Elephant Butte (Washington) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Elephant Butte |
|
|---|---|

Elephant Butte
|
|
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 7,380 ft (2,250 m) |
| Prominence | 1,060 ft (320 m) |
| Geography | |
| Parent range | North Cascades |
| Topo map | USGS Mount Prophet |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | Scramble |
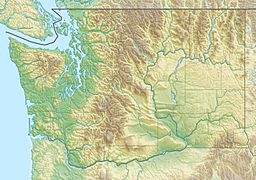
Elephant Butte is a mountain peak that stands 7,380 feet tall. It is part of the Picket Range, which is a smaller group of mountains within the larger North Cascades Range in Washington, United States. You can find Elephant Butte inside North Cascades National Park and the Stephen Mather Wilderness.
Even though it's not the highest mountain, Elephant Butte is famous for how steeply it rises from the land around it. Rain and melting snow from the mountain flow into the Skagit River through Stetattle Creek and McMillan Creek.
Weather at Elephant Butte
Elephant Butte is in a "marine west coast" climate zone. This means it gets a lot of moisture from the Pacific Ocean. Most weather systems start over the Pacific and move northeast towards the Cascade Mountains.
When these weather systems hit the tall peaks of the North Cascades, the air is forced to rise. As the air goes higher, it cools down and drops its moisture as rain or snowfall. This process is called orographic lift. Because of this, the western side of the North Cascades gets a lot of rain and snow, especially in winter.
During winter, the weather is often cloudy. But in summer, high-pressure systems over the Pacific Ocean bring clear skies. The snow here tends to be wet and heavy because of the ocean's influence. This can create a high risk of avalanches, which are large slides of snow down a mountain.
How Elephant Butte Was Formed
The North Cascades mountains have very rugged land. You can see jagged peaks, long ridges, and deep valleys carved by glaciers. These amazing shapes and big changes in height were created by geological events over millions of years. These events also led to different climates and types of plants in the area.
The Cascade Mountains started forming millions of years ago, during the late Eocene Epoch. The North American Plate (a huge piece of Earth's crust) was slowly moving over the Pacific Plate. This movement caused many volcanic eruptions.
Also, small pieces of the Earth's crust, called terranes, crashed into North America. These collisions helped build the North Cascades about 50 million years ago.
During the Pleistocene period, which began over two million years ago, huge sheets of ice called glaciers moved across the land many times. As they advanced and then melted back, they scraped away rock and left behind debris. The "U"-shaped valleys you see in the mountains today were carved out by these glaciers.
The combination of the land being pushed up (called uplift) and cracks forming in the Earth's crust (called faulting), along with the glaciers, created the tall peaks and deep valleys of the North Cascades.
More Information
- Weather forecast: Elephant Butte
Images for kids
 | Percy Lavon Julian |
 | Katherine Johnson |
 | George Washington Carver |
 | Annie Easley |