)
- Datong No.2 Middle School (大同市第二中学)
- Datong Locomotive Middle School (大同机车中学)
- Datong No.3 Middle School (大同市第三中学)
- BeiYue Middle School (北岳中学)
- Datong Experimental Secondary School (大同市实验中学)
- The No.1 Middle School of DCMG (Datong Coal Mine Group) (同煤一中)
- Datong No.14 Elementary School (大同市第十四小学)
- Datong No.18 Elementary School (大同市第十八小学)
- Datong Experimental Elementary School (大同市实验小学)
Images for kids
-
Loess landscape near Hunyuan
See also
 In Spanish: Datong para niños
In Spanish: Datong para niños