Den Helder facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Den Helder
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Den Helder water tower in the village
|
|||
|
|||
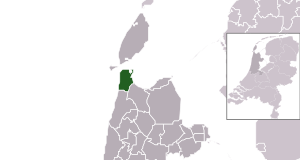
Location in North Holland
|
|||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Province | North Holland | ||
| Government | |||
| • Body | Municipal council | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 178.80 km2 (69.04 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 45.25 km2 (17.47 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 133.55 km2 (51.56 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 1 m (3 ft) | ||
| Population
(December 2021)
|
|||
| • Total | 56,369 | ||
| • Density | 1,249/km2 (3,230/sq mi) | ||
| Demonym(s) | Heldernaar | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | ||
| Postcode |
1780–1789
|
||
| Area code | 0223 | ||
Den Helder is a city and a municipality in the Netherlands. It is located in the province of North Holland. Den Helder is at the very northern tip of the North Holland peninsula. It is famous for being home to the main naval base of the country. From Den Helder, you can take a ferry to the nearby Dutch Wadden island of Texel.
Contents
What's in a Name?
Before 1928, the city was simply called Helder. No one is completely sure where the name Helder came from. It might have come from Helle or Helde, which means "hill" or "hilly ground". Another idea is that it came from Helre, meaning a sandy ridge.
Some people think the name came from Helsdeur, which means "Hell's Door". This is because the water between Den Helder and Texel, called Marsdiep, had very strong currents. Many ships were lost there, making it a dangerous place.
A Look at History
The older part of the city was originally a place called Huisduinen. Helder was just a small village nearby. When a harbor was built near Helder, the village started to grow. It soon became the main center for the area, instead of Huisduinen. Because of its important location at the end of the North Holland peninsula, many forts were built there. These forts helped protect the area.
Den Helder has always been important for Dutch shipping. During the Dutch Golden Age (a time when the Netherlands was very rich and powerful), ships were built near Den Helder. These ships then sailed all over the world.
In 1795, French forces captured 14 Dutch ships in Den Helder's frozen harbor. In 1799, the city was attacked during the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland.
In the 1820s, the North Holland Canal was dug. This canal connected Amsterdam to Den Helder. The famous lighthouse, Lange Jaap, was built in 1877. It is the tallest cast-iron lighthouse in Europe, standing at 63.45 meters (about 208 feet) tall. During World War II, most of Den Helder was emptied of people. The old city center was sadly destroyed.
Geography and Climate
Den Helder's Weather
Den Helder is located on a peninsula that sticks out into the North Sea. This means the sea greatly affects its weather. The climate is mild because of the ocean. Den Helder is also known for being one of the sunniest cities in the Netherlands!
| Climate data for De Kooy, Den Helder (1991-2020 normals, extremes 1906−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.7 (56.7) |
17.2 (63.0) |
20.5 (68.9) |
27.9 (82.2) |
31.0 (87.8) |
31.7 (89.1) |
34.8 (94.6) |
33.8 (92.8) |
32.6 (90.7) |
25.1 (77.2) |
17.7 (63.9) |
15.3 (59.5) |
34.8 (94.6) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
6.2 (43.2) |
8.7 (47.7) |
12.4 (54.3) |
15.8 (60.4) |
18.5 (65.3) |
20.8 (69.4) |
21.1 (70.0) |
18.3 (64.9) |
14.3 (57.7) |
10.0 (50.0) |
7.0 (44.6) |
13.3 (55.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.0 (39.2) |
3.9 (39.0) |
5.9 (42.6) |
9.0 (48.2) |
12.4 (54.3) |
15.2 (59.4) |
17.5 (63.5) |
17.8 (64.0) |
15.4 (59.7) |
11.6 (52.9) |
7.8 (46.0) |
5.0 (41.0) |
10.5 (50.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.7 (35.1) |
1.4 (34.5) |
3.0 (37.4) |
5.5 (41.9) |
9.0 (48.2) |
11.8 (53.2) |
14.1 (57.4) |
14.4 (57.9) |
12.1 (53.8) |
8.7 (47.7) |
5.2 (41.4) |
2.6 (36.7) |
7.5 (45.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −18.8 (−1.8) |
−20.0 (−4.0) |
−16.0 (3.2) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
4.2 (39.6) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−11.9 (10.6) |
−13.4 (7.9) |
−20.0 (−4.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 65.6 (2.58) |
50.1 (1.97) |
43.7 (1.72) |
34.9 (1.37) |
42.0 (1.65) |
58.7 (2.31) |
62.5 (2.46) |
89.1 (3.51) |
84.7 (3.33) |
96.5 (3.80) |
83.5 (3.29) |
75.3 (2.96) |
786.6 (30.97) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 87.8 | 86.3 | 83.9 | 80.5 | 79.0 | 79.1 | 79.4 | 79.1 | 81.2 | 83.3 | 86.6 | 87.5 | 82.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 70.2 | 97.8 | 155.7 | 214.5 | 246.6 | 230.4 | 240.5 | 219.7 | 161.2 | 122.1 | 68.5 | 60.6 | 1,887.8 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 27.6 | 35.0 | 42.2 | 51.3 | 50.4 | 45.7 | 47.4 | 48.0 | 42.2 | 36.9 | 26.0 | 25.5 | 39.8 |
| Source: Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute | |||||||||||||
Parts of Den Helder
The municipality of Den Helder includes several areas. These are the cities, towns, and villages of Den Helder, Huisduinen, and Julianadorp. It also includes the smaller hamlets of Friese Buurt and De Kooy.
The main parts of Den Helder city are Stad Binnen de Linie, Nieuw-Den Helder, and De Schooten. Nieuw-Den Helder was built in the 1950s. This was after World War II when many new homes were needed. De Schooten was built in the 1960s.
Den Helder's Landscape
Den Helder has been home to a naval base since the 1700s. This means it has always been important for ships and navies. In 1799, an invasion force from Britain and Russia landed here. They captured the Dutch navy that was stationed there.
The French emperor Napoleon Bonaparte visited Den Helder in 1811. He was very impressed by its important location. He ordered a fort (Kijkduin) and naval shipyards (Willemsoord) to be built. These shipyards were built between 1813 and 1827. In 1947, Den Helder officially became the main base for the Royal Netherlands Navy. It is still the navy's main base today. The Royal Netherlands Naval College, where naval officers are trained, is also in the city. You can also visit the Dutch Navy Museum here.
The old naval shipyards at Willemsoord are in the north of the city. They are no longer used for building ships. Instead, they now have restaurants, a movie theater, and other fun places to visit. The navy's docks and offices have moved to a newer location.
The Fortifications of Den Helder were built to protect the naval base. They also guarded the entrance to the Noordhollandsch Kanaal. These forts changed the landscape around Den Helder a lot. Many of these old forts are now used for tourism. You can visit them and learn about their history.
Getting Around Den Helder
Den Helder has two train stations:
- Den Helder
- Den Helder Zuid (South Den Helder)
You can reach Den Helder by these main roads:
- N9
- N99
- N250
- N502
These roads have two lanes. There are no big highways that lead directly to Den Helder.
Famous People from Den Helder
Many interesting people were born or lived in Den Helder.
Public Service and Thinkers
- Marleen Barth (born 1964), a politician and journalist.
- Petrus Johannes Blok (1855–1929), a Dutch historian.
- Edward W. Bok (1863-1930), a Dutch-American editor who won a Pulitzer Prize.
- Esther Welmoet Wijnaendts Francken-Dyserinck (1876-1956), a journalist and a founder of Dutch Girl Guiding.
- Gerard 't Hooft (born 1946), a physicist and professor. He shared the 1999 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Theo de Meester (1851–1919), a politician who was Prime Minister of the Netherlands from 1905 to 1908.
- Ed Nijpels (born 1950), a former government minister and mayor.
- Dorus Rijkers (1847-1928), a brave lifeboat captain and a local hero.
- Paul Rosenmöller (born 1956), a TV presenter and former politician.
Artists and Performers
- IJf Blokker (born 1930), a Dutch musician, TV actor, and presenter.
- Gré Brouwenstijn (1915-1999), a famous opera singer.
- Dick Ket (1902–1940), a Dutch painter known for his still lifes and self-portraits.
- Hanco Kolk (born 1957), a Dutch cartoonist and comics artist.
- Anton Pieck (1895-1987), a painter and graphic artist.
- Milly Scott (born 1933), a Dutch singer and actress.
- Quintino (born 1985), a Dutch DJ.
Sports Stars
- Jorina Baars (born 1988), a Dutch female kickboxing and Thai fighter.
- Edith Bosch (born 1980), a Judo world champion and Olympic medalist.
- Anthonij Guépin (1897–1964), a sailor who won a bronze medal at the 1924 Summer Olympics.
- Elien Meijer (born 1970), a retired rower who won a silver medal at the 2000 Summer Olympics.
- Swen Nater (born 1950), a basketball player.
- Martine Ohr (born 1964), a field hockey player who won a gold medal at the 1984 Summer Olympics.
- Hans Smits (born 1956), a water polo player who won a bronze medal at the 1976 Summer Olympics.
- Mark de Vries (born 1975), a Dutch footballer.
See also
 In Spanish: Den Helder para niños
In Spanish: Den Helder para niños