Skagit River facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Skagit River |
|
|---|---|

Gorge Lake portion of the Skagit River in Washington
|
|
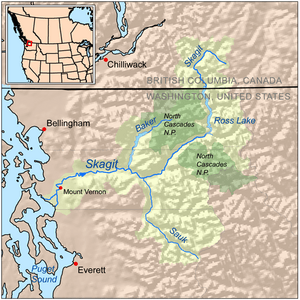
Map of the Skagit River drainage basin
|
|
| Country | Canada, United States |
| Region | British Columbia, Washington |
| Cities | Newhalem, Marblemount, Rockport, Concrete, Sedro-Woolley, Mount Vernon |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Main source | Allison Pass E. C. Manning Provincial Park, British Columbia 4,480 ft (1,370 m) 49°07′23″N 120°52′39″W / 49.12306°N 120.87750°W |
| River mouth | Skagit forks near Puget Sound Skagit City, Washington 10 ft (3.0 m) 48°23′14″N 122°22′01″W / 48.38722°N 122.36694°W |
| Length | 150 mi (240 km) |
| Basin features | |
| Basin size | 2,656 sq mi (6,880 km2) |
| Tributaries |
|
| Type: | Scenic, Recreational |
| Designated: | November 10, 1978 |
The Skagit River is a long and important river that flows through two countries: Canada and the United States. It starts in British Columbia, Canada, and travels about 120 miles (193 km) into the state of Washington. Finally, it empties into the Pacific Ocean just north of the city of Seattle.
The Skagit River is special because it flows through beautiful natural areas. It helps power homes and provides a home for many animals.
Contents
The Skagit River's Journey
The Skagit River begins its journey by flowing south from its source. It soon enters the amazing North Cascades National Park. Here, the river is stopped by a large dam called Ross Dam. This dam creates a big reservoir known as Ross Lake.
Dams and Lakes Along the Way
After leaving Ross Lake, the river flows into another reservoir called Diablo Lake. These dams are important because they help create hydroelectricity, which is clean energy for people. The river then continues its path southwest through a deep valley called the Skagit Gorge.
Meeting Other Rivers
As the Skagit River flows, it meets other smaller rivers that join it. These smaller rivers are called tributaries. Its biggest tributary is the Sauk River, which is about 45 miles (72 km) long. After the Sauk River joins, the Skagit River turns west.
Another important tributary is the Baker River. It flows south for about 30 miles (48 km) before joining the Skagit. The Baker River also has two dams, creating Baker Lake and Lake Shannon.
Reaching the Ocean
After passing through these areas, the Skagit River flows alongside the North Cascades Highway. It then leaves the national park and continues its journey. Finally, the river reaches the sea near the city of Mount Vernon, Washington. The entire area that drains into the Skagit River is huge, covering about 1,505 square miles (3,900 square kilometers).
Wildlife and Nature
The Skagit River and its surrounding areas are home to many different kinds of wildlife. The river is known for its salmon runs, especially Chinook salmon, which are very important for the ecosystem.
Important Bird Habitat
The area where the Skagit River meets the sea, called the Skagit River Delta, is a very important place for birds. In winter, thousands of snow geese and trumpeter swans come here. They find food and shelter in this rich natural habitat.
See also
 In Spanish: Río Skagit para niños
In Spanish: Río Skagit para niños
Images for kids
-
The Skagit River Delta is an important winter habitat for snow geese (pictured) and trumpeter swans
-
The Skagit River near Marblemount, Washington
-
Looking upstream from 26 Mile Bridge in British Columbia, Canada
-
Aerial view of the Skagit River at Burlington and Mount Vernon
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |








